16. Linked List 1
15 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
- Problem with Arrays
- Difference B/W array & Linked lists
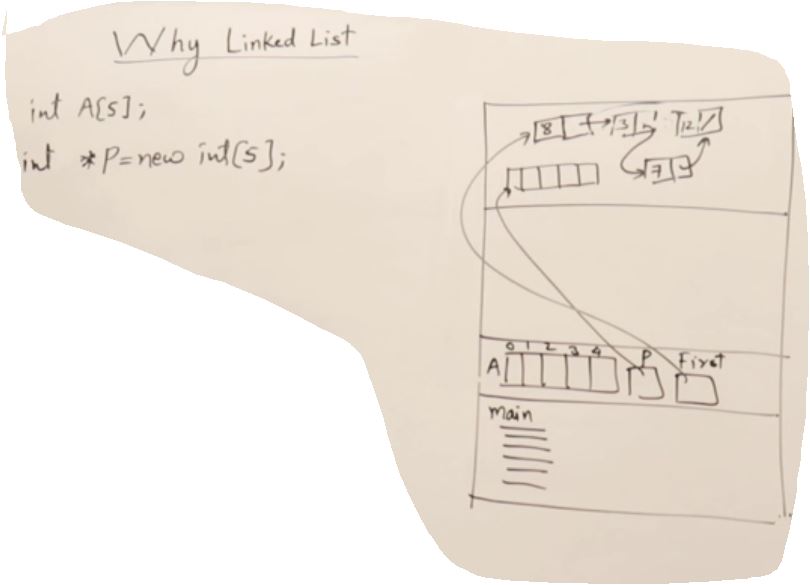
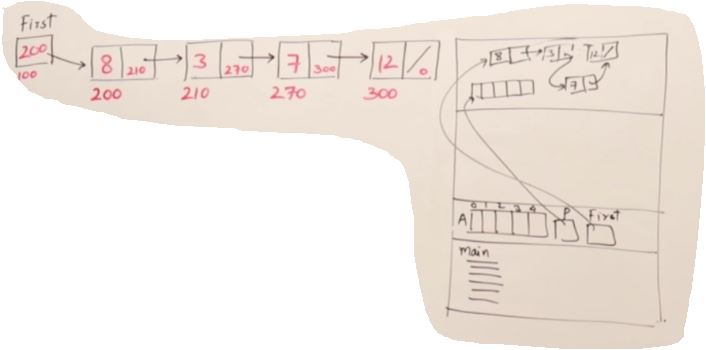
Why linked list
- Array 말고 Linked list 쓰는 이유는 사용자가 얼마나 많은 어레이가 필요한지 모르는 동적 상태일때 쓰인다.
- Linked list는 Array 보다 느리지만 이런 동적인 상태에서는 더 효과적이다.
- pre, current, post 데이터가 나누어져있어 서칭하기도 쉽다.
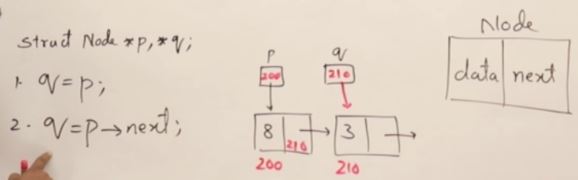
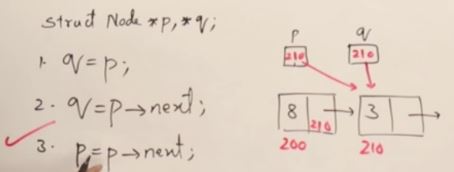
- Linked List는 Node들이 post, prev로 연결되어있는 구조이다.
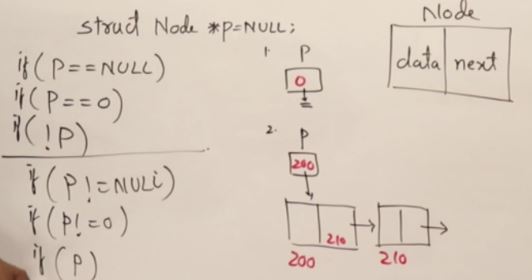
- point 값들은 랜덤으로 initilize되기 때문에 항상 Null을 해줘야 한다.
Checking Linked List
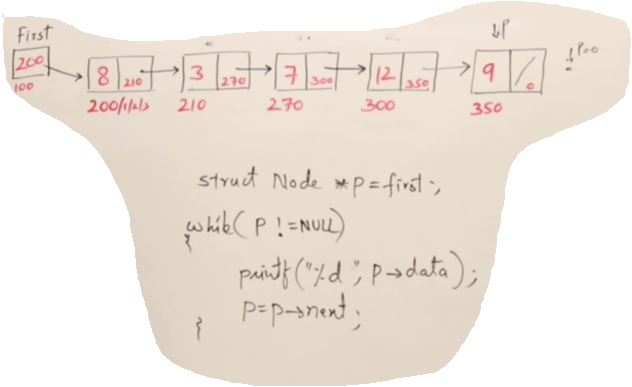
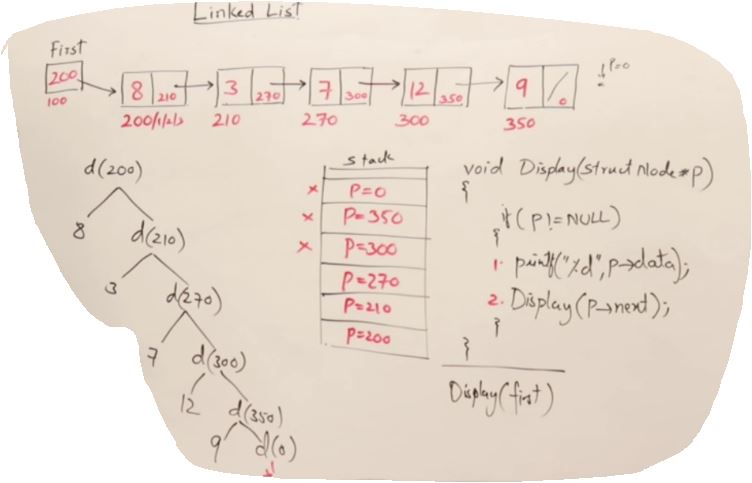
Display for Linked List
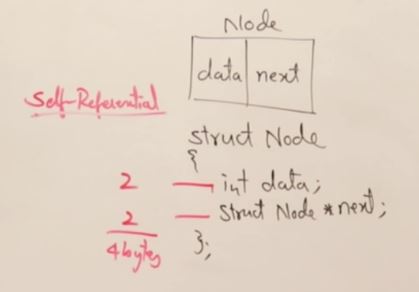
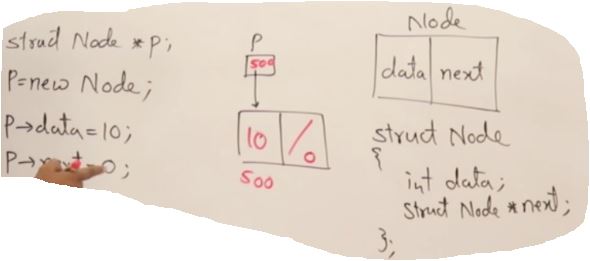
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
int main()
{
int A[]={3,5,7,10,15};
Node* head = new Node;
Node* temp;
Node* last;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = nullptr;
last = head;
//Create a Linked list
for(int i=1;i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
// Create Temporary node
temp = new Node;
// Populate Temporary Node
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
// last's next is poting to temp
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
//Distplay Linked List
Node* p= haed;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
cout<<p->data<<"->"<<flush;
p=p->next;
}
}
Recursive Method
- O(n)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
Display(temp);
return 0;
}
Counting and sum for Linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int count_(Node* p)
{
int l =0;
while(p)
{
l++;
p=p->next;
}
return l;
}
int sum_(Node* p)
{
int i =0;
while(p)
{
i=p->data+i;
p=p->next;
}
return i;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout<< "count is "<<count_(temp)<<endl;
cout<< "sum is "<<sum_(temp)<<endl;
return 0;
}
Recursive Method
Max and Min
- Max = Min-INT
- Max = -32768
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int count_(Node* p)
{
int l =0;
while(p)
{
l++;
p=p->next;
}
return l;
}
int sum_(Node* p)
{
int i =0;
while(p)
{
i=p->data+i;
p=p->next;
}
return i;
}
int max_(Node* p)
{
int maxx = INT32_MIN;
while(p)
{
if(p->data>maxx)
maxx = p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return maxx;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout<< "max is "<<max_(temp)<<endl;
return 0;
}
- Problem with Arrays
- Difference B/W array & Linked lists
Why linked list
- Array 말고 Linked list 쓰는 이유는 사용자가 얼마나 많은 어레이가 필요한지 모르는 동적 상태일때 쓰인다.
- Linked list는 Array 보다 느리지만 이런 동적인 상태에서는 더 효과적이다.
- pre, current, post 데이터가 나누어져있어 서칭하기도 쉽다.
- Linked List는 Node들이 post, prev로 연결되어있는 구조이다.
- point 값들은 랜덤으로 initilize되기 때문에 항상 Null을 해줘야 한다.
Checking Linked List
Display for Linked List
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
int main()
{
int A[]={3,5,7,10,15};
Node* head = new Node;
Node* temp;
Node* last;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = nullptr;
last = head;
//Create a Linked list
for(int i=1;i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
// Create Temporary node
temp = new Node;
// Populate Temporary Node
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
// last's next is poting to temp
last->next = temp;
last = temp;
}
//Distplay Linked List
Node* p= haed;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
cout<<p->data<<"->"<<flush;
p=p->next;
}
}
Recursive Method
- O(n)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
Display(temp);
return 0;
}
Counting and sum for Linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int count_(Node* p)
{
int l =0;
while(p)
{
l++;
p=p->next;
}
return l;
}
int sum_(Node* p)
{
int i =0;
while(p)
{
i=p->data+i;
p=p->next;
}
return i;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout<< "count is "<<count_(temp)<<endl;
cout<< "sum is "<<sum_(temp)<<endl;
return 0;
}
Recursive Method
Max and Min
- Max = Min-INT
- Max = -32768
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
int count_(Node* p)
{
int l =0;
while(p)
{
l++;
p=p->next;
}
return l;
}
int sum_(Node* p)
{
int i =0;
while(p)
{
i=p->data+i;
p=p->next;
}
return i;
}
int max_(Node* p)
{
int maxx = INT32_MIN;
while(p)
{
if(p->data>maxx)
maxx = p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return maxx;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout<< "max is "<<max_(temp)<<endl;
return 0;
}


Comments