18. Linked List 3
16 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
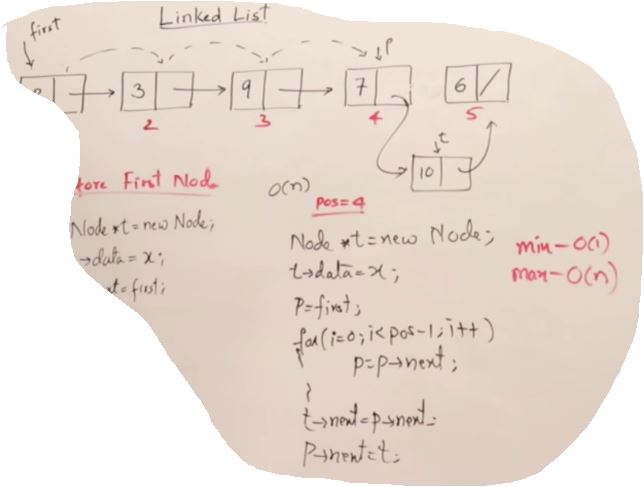
Delete on Linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Delete(Node* p, int index)
{
Node* q = NULL;
Node* head;
head = p;
int i;
if(index<1 || index>5)
return;
if(index==1)
{
q=head;
head = head->next;
free(q);
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
Delete(head,2);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
check if a Linked List is sorted
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
isSorted(head);
return 0;
}
Reverse a Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
void Reverse1(Node* p)
{
int* A;
int i=0;
Node* q = p;
A = new int[5];
while(q!=NULL)
{
A[i]=q->data;
q= q->next;
i++;
}
q=p;
i--;
while(q!=NULL)
{
q->data = A[i];
q = q->next;
i--;
}
}
void Reverse2(Node* p)
{
Node* q=NULL, * r=NULL;
while(p!=NULL)
{
r=q;
q=p;
p=p->next;
q->next=r;
}
}
void Reverse3(Node* q, Node* p)
{
if(p)
{
Reverse3(p,p->next);
p->next = q;
}
else
q=p;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
Reverse1(head);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
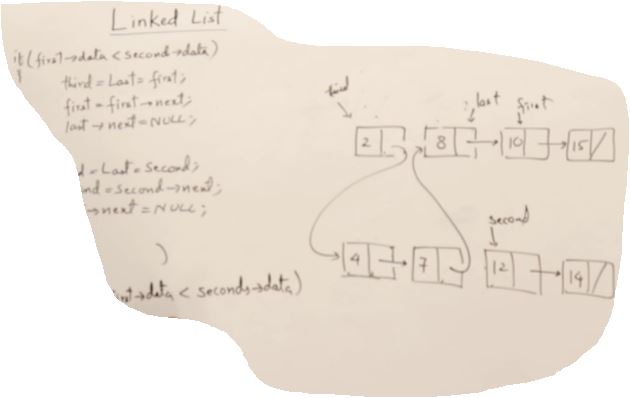
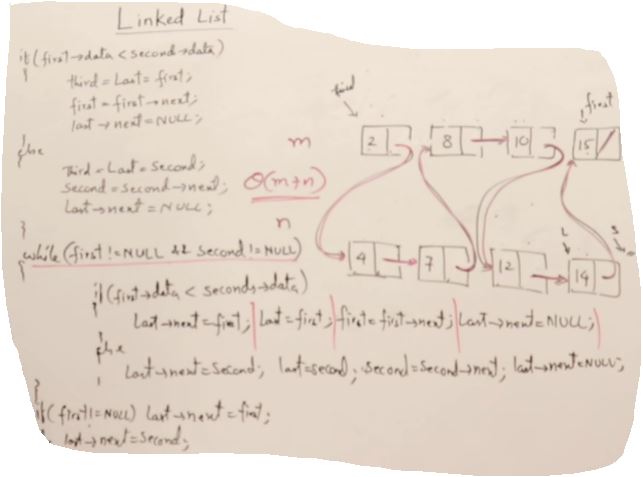
Concatenate and Merge Linked lists
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
Node* Merge(Node* p, Node* q)
{
Node* last;
Node* Merged;
if(p->data < q->data)
{
Merged = last = p;
p=p->next;
Merged->next=NULL;
}
else
{
Merged = last = q;
q = q->next;
Merged->next = NULL;
}
while(p && q)
{
if(p->data < q->data)
{
last->next = p;
last = p;
p=p->next;
last->next = NULL;
}
else
{
last->next = q;
last = q;
q = q->next;
last->next = NULL;
}
if(p)
last->next = p;
if(q)
last->next = q;
}
return Merged;
}
int main()
{
Node* head_A;
Node* head_B;
Node* Merged;
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
int B[]={15,18,25,30,55};
head_A = create(A,5);
head_B = create(B,5);
Merged = Merge(head_A,head_B);
Display(Merged);
return 0;
}
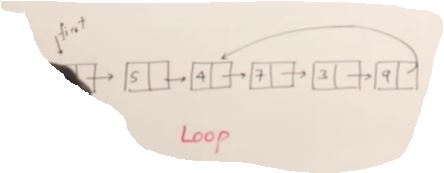
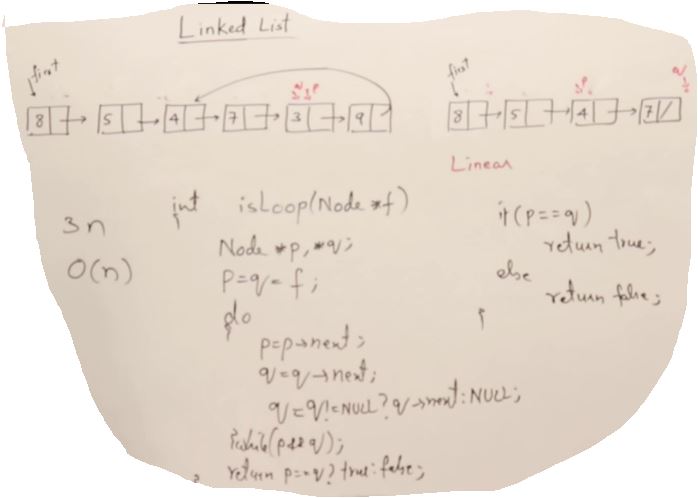
Check Loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int isLoop(Node* f)
{
Node* p,* q;
p=q=f;
do
{
p=p->next;
q=q->next; //여기서 부터 q 체크(약 두번씩 점프)
q=q?q->next:q; // if(q) q->next else q;
}while(p && q && p=!q);
// 사이클에서 같아버리면 나가게 된다.
if(p==q)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Node* head_A;
Node* t1, * t2;
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
head_A = create(A,5);
t1=head_A->next->next;
t2=head_A->next->next->next->next;
t2->next = t1;
cout<<isLoop(head_A);
return 0;
}
Delete on Linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void Delete(Node* p, int index)
{
Node* q = NULL;
Node* head;
head = p;
int i;
if(index<1 || index>5)
return;
if(index==1)
{
q=head;
head = head->next;
free(q);
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
Delete(head,2);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
check if a Linked List is sorted
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
isSorted(head);
return 0;
}
Reverse a Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
void Reverse1(Node* p)
{
int* A;
int i=0;
Node* q = p;
A = new int[5];
while(q!=NULL)
{
A[i]=q->data;
q= q->next;
i++;
}
q=p;
i--;
while(q!=NULL)
{
q->data = A[i];
q = q->next;
i--;
}
}
void Reverse2(Node* p)
{
Node* q=NULL, * r=NULL;
while(p!=NULL)
{
r=q;
q=p;
p=p->next;
q->next=r;
}
}
void Reverse3(Node* q, Node* p)
{
if(p)
{
Reverse3(p,p->next);
p->next = q;
}
else
q=p;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
Reverse1(head);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
Concatenate and Merge Linked lists
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
Node* Merge(Node* p, Node* q)
{
Node* last;
Node* Merged;
if(p->data < q->data)
{
Merged = last = p;
p=p->next;
Merged->next=NULL;
}
else
{
Merged = last = q;
q = q->next;
Merged->next = NULL;
}
while(p && q)
{
if(p->data < q->data)
{
last->next = p;
last = p;
p=p->next;
last->next = NULL;
}
else
{
last->next = q;
last = q;
q = q->next;
last->next = NULL;
}
if(p)
last->next = p;
if(q)
last->next = q;
}
return Merged;
}
int main()
{
Node* head_A;
Node* head_B;
Node* Merged;
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
int B[]={15,18,25,30,55};
head_A = create(A,5);
head_B = create(B,5);
Merged = Merge(head_A,head_B);
Display(Merged);
return 0;
}
Check Loop
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
int isSorted(Node* p)
{
int x=-65536;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->data < x)
return 0;
x=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
return 1;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int isLoop(Node* f)
{
Node* p,* q;
p=q=f;
do
{
p=p->next;
q=q->next; //여기서 부터 q 체크(약 두번씩 점프)
q=q?q->next:q; // if(q) q->next else q;
}while(p && q && p=!q);
// 사이클에서 같아버리면 나가게 된다.
if(p==q)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Node* head_A;
Node* t1, * t2;
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
head_A = create(A,5);
t1=head_A->next->next;
t2=head_A->next->next->next->next;
t2->next = t1;
cout<<isLoop(head_A);
return 0;
}


Comments