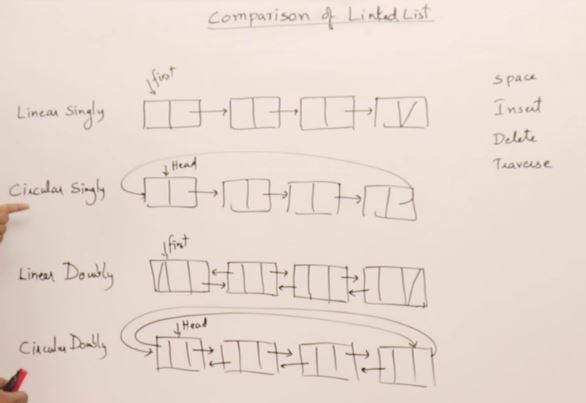
19. Linked List 4
17 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
C++ Class for Linked list
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* first;
public:
LinkedList(){first=NULL;}
LinkedList(int A[], int n);
~LinkedList();
void Display();
void Insert(int index, int x);
int Length();
int Delete(int index);
};
LinkedList::LinkedList(int A[],int n)
{
Node* last, * t;
int i=0;
first = new Node;
first->data = A[0];
first->next = NULL;
last = first;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = NULL;
last->next =t;
last = t;
}
}
LinkedList::~LinkedList()
{
Node* p =first;
while(first)
{
first = first->next;
delete p;
p = first;
}
}
void LinkedList::Display()
{
Node * p = first;
while(p)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void LinkedList::Insert(int index, int x)
{
Node* t;
Node* p = first;
if(index<0||index> Length())
return;
t = new Node;
t->data = x;
t->next = NULL;
if(index=0)
{
t->next = first;
first = t;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<index-1;i++)
p=p->next;
t->next = p->next
p->next = t;
}
}
int LinkedList::Length()
{
Node* p = first;
int len=0;
while(p)
{
len++
p=p->next;
}
return len;
}
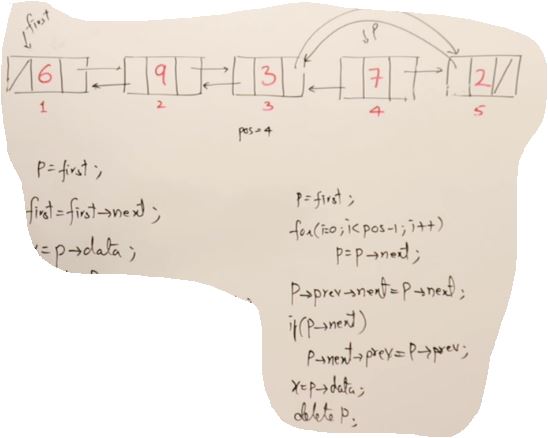
int LinkedList::Delete(int index)
{
Node* p;
Node* q = NULL;
int x=-1;
if (index<1 || index>Length())
return -1;
if(index==1)
{
p=first;
first=first->next;
x=p->data;
delete p ;
}
else
{
p=first;
for(int i=0; i<index-1; i++)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
x=p->data;
delete p;
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1,2,3,4,5};
LinkedList l(A,5);
l.Insert(3,10);
l.Display();
return 0;
}
Circular Linked list
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class CircularLinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
CircularLinkedList(int[] A, int n);
~CircularLinkedList();
void Display();
Node* getHead()
{
return head;
}
void recursiveDisplay(Node* p);
};
CircularLinkedList::CircularLinkedList(int[] A, int n)
{
Node* t;
Node* tail;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = head;
tail = head;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = tail->next;
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}
}
CircularLinkedList::~CircularLinkedList()
{
Node* p = head;
while(p->next!=head)
{p=p->next;}
while(p!=head)
{
p->next = head->next;
delete head;
head = p->next;
}
if(p==head)
{
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
}
void CircularLinkedList::Display()
{
Node* p = head;
do{
cout<<p->data<<"->"<<flush;
p=p->next;
}while(p!=head);
cout << endl;
}
void CircularLinkedList::recursiveDisplay(Node *p)
{
static int flag = 0;
if(p!=head || flag ==0)
{
flag = 1;
cout<<p->data<<"->"<<flush;
recursiveDisplay(p->next);
// Recursive를 해도 계속 flag는 1로 남는다.
}
flag =0;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1,3,5,7,9};
CircularLinkedList cl(A, sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cl.Display();
Node* h = cl.getHead();
cl.recursiveDisplay(h);
}
Inserting or Deleting in circular linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class CircularLinkedList{
private:
Node* head;
public:
CircularLinkedList(int A[], int n);
void Display();
void recursiveDisplay(Node* p);
Node* getHead(){ return head; }
~CircularLinkedList();
void Inserting(int index, int key);
int Length();
void Delete(int index);
};
CircularLinkedList::CircularLinkedList(int *A, int n) {
Node* t;
Node* tail;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = head;
tail = head;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++){
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = tail->next;
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}
}
void CircularLinkedList::Display() {
Node* p = head;
do {
cout << p->data << " -> " << flush;
p = p->next;
} while (p != head);
cout << endl;
}
void CircularLinkedList::recursiveDisplay(Node *p) {
static int flag = 0;
if (p != head || flag == 0){
flag = 1;
cout << p->data << " -> " << flush;
recursiveDisplay(p->next);
}
flag = 0;
cout << endl;
}
int CircularLinkedList::Length()
{
Node* p = head;
int len=0;
do
{
len++;
p=p->next;
}while(p!=head);
return len;
}
void CircularLinkedList::Inserting(int index, int key)
{
Node* t;
Node* p = head;
int i;
if(index<0 || index>Length())
return;
if(index ==0)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = key;
if(head==NULL)
{
head = t;
head->next = head;
}
else
{
while(p->next!=head)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = t;
t->next = head;
head = t;
}
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
t = new Node;
t->data = key;
t->next = p->next;
p->next = t;
}
}
void CircularLinkedList::Delete(int index)
{
Node* q;
Node* p = head;
int i,x;
if(index<0 || index>Length())
return;
if(index==1)
{
while(p->next != head)
{
p=p->next;
}
x= head->data;
if(head = p)
{
delete head;
head =NULL;
}
else
{
p->next = head->next;
delete head;
head = p->next;
}
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-2;i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
x=q->data;
delete q;
}
}
CircularLinkedList::~CircularLinkedList() {
Node* p = head;
while (p->next != head){
p = p->next;
}
while (p != head){
p->next = head->next;
delete head;
head = p->next;
}
if (p == head){
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
}
int main() {
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
CircularLinkedList cl(A, sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cl.Display();
cl.Inserting(3,6);
Node* h = cl.getHead();
cl.recursiveDisplay(h);
cl.Delete(3);
cl.Display();
return 0;
}
Reserve for Doubly Linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
class DoublyLinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
DoublyLinkedList();
DoublyLinkedList(int A[], int n);
~DoublyLinkedList();
int Length();
void insert_(int index, int x);
void Display();
void Delete(int index);
void Reverse();
};
void DoublyLinkedList::Delete(int index)
{
Node* p = head;
if(index<0 || index>Length())
{
return;
}
if(index ==1)
{
head = head->next;
if(head)
{
head->prev =nullptr;
}
delete p;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<index-1; i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->prev->next = p->next;
if(p->next)
{
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}
delete p;
}
}
void DoublyLinkedList::Display()
{
Node* p = head;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
cout<<p->data<<flush;
p=p->next;
if(p!=nullptr)
cout<<" <-> "<<flush;
}
cout<<endl;
}
DoublyLinkedList::Length()
{
int length = 0;
Node* p =head;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
length++;
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
return length;
}
DoublyLinkedList::DoublyLinkedList()
{
head = new Node;
head->prev = nullptr;
head->next = nullptr;
}
DoublyLinkedList::DoublyLinkedList(int A[], int n)
{
head = new Node;
head->prev = nullptr;
head->next = nullptr;
head->data = A[0];
Node* tail = head;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
Node* t = new Node;
t->prev = tail;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = tail->next; // tail->next is points to null
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}
}
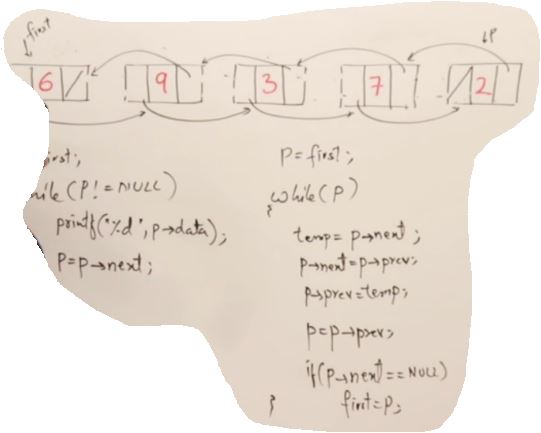
void DoublyLinkedList::Reverse()
{
Node* p = head;
Node* temp;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
temp = p->next;
p->next = p->prev;
p->prev = temp;
p = p->prev;
//Need to check the following condition again
if(p->next == nullptr)
{
p->next = p->prev;
p->prev = nullptr;
head = p;
break;
}
}
}
void DoublyLinkedList::insert_(int index, int x)
{
if(index<0 || index> Length())
return;
Node* p=head;
Node* t= new Node;
t->data = x;
if(index ==0)
{
t->prev = nullptr;
t->next = head;
head->prev = t;
head = t; // pointing the "head" changed to t as new head pointer;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<index-1;i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
t->prev = p;
t->next = p->next;
if(p->next){
p->next->prev = t;
}
p->next = t;
}
}
DoublyLinkedList::~DoublyLinkedList()
{
Node* p =head;
while(head)
{
head = head->next;
delete p;
p = head;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1,3,5,7,9};
DoublyLinkedList dll(A, sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout<<"length : "<<dll.Length();
dll.insert_(0,11);
dll.insert_(6,13);
dll.Display();
dll.Delete(6);
dll.Delete(1);
dll.Display();
dll.Reverse();
dll.Display();
return 0;
}
Finding Middle Element of a Linked list
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* head = new Node;
void create(int A[], int n)
{
Node* temp;
Node* tail;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = nullptr;
tail = head;
for(int i=1; i<n;i++)
{
temp = new Node;
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
tail->next = temp;
tail = temp;
}
}
void middleNode1(Node* p)
{
Node* t = p;
int length =0;
while(t)
{
length++;
t=t->next;
}
int index = length/2;
Node* q=head;
for(int i =0; index-1; i++)
{
q = q->next;
}
cout << "Middle Element (Method-I): " << q->data << endl;
}
void middleNode2(Node* p){
Node* q = p;
while (q){
q = q->next;
if (q){
q = q->next;
}
if (q){
p = p->next;
}
}
cout << "Middle Element (Method-II): " << p->data << endl;
}
void middleNode3(Node* p){
stack<Node*> s;
while (p){
s.push(p);
p = p->next;
}
int length = s.size();
int popLength = (int)(floor(length/2.0));
while (popLength){
s.pop();
popLength--;
}
cout << "Middle Element (Method-III): " << s.top()->data << endl;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21};
create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout << endl;
middleNode1(head);
return 0;
}
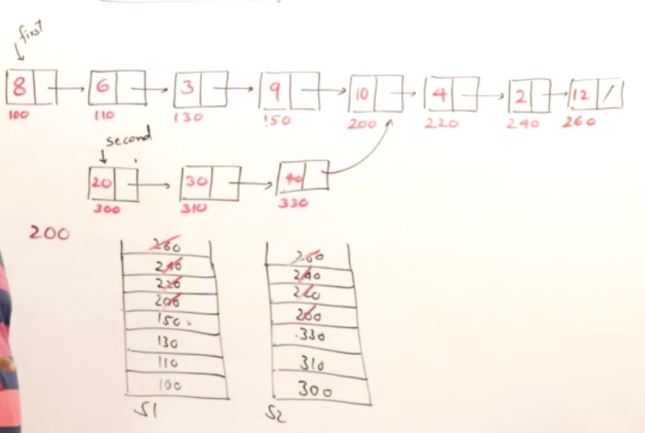
Finding Intersecting point of two linked list.
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* head = new Node;
void create(int A[], int n){
Node* temp;
Node* tail;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = nullptr;
tail = head;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++){
temp = new Node;
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
tail->next = temp;
tail = temp;
}
}
Node* second = new Node;
void createSecond(int A[], int n, Node* p)
{
Node* temp;
Node* tail;
second->data = A[0];
second->next = nullptr;
tail = second;
for(int i=1; i<n;i++)
{
temp = new Node;
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
tail->next = temp;
tail = temp;
}
tail->next = p;
}
void Intersection(Node* p, Node* q)
{
//Populate first stack;
stack<Node*> stk1;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
stk1.push(p);
p=p->next;
}
//Populate second stack
stack<Node*> stk2;
while(q!=nullptr)
{
stk1.push(q);
q=q->next;
}
Node* r;
while(stk1.top()==stk2.top())
{
r = stk1.top();
stk1.pop();
stk2.pop();
}
cout << "Intersecting Node: " << r->data << endl;
}
int main()
{
// Create First Linked List
int A[]={1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21};
create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
// Create Second Linked List
Node* temp = head;
int i = 5;
while (i>0)
{
temp = temp->next;
i--;
}
cout << temp->data << endl;
int B[] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
createSecond(B, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]), temp);
//Find Intersection
Intersection(head,second);
return 0;
}
Quiz
C++ Class for Linked list
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* first;
public:
LinkedList(){first=NULL;}
LinkedList(int A[], int n);
~LinkedList();
void Display();
void Insert(int index, int x);
int Length();
int Delete(int index);
};
LinkedList::LinkedList(int A[],int n)
{
Node* last, * t;
int i=0;
first = new Node;
first->data = A[0];
first->next = NULL;
last = first;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = NULL;
last->next =t;
last = t;
}
}
LinkedList::~LinkedList()
{
Node* p =first;
while(first)
{
first = first->next;
delete p;
p = first;
}
}
void LinkedList::Display()
{
Node * p = first;
while(p)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
void LinkedList::Insert(int index, int x)
{
Node* t;
Node* p = first;
if(index<0||index> Length())
return;
t = new Node;
t->data = x;
t->next = NULL;
if(index=0)
{
t->next = first;
first = t;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<index-1;i++)
p=p->next;
t->next = p->next
p->next = t;
}
}
int LinkedList::Length()
{
Node* p = first;
int len=0;
while(p)
{
len++
p=p->next;
}
return len;
}
int LinkedList::Delete(int index)
{
Node* p;
Node* q = NULL;
int x=-1;
if (index<1 || index>Length())
return -1;
if(index==1)
{
p=first;
first=first->next;
x=p->data;
delete p ;
}
else
{
p=first;
for(int i=0; i<index-1; i++)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
x=p->data;
delete p;
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1,2,3,4,5};
LinkedList l(A,5);
l.Insert(3,10);
l.Display();
return 0;
}
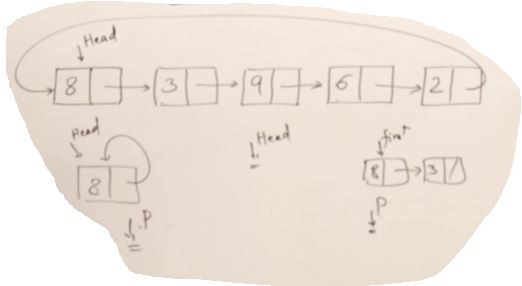
Circular Linked list
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class CircularLinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
CircularLinkedList(int[] A, int n);
~CircularLinkedList();
void Display();
Node* getHead()
{
return head;
}
void recursiveDisplay(Node* p);
};
CircularLinkedList::CircularLinkedList(int[] A, int n)
{
Node* t;
Node* tail;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = head;
tail = head;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = tail->next;
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}
}
CircularLinkedList::~CircularLinkedList()
{
Node* p = head;
while(p->next!=head)
{p=p->next;}
while(p!=head)
{
p->next = head->next;
delete head;
head = p->next;
}
if(p==head)
{
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
}
void CircularLinkedList::Display()
{
Node* p = head;
do{
cout<<p->data<<"->"<<flush;
p=p->next;
}while(p!=head);
cout << endl;
}
void CircularLinkedList::recursiveDisplay(Node *p)
{
static int flag = 0;
if(p!=head || flag ==0)
{
flag = 1;
cout<<p->data<<"->"<<flush;
recursiveDisplay(p->next);
// Recursive를 해도 계속 flag는 1로 남는다.
}
flag =0;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1,3,5,7,9};
CircularLinkedList cl(A, sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cl.Display();
Node* h = cl.getHead();
cl.recursiveDisplay(h);
}
Inserting or Deleting in circular linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class CircularLinkedList{
private:
Node* head;
public:
CircularLinkedList(int A[], int n);
void Display();
void recursiveDisplay(Node* p);
Node* getHead(){ return head; }
~CircularLinkedList();
void Inserting(int index, int key);
int Length();
void Delete(int index);
};
CircularLinkedList::CircularLinkedList(int *A, int n) {
Node* t;
Node* tail;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = head;
tail = head;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++){
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = tail->next;
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}
}
void CircularLinkedList::Display() {
Node* p = head;
do {
cout << p->data << " -> " << flush;
p = p->next;
} while (p != head);
cout << endl;
}
void CircularLinkedList::recursiveDisplay(Node *p) {
static int flag = 0;
if (p != head || flag == 0){
flag = 1;
cout << p->data << " -> " << flush;
recursiveDisplay(p->next);
}
flag = 0;
cout << endl;
}
int CircularLinkedList::Length()
{
Node* p = head;
int len=0;
do
{
len++;
p=p->next;
}while(p!=head);
return len;
}
void CircularLinkedList::Inserting(int index, int key)
{
Node* t;
Node* p = head;
int i;
if(index<0 || index>Length())
return;
if(index ==0)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = key;
if(head==NULL)
{
head = t;
head->next = head;
}
else
{
while(p->next!=head)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = t;
t->next = head;
head = t;
}
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
t = new Node;
t->data = key;
t->next = p->next;
p->next = t;
}
}
void CircularLinkedList::Delete(int index)
{
Node* q;
Node* p = head;
int i,x;
if(index<0 || index>Length())
return;
if(index==1)
{
while(p->next != head)
{
p=p->next;
}
x= head->data;
if(head = p)
{
delete head;
head =NULL;
}
else
{
p->next = head->next;
delete head;
head = p->next;
}
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-2;i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
x=q->data;
delete q;
}
}
CircularLinkedList::~CircularLinkedList() {
Node* p = head;
while (p->next != head){
p = p->next;
}
while (p != head){
p->next = head->next;
delete head;
head = p->next;
}
if (p == head){
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
}
int main() {
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
CircularLinkedList cl(A, sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cl.Display();
cl.Inserting(3,6);
Node* h = cl.getHead();
cl.recursiveDisplay(h);
cl.Delete(3);
cl.Display();
return 0;
}
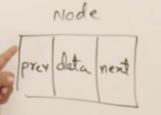
Reserve for Doubly Linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
class DoublyLinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
DoublyLinkedList();
DoublyLinkedList(int A[], int n);
~DoublyLinkedList();
int Length();
void insert_(int index, int x);
void Display();
void Delete(int index);
void Reverse();
};
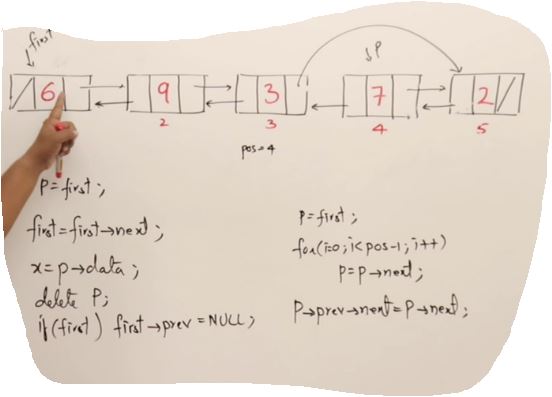
void DoublyLinkedList::Delete(int index)
{
Node* p = head;
if(index<0 || index>Length())
{
return;
}
if(index ==1)
{
head = head->next;
if(head)
{
head->prev =nullptr;
}
delete p;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<index-1; i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->prev->next = p->next;
if(p->next)
{
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}
delete p;
}
}
void DoublyLinkedList::Display()
{
Node* p = head;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
cout<<p->data<<flush;
p=p->next;
if(p!=nullptr)
cout<<" <-> "<<flush;
}
cout<<endl;
}
DoublyLinkedList::Length()
{
int length = 0;
Node* p =head;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
length++;
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
return length;
}
DoublyLinkedList::DoublyLinkedList()
{
head = new Node;
head->prev = nullptr;
head->next = nullptr;
}
DoublyLinkedList::DoublyLinkedList(int A[], int n)
{
head = new Node;
head->prev = nullptr;
head->next = nullptr;
head->data = A[0];
Node* tail = head;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++)
{
Node* t = new Node;
t->prev = tail;
t->data = A[i];
t->next = tail->next; // tail->next is points to null
tail->next = t;
tail = t;
}
}
void DoublyLinkedList::Reverse()
{
Node* p = head;
Node* temp;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
temp = p->next;
p->next = p->prev;
p->prev = temp;
p = p->prev;
//Need to check the following condition again
if(p->next == nullptr)
{
p->next = p->prev;
p->prev = nullptr;
head = p;
break;
}
}
}
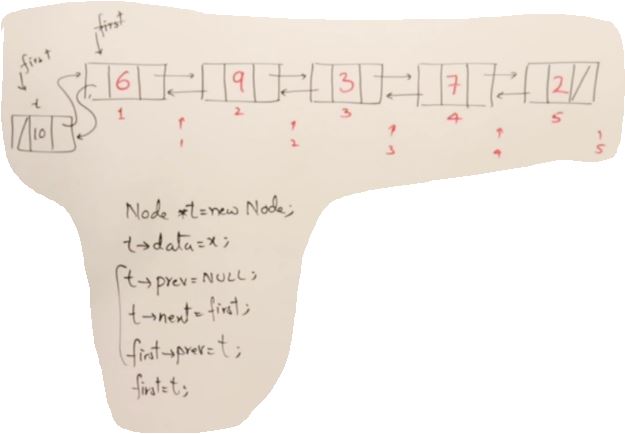
void DoublyLinkedList::insert_(int index, int x)
{
if(index<0 || index> Length())
return;
Node* p=head;
Node* t= new Node;
t->data = x;
if(index ==0)
{
t->prev = nullptr;
t->next = head;
head->prev = t;
head = t; // pointing the "head" changed to t as new head pointer;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<index-1;i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
t->prev = p;
t->next = p->next;
if(p->next){
p->next->prev = t;
}
p->next = t;
}
}
DoublyLinkedList::~DoublyLinkedList()
{
Node* p =head;
while(head)
{
head = head->next;
delete p;
p = head;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1,3,5,7,9};
DoublyLinkedList dll(A, sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout<<"length : "<<dll.Length();
dll.insert_(0,11);
dll.insert_(6,13);
dll.Display();
dll.Delete(6);
dll.Delete(1);
dll.Display();
dll.Reverse();
dll.Display();
return 0;
}
Finding Middle Element of a Linked list
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* head = new Node;
void create(int A[], int n)
{
Node* temp;
Node* tail;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = nullptr;
tail = head;
for(int i=1; i<n;i++)
{
temp = new Node;
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
tail->next = temp;
tail = temp;
}
}
void middleNode1(Node* p)
{
Node* t = p;
int length =0;
while(t)
{
length++;
t=t->next;
}
int index = length/2;
Node* q=head;
for(int i =0; index-1; i++)
{
q = q->next;
}
cout << "Middle Element (Method-I): " << q->data << endl;
}
void middleNode2(Node* p){
Node* q = p;
while (q){
q = q->next;
if (q){
q = q->next;
}
if (q){
p = p->next;
}
}
cout << "Middle Element (Method-II): " << p->data << endl;
}
void middleNode3(Node* p){
stack<Node*> s;
while (p){
s.push(p);
p = p->next;
}
int length = s.size();
int popLength = (int)(floor(length/2.0));
while (popLength){
s.pop();
popLength--;
}
cout << "Middle Element (Method-III): " << s.top()->data << endl;
}
int main()
{
int A[]={1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21};
create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
cout << endl;
middleNode1(head);
return 0;
}
Finding Intersecting point of two linked list.
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* head = new Node;
void create(int A[], int n){
Node* temp;
Node* tail;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = nullptr;
tail = head;
for (int i=1; i<n; i++){
temp = new Node;
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
tail->next = temp;
tail = temp;
}
}
Node* second = new Node;
void createSecond(int A[], int n, Node* p)
{
Node* temp;
Node* tail;
second->data = A[0];
second->next = nullptr;
tail = second;
for(int i=1; i<n;i++)
{
temp = new Node;
temp->data = A[i];
temp->next = nullptr;
tail->next = temp;
tail = temp;
}
tail->next = p;
}
void Intersection(Node* p, Node* q)
{
//Populate first stack;
stack<Node*> stk1;
while(p!=nullptr)
{
stk1.push(p);
p=p->next;
}
//Populate second stack
stack<Node*> stk2;
while(q!=nullptr)
{
stk1.push(q);
q=q->next;
}
Node* r;
while(stk1.top()==stk2.top())
{
r = stk1.top();
stk1.pop();
stk2.pop();
}
cout << "Intersecting Node: " << r->data << endl;
}
int main()
{
// Create First Linked List
int A[]={1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21};
create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
// Create Second Linked List
Node* temp = head;
int i = 5;
while (i>0)
{
temp = temp->next;
i--;
}
cout << temp->data << endl;
int B[] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
createSecond(B, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]), temp);
//Find Intersection
Intersection(head,second);
return 0;
}



Comments