32. Sorting Technique 2
24 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
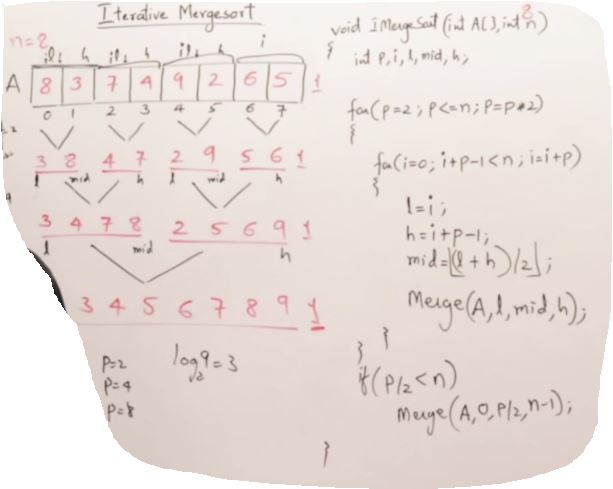
Iterative Merging
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void Merge(int A[], int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i =low;
int j = mid +1;
int k = low;
int B[high+1];
while(i<mid && j < high)
{
if(A[i]<A[j])
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
else
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid)
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
while(j<=high)
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
for(int i = low; i<=high; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i];
}
}
void IterativeMergeSort(int A[], int n)
{
int p;
for(p=2;p<=n;p=p*2)
{
for(int i=0; i+p-1<n; i=i+p)
{
int low = i;
int high = i+p-1;
int mid = (low+high)/2;
Merge(A, low, mid, high);
}
}
if(p/2<n)
{
Merge(A,0,p/2-1,n-1);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "\t\tA");
IterativeMergeSort(A, n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Recursive Merging
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void Merge(int A[], int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i =low;
int j = mid +1;
int k = low;
int B[high+1];
while(i<mid && j < high)
{
if(A[i]<A[j])
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
else
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid)
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
while(j<=high)
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
for(int i = low; i<=high; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i];
}
}
void RecursiveMergeSort(int A[], int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
// Calculate mid point
int mid = low + (high-low)/2;
// Sort SUb-lists;
RecursiveMergeSort(A, low, mid);
RecursiveMergeSort(A, mid+1, high);
// Merge Sorted sub-lists;
Merge(A, low, mid, high);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "\t\tA");
RecursiveMergeSort(A,0, n-1);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Count Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
int Max(int A[], int n)
{
int Max_ = -32768; // int min;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(A[i]>Max_)
Max_ = A[i];
}
return Max_;
}
void CountSort(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ = Max(A,n); //12
// Create count array
int* count_ = new int[max_+1]; // making hash table to check the size of index;
// initilize count array with 0
for(int i = 0; i< max_+1; i++)
{
count_[i] = 0;
}
// Update count array values based on A values;
for(int i = 0; i< n; i++)
{
count_[A[i]]++;
}
// Update A with sorted elements
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while(j<max_+1)
{
if(count_[j]>0)
{
A[i++] = j;
count_[j]--;
}
else
{
j++;
}
}
delete[] count_;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
CountSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
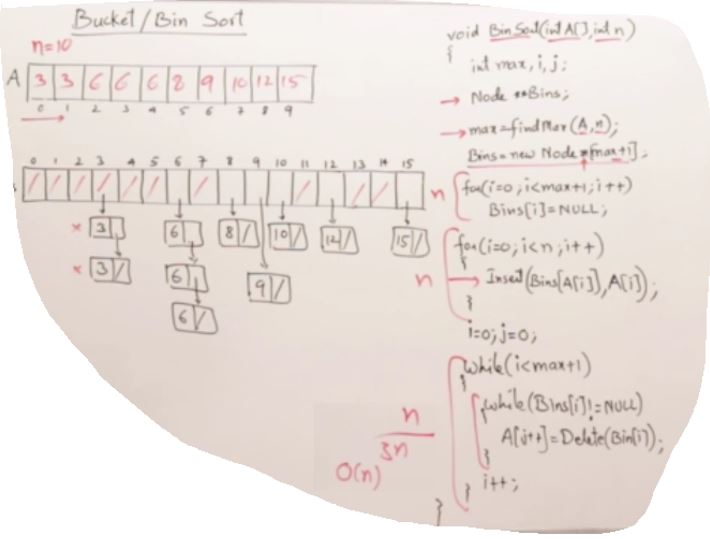
Bin/Bucket Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int value;
Node* next;
};
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
int Max(int A[], int n)
{
int Max_ = -32768; // int min;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(A[i]>Max_)
Max_ = A[i];
}
return Max_;
}
void Insert(Node** bins, int inx)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->value = inx;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(bins[inx]==nullptr)
{
bins[inx] = temp;
}
else
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
while(p->next!=nullptr)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next = temp;
}
}
int Delete(Node** bins, int inx)
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
bins[inx] = bins[inx]->next;
int x = p->value;
delete p;
return x;
}
void BinSort(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ = Max(A,n); //12
// Create count array
Node** bins = new Node*[max_+1];// if just use one star here only create a one Node
// but if we do doulbe star, we can set a size of Node as array in heap memory
// initilize bin array with 0
for(int i = 0; i< max_+1; i++)
{
bins[i] = nullptr;
}
// Update bin array values based on A values;
for(int i=0; i<n;i++)
{
Insert(bins, A[i]);
}
// Update A with sorted elements
int i=0;
int j=0;
while(i<max_+1)
{
while(bins[i]!=nullptr)
{
A[j++] = Delete(bins,i);
}
i++;
}
delete[] bins;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
BinSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
- Node** bins = new Node*[max_+1];// if just use one star here only create a one Node but if we do doulbe star, we can set a size of Node as array in heap memory
Radix Sort
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int value;
Node* next;
};
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
int Max(int A[], int n)
{
int Max_ = -32768; // int min;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(A[i]>Max_)
Max_ = A[i];
}
return Max_;
}
void Insert(Node** bins, int value, int inx)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->value = value;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(bins[inx]==nullptr)
{
bins[inx] = temp;
}
else
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
while(p->next!=nullptr)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next = temp;
}
}
int Delete(Node** bins, int inx)
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
bins[inx] = bins[inx]->next;
int x = p->value;
delete p;
return x;
}
int countDigits(int x)
{
int count_ =0;
while(x != 0)
{
x = x/10;
count_ ++;
}
return count_;
}
void initializeBins(Node** bins, int n)
{
for(int i =0; i<n; i++)
{
bins[i] = nullptr;
}
}
int getBinindex(int x, int idx)
{
return (int)(x/pow(10,idx))%10;
}
void RadixSort(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ = Max(A,n); //12
int nPass = countDigits(max_);
// Create count array
Node** bins = new Node*[10];// if just use one star here only create a one Node
// but if we do doulbe star, we can set a size of Node as array in heap memory
// initilize bin array with 0
initializeBins(bins,10);
// Update bin array values based on A values;
for(int pass = 0; pass<nPass; pass++)
{
// Update bins based on A values;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
int binidx = getBinindex(A[i],pass);
Insert(bins,A[i],binidx);
}
// Update A with sorted elements
int i=0;
int j=0;
while(i<10)
{
while(bins[i]!=nullptr)
{
A[j++] = Delete(bins,i);
}
i++;
}
// Initialize bins with nullptr again
initializeBins(bins, 10);
}
delete[] bins;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {237, 146, 259, 348, 152, 163, 235, 48, 36, 62};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
RadixSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Shell Sort
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
// Code is similar to Insertion Sort with some modifications
void ShellSort(int A[], int n)
{
for(int gap=n/2; gap>=1; gap/=2)
{
for(int j= gap; j<n; j++)
{
int temp = A[j];
int i = j - gap;
while(i>=0 && A[i]>temp)
{
A[i+gap] = A[i];
i = i-gap;
}
A[i+gap] = temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {11, 13, 7, 12, 16, 9, 24, 5, 10, 3};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
ShellSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Iterative Merging
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void Merge(int A[], int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i =low;
int j = mid +1;
int k = low;
int B[high+1];
while(i<mid && j < high)
{
if(A[i]<A[j])
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
else
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid)
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
while(j<=high)
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
for(int i = low; i<=high; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i];
}
}
void IterativeMergeSort(int A[], int n)
{
int p;
for(p=2;p<=n;p=p*2)
{
for(int i=0; i+p-1<n; i=i+p)
{
int low = i;
int high = i+p-1;
int mid = (low+high)/2;
Merge(A, low, mid, high);
}
}
if(p/2<n)
{
Merge(A,0,p/2-1,n-1);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "\t\tA");
IterativeMergeSort(A, n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Recursive Merging
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void Merge(int A[], int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i =low;
int j = mid +1;
int k = low;
int B[high+1];
while(i<mid && j < high)
{
if(A[i]<A[j])
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
else
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid)
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
while(j<=high)
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
for(int i = low; i<=high; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i];
}
}
void RecursiveMergeSort(int A[], int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
// Calculate mid point
int mid = low + (high-low)/2;
// Sort SUb-lists;
RecursiveMergeSort(A, low, mid);
RecursiveMergeSort(A, mid+1, high);
// Merge Sorted sub-lists;
Merge(A, low, mid, high);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "\t\tA");
RecursiveMergeSort(A,0, n-1);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Count Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
int Max(int A[], int n)
{
int Max_ = -32768; // int min;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(A[i]>Max_)
Max_ = A[i];
}
return Max_;
}
void CountSort(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ = Max(A,n); //12
// Create count array
int* count_ = new int[max_+1]; // making hash table to check the size of index;
// initilize count array with 0
for(int i = 0; i< max_+1; i++)
{
count_[i] = 0;
}
// Update count array values based on A values;
for(int i = 0; i< n; i++)
{
count_[A[i]]++;
}
// Update A with sorted elements
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
while(j<max_+1)
{
if(count_[j]>0)
{
A[i++] = j;
count_[j]--;
}
else
{
j++;
}
}
delete[] count_;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
CountSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Bin/Bucket Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int value;
Node* next;
};
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
int Max(int A[], int n)
{
int Max_ = -32768; // int min;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(A[i]>Max_)
Max_ = A[i];
}
return Max_;
}
void Insert(Node** bins, int inx)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->value = inx;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(bins[inx]==nullptr)
{
bins[inx] = temp;
}
else
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
while(p->next!=nullptr)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next = temp;
}
}
int Delete(Node** bins, int inx)
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
bins[inx] = bins[inx]->next;
int x = p->value;
delete p;
return x;
}
void BinSort(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ = Max(A,n); //12
// Create count array
Node** bins = new Node*[max_+1];// if just use one star here only create a one Node
// but if we do doulbe star, we can set a size of Node as array in heap memory
// initilize bin array with 0
for(int i = 0; i< max_+1; i++)
{
bins[i] = nullptr;
}
// Update bin array values based on A values;
for(int i=0; i<n;i++)
{
Insert(bins, A[i]);
}
// Update A with sorted elements
int i=0;
int j=0;
while(i<max_+1)
{
while(bins[i]!=nullptr)
{
A[j++] = Delete(bins,i);
}
i++;
}
delete[] bins;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
BinSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
- Node** bins = new Node*[max_+1];// if just use one star here only create a one Node but if we do doulbe star, we can set a size of Node as array in heap memory
Radix Sort
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int value;
Node* next;
};
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
int Max(int A[], int n)
{
int Max_ = -32768; // int min;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
if(A[i]>Max_)
Max_ = A[i];
}
return Max_;
}
void Insert(Node** bins, int value, int inx)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->value = value;
temp->next = nullptr;
if(bins[inx]==nullptr)
{
bins[inx] = temp;
}
else
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
while(p->next!=nullptr)
{
p=p->next;
}
p->next = temp;
}
}
int Delete(Node** bins, int inx)
{
Node* p = bins[inx];
bins[inx] = bins[inx]->next;
int x = p->value;
delete p;
return x;
}
int countDigits(int x)
{
int count_ =0;
while(x != 0)
{
x = x/10;
count_ ++;
}
return count_;
}
void initializeBins(Node** bins, int n)
{
for(int i =0; i<n; i++)
{
bins[i] = nullptr;
}
}
int getBinindex(int x, int idx)
{
return (int)(x/pow(10,idx))%10;
}
void RadixSort(int A[], int n)
{
int max_ = Max(A,n); //12
int nPass = countDigits(max_);
// Create count array
Node** bins = new Node*[10];// if just use one star here only create a one Node
// but if we do doulbe star, we can set a size of Node as array in heap memory
// initilize bin array with 0
initializeBins(bins,10);
// Update bin array values based on A values;
for(int pass = 0; pass<nPass; pass++)
{
// Update bins based on A values;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
int binidx = getBinindex(A[i],pass);
Insert(bins,A[i],binidx);
}
// Update A with sorted elements
int i=0;
int j=0;
while(i<10)
{
while(bins[i]!=nullptr)
{
A[j++] = Delete(bins,i);
}
i++;
}
// Initialize bins with nullptr again
initializeBins(bins, 10);
}
delete[] bins;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {237, 146, 259, 348, 152, 163, 235, 48, 36, 62};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
RadixSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}
Shell Sort
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
// Code is similar to Insertion Sort with some modifications
void ShellSort(int A[], int n)
{
for(int gap=n/2; gap>=1; gap/=2)
{
for(int j= gap; j<n; j++)
{
int temp = A[j];
int i = j - gap;
while(i>=0 && A[i]>temp)
{
A[i+gap] = A[i];
i = i-gap;
}
A[i+gap] = temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {11, 13, 7, 12, 16, 9, 24, 5, 10, 3};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, n, "A");
ShellSort(A,n);
Print(A, n, "Sorted A");
return 0;
}











Comments