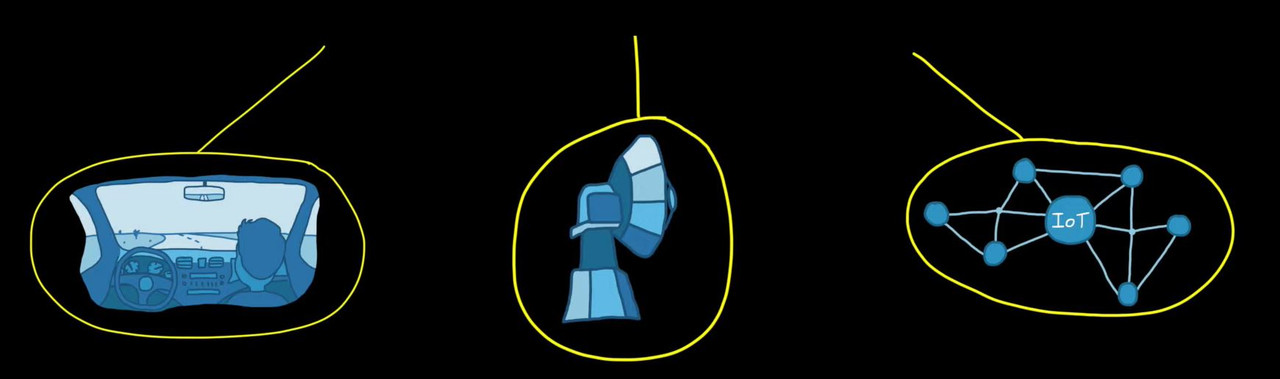
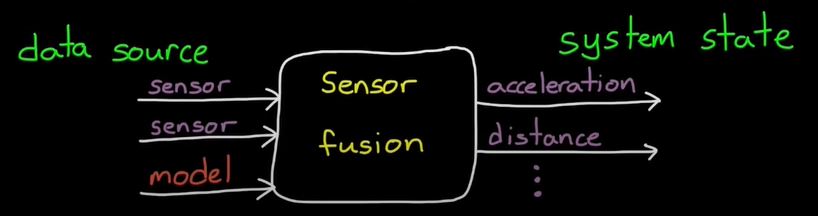
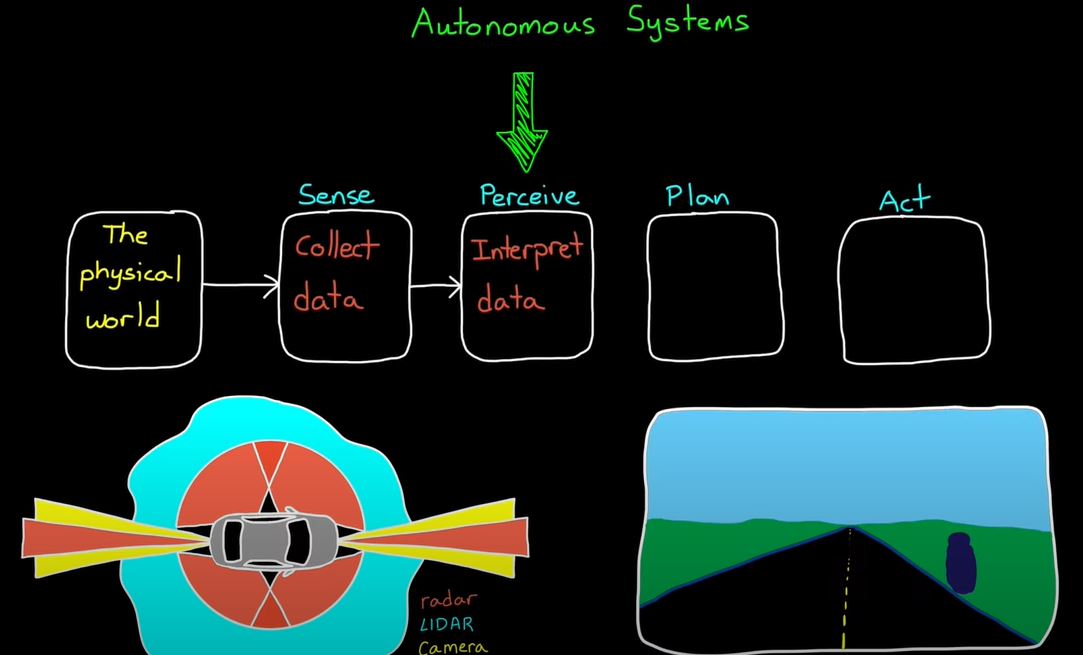
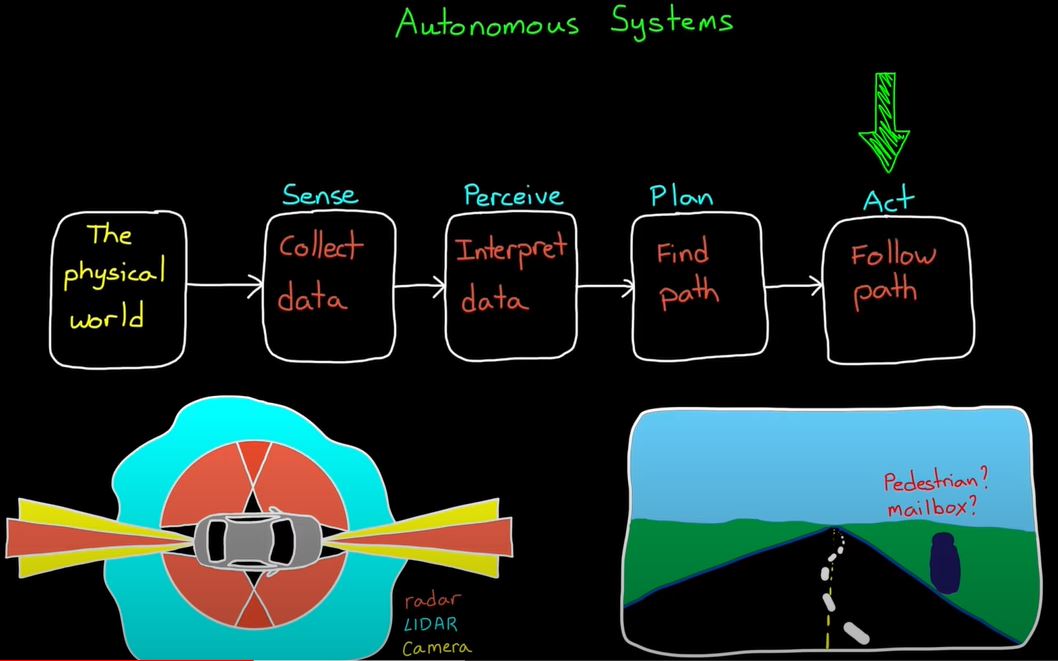
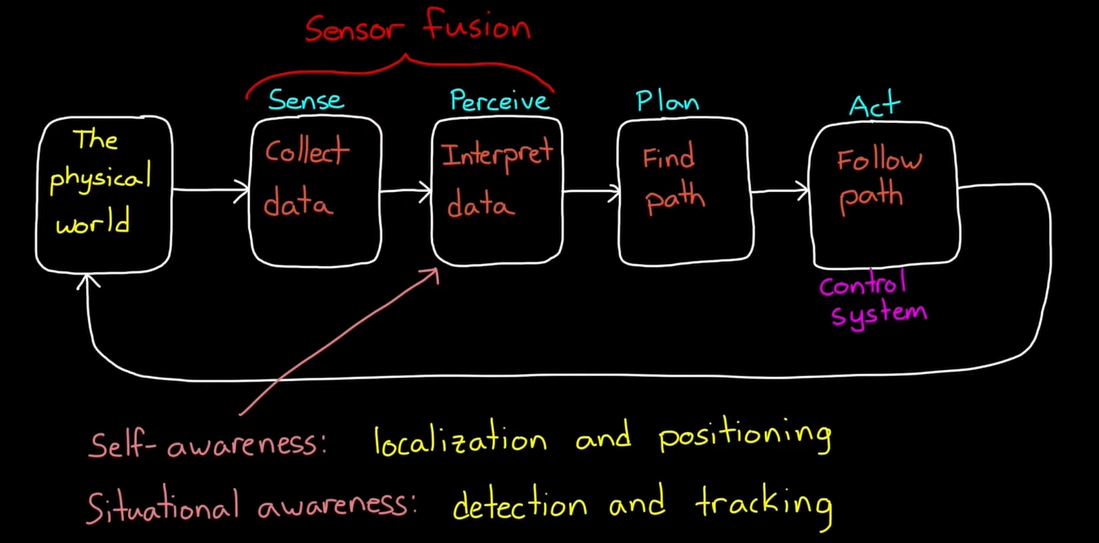
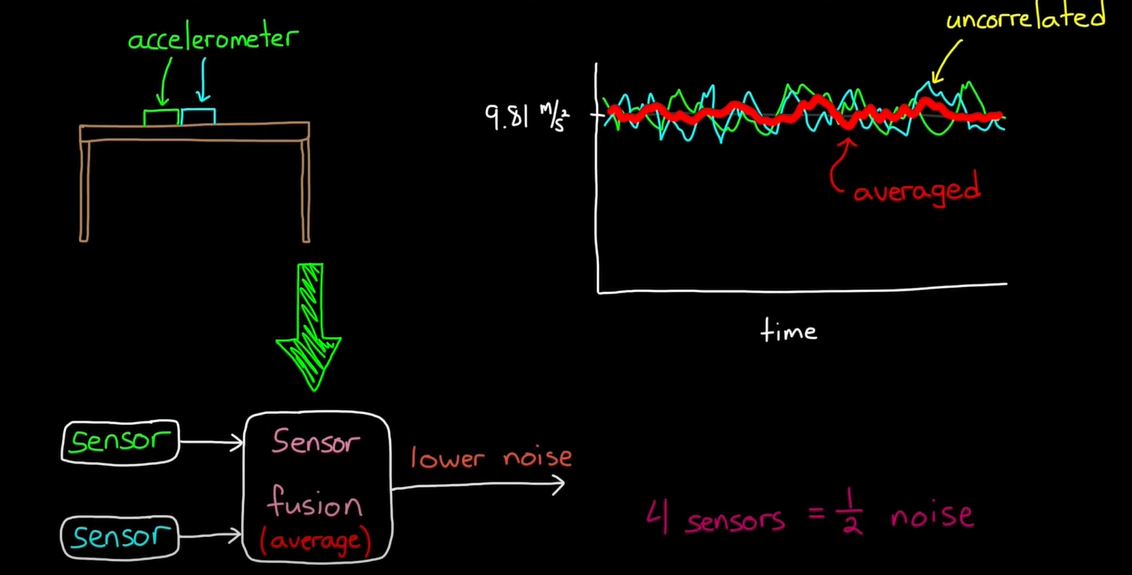
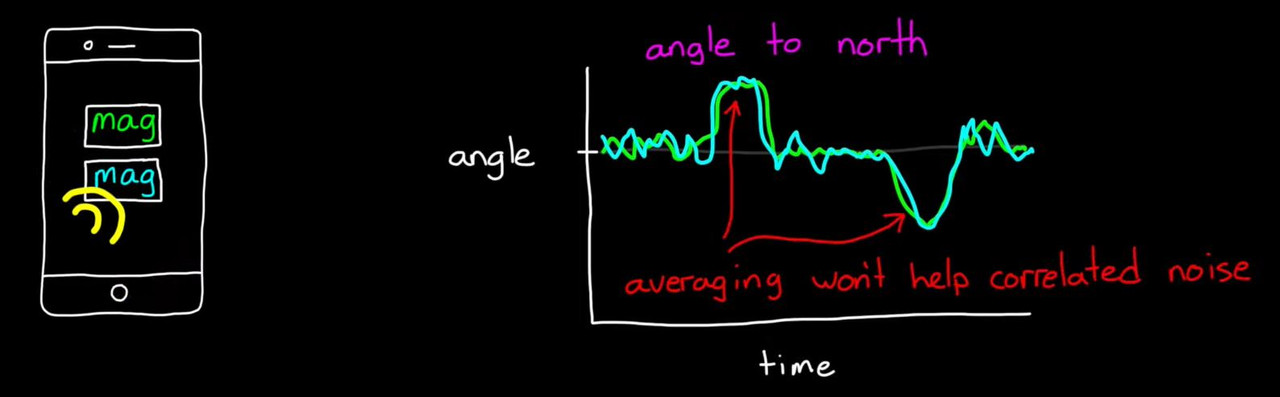
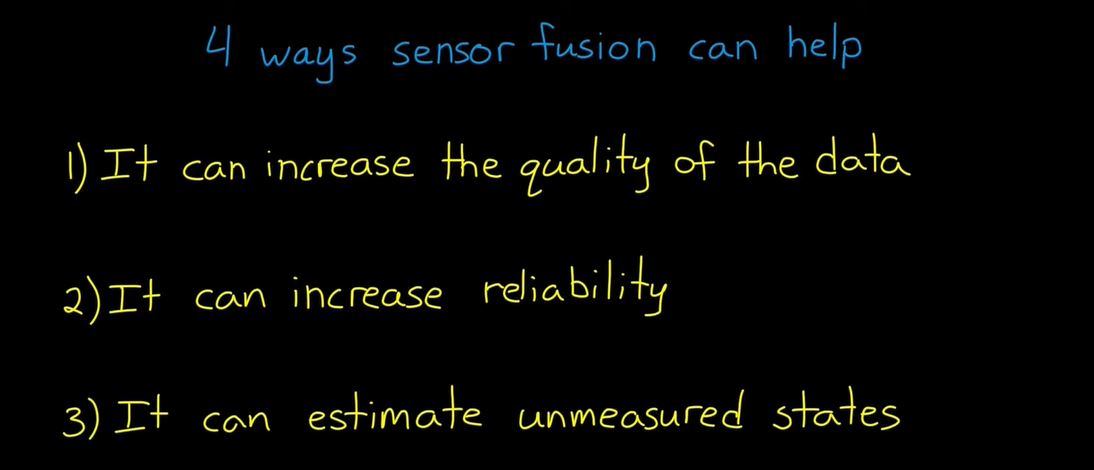
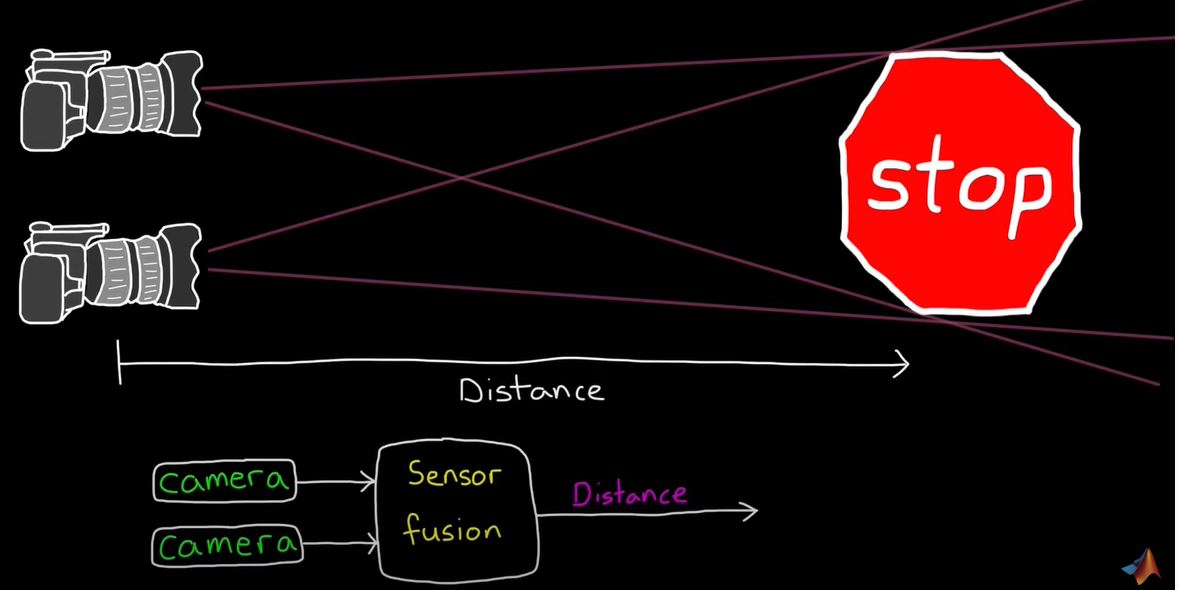
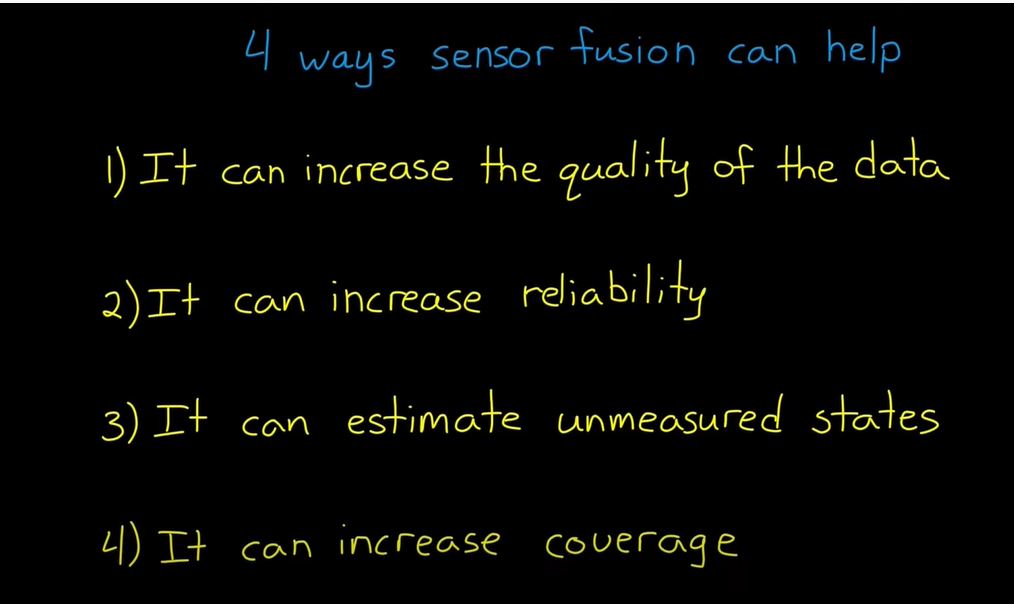
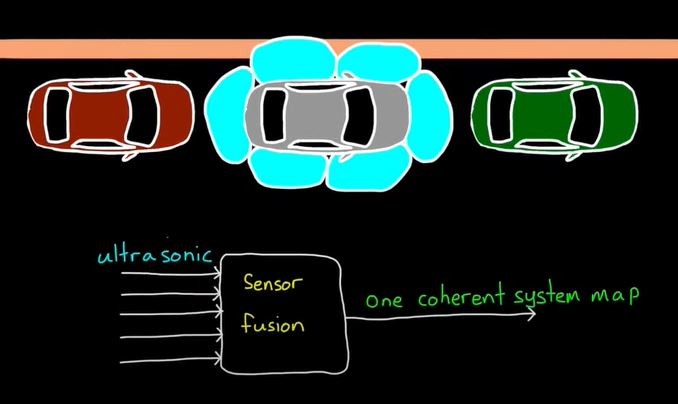
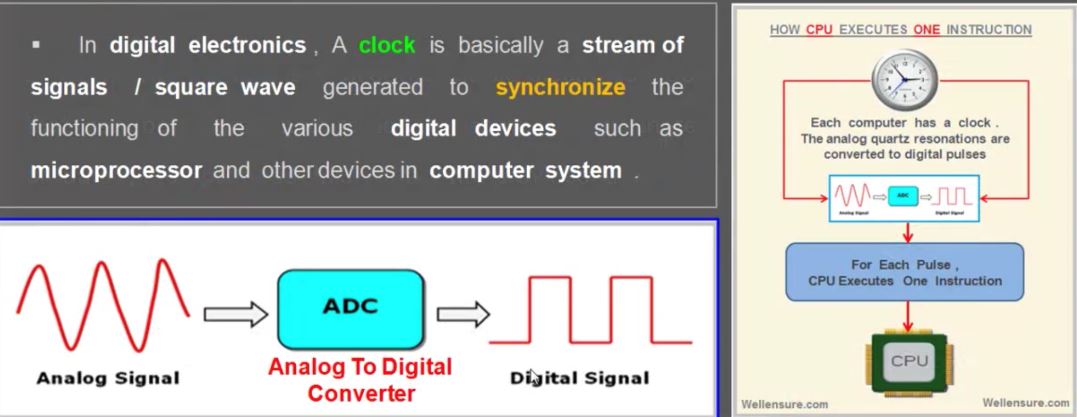
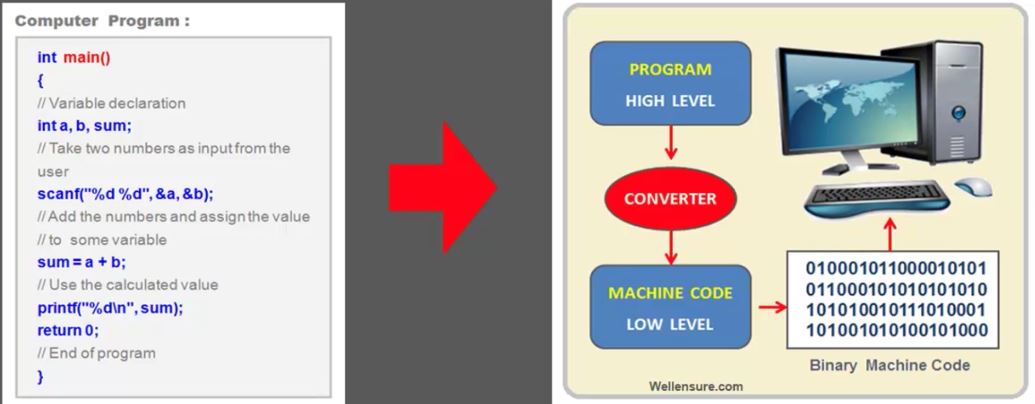
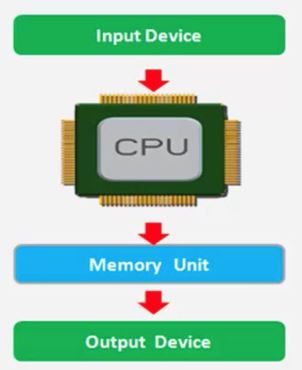
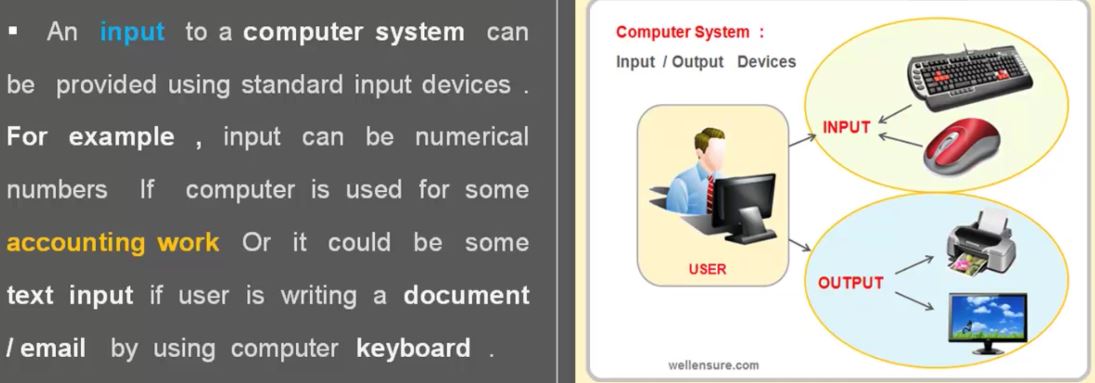
2. Sensor Fusion for Localization and Multi-object Tracking
12 May 2020 | Sensor fusion
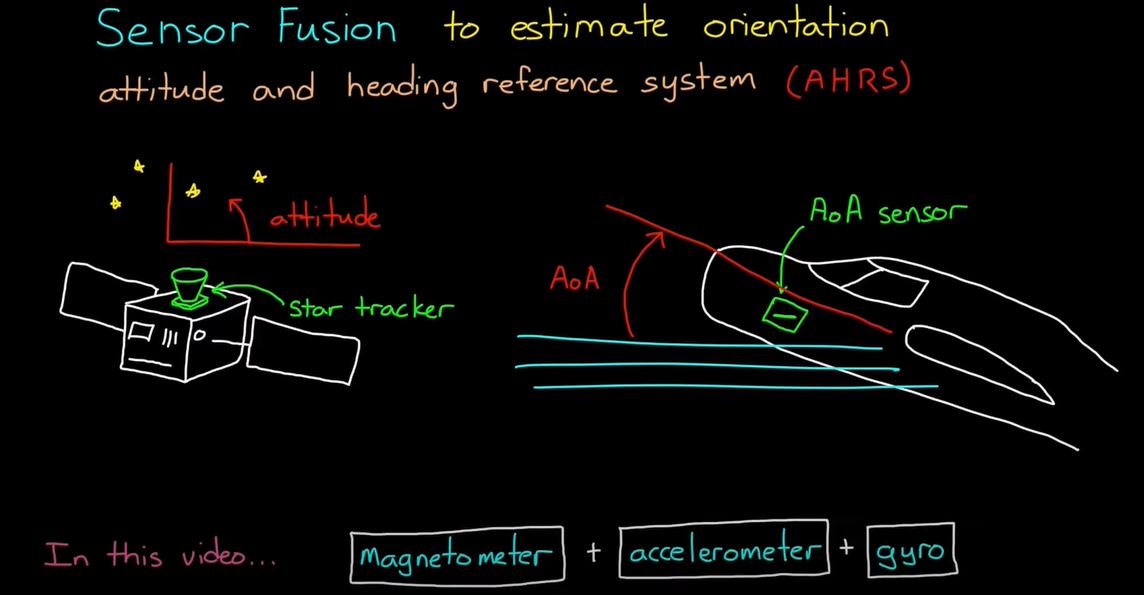
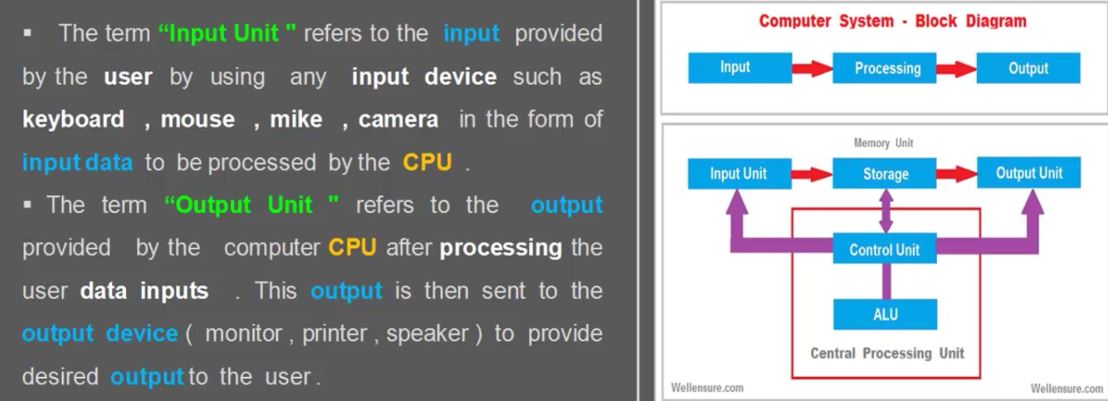
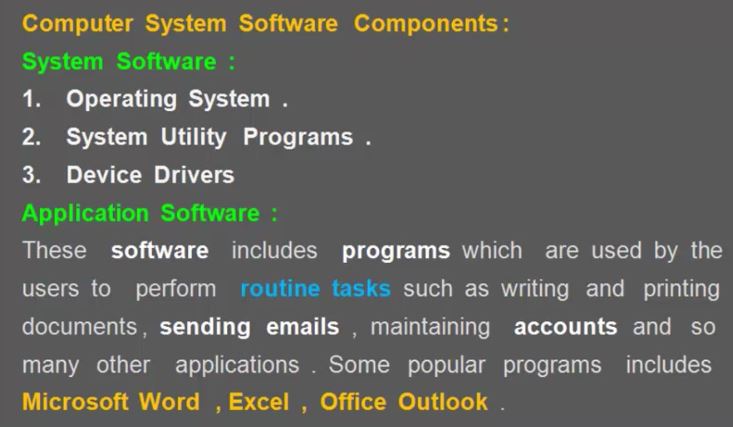
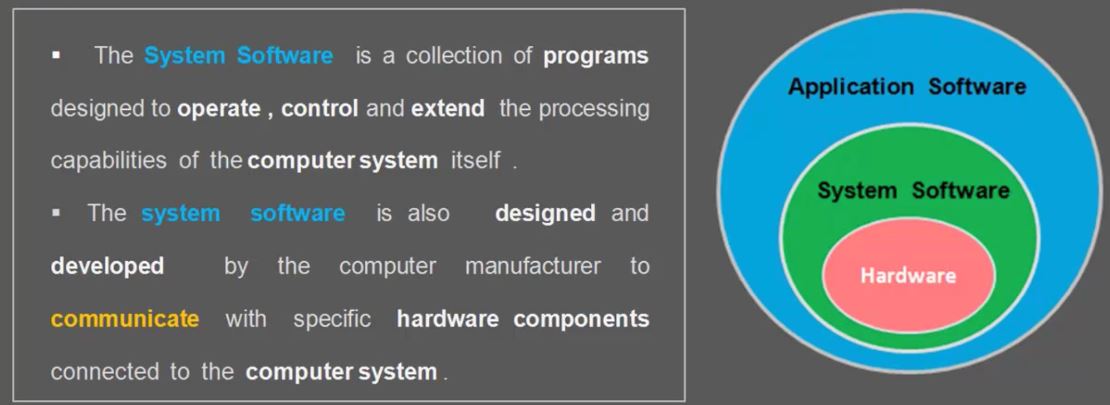
Sensor Fusion to estimate orientation
- Attitude and Heading reference system(AHRM)
- 자력계 [magnetometer, 磁力計]
- we can find orientation using Magnetometer, Accelerometer, Gyro
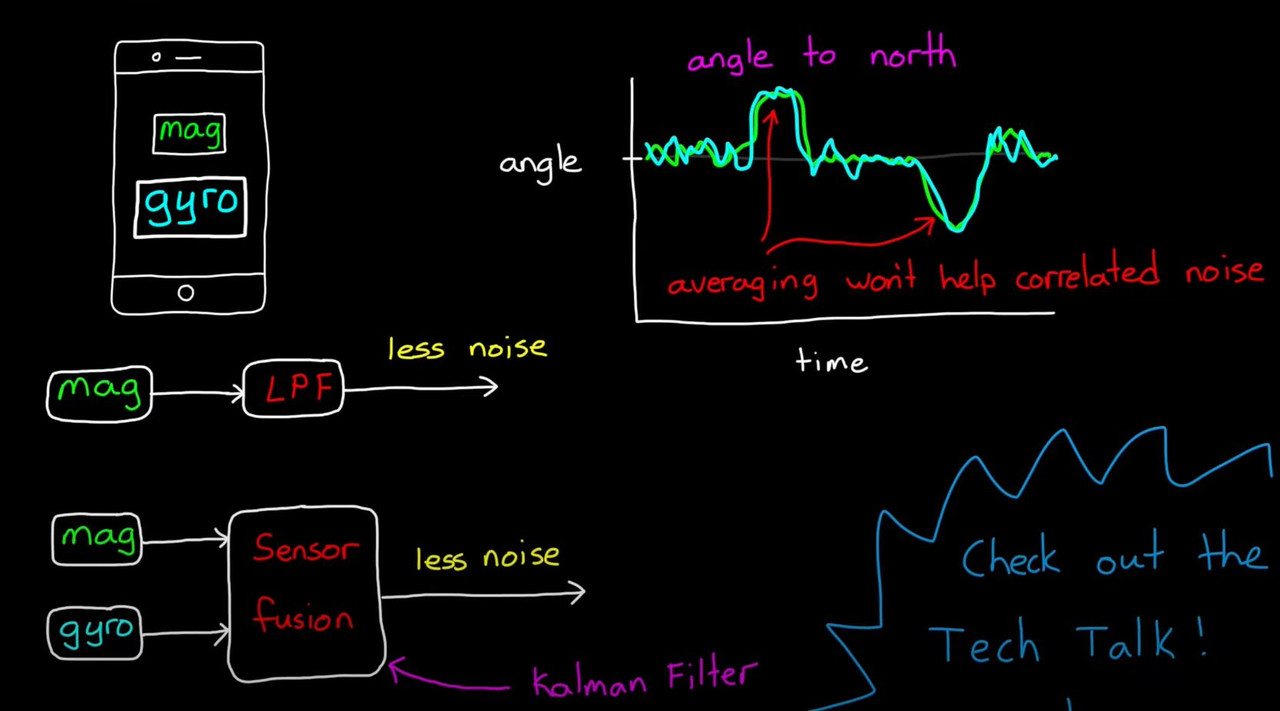
- Accleromter : 중력 방향을 이용해서 orientation을 찾는다 (accleration은 오직 위아래 Gravity만 얻는다.)
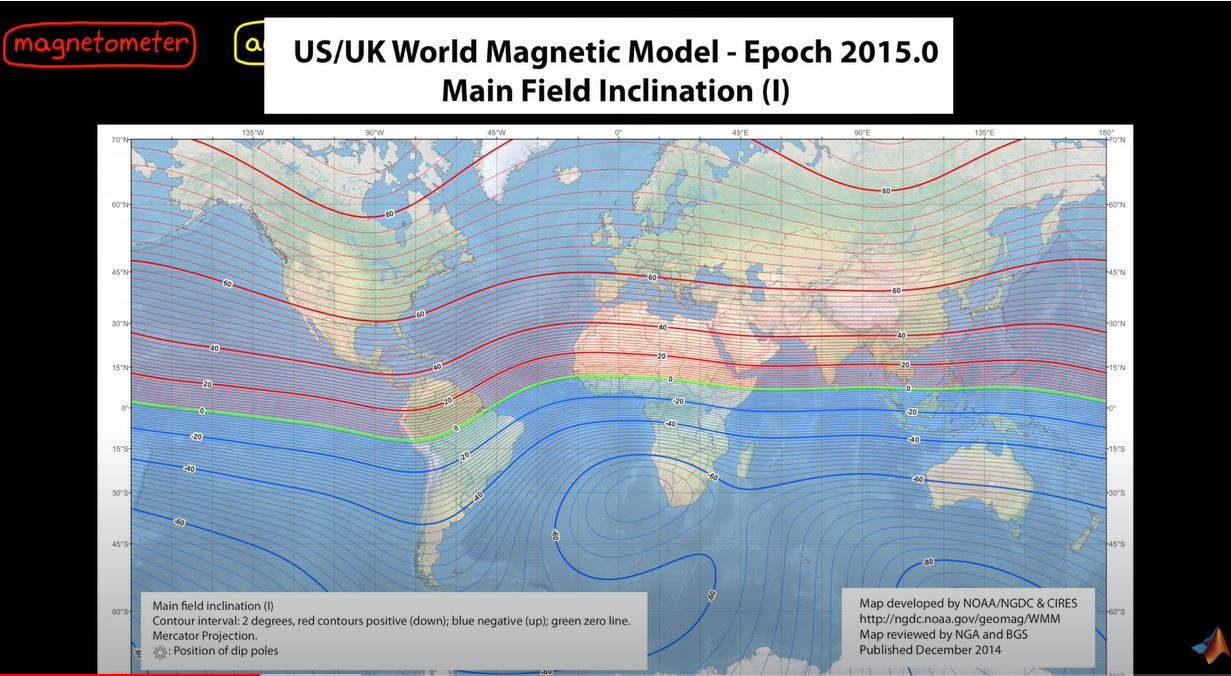
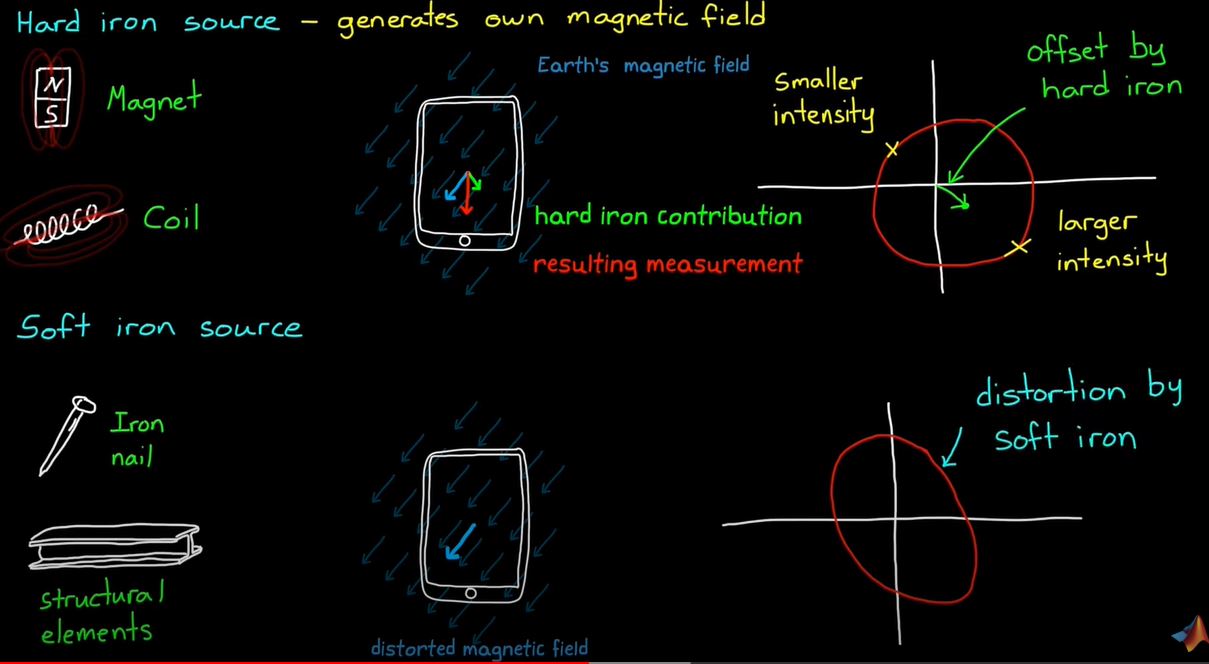
- Magnetometer : 자기력을 이용하여 북쪽을 결정한다. (기준점을 이용한 orientation구한다, 만약 Magnetic 물체가 있으면 방해를 받는다.)
- 하지만 남반구인지 북반구인지에 따라 북쪽을 가르키는 방향이 다르다.
-
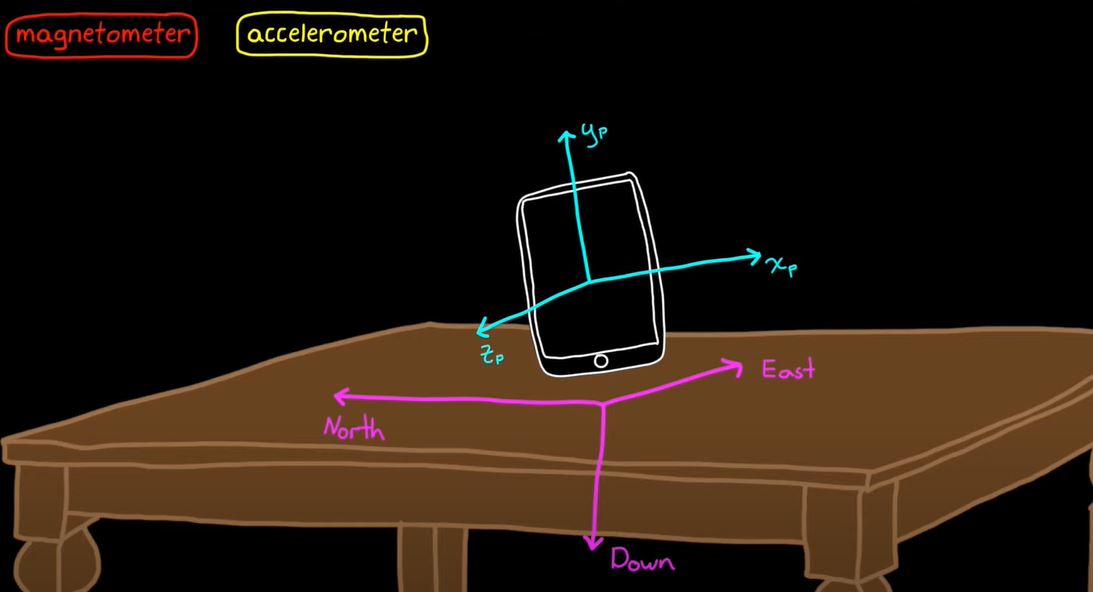
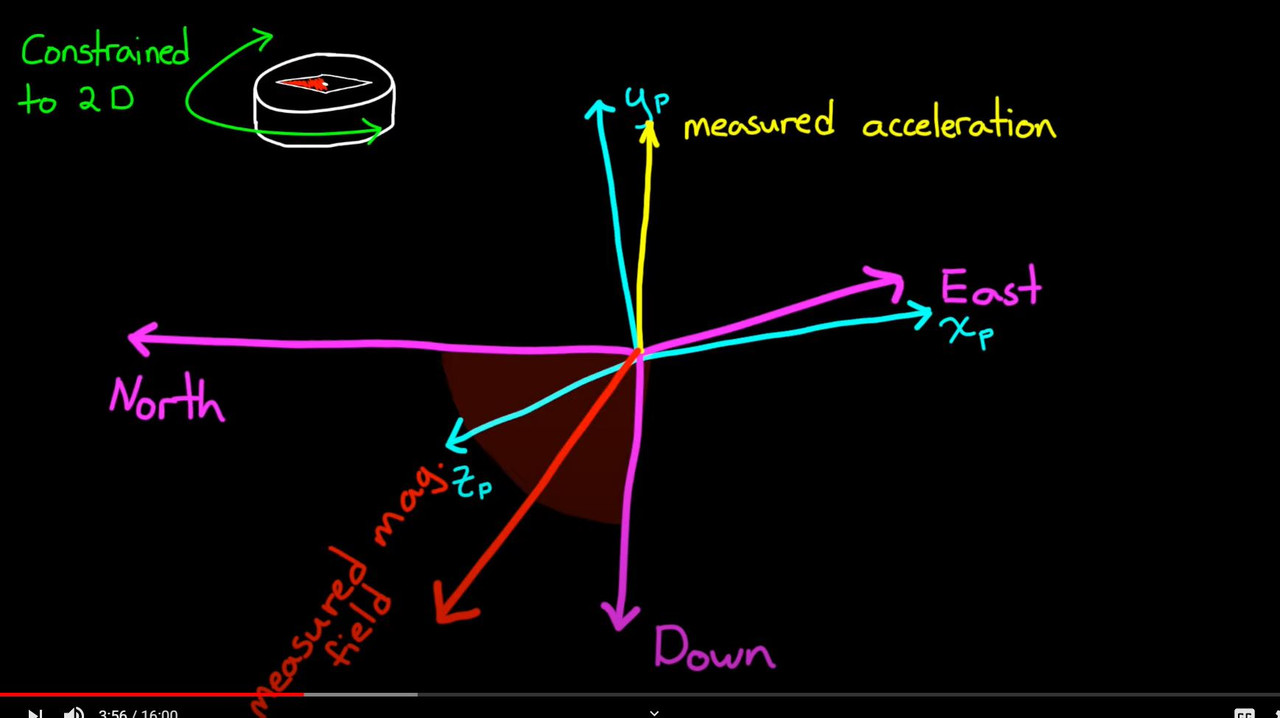
- 아래쪽은 가속도 벡터의 반대 방향( Measure accleration)
- East는 아래쪽과 Magnetic field의 외적이고
- 북쪽은 동쪽과 아래쪽의 외적이다.
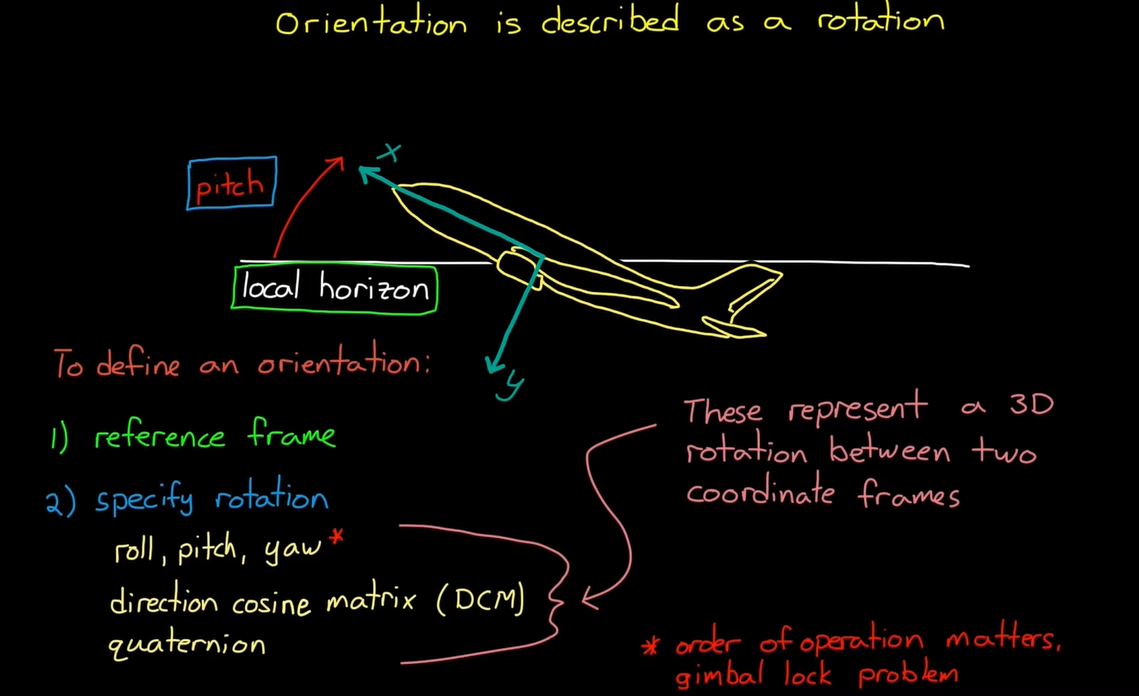
- 따라서 본체의 방향은 본체 프레임과 NED(North, East, Down) 프레임 사이의 회전이다.
- 방금 계산한 NED 벡터에서 Direction Consine Matrix directly하게 구할 수 있다.
let’s check real device
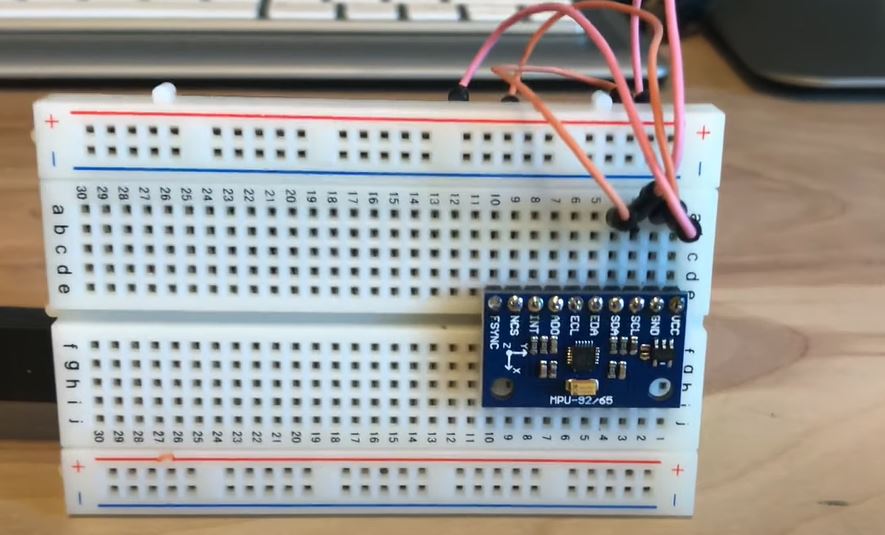
- there is a physical IMU and Accelerometer.
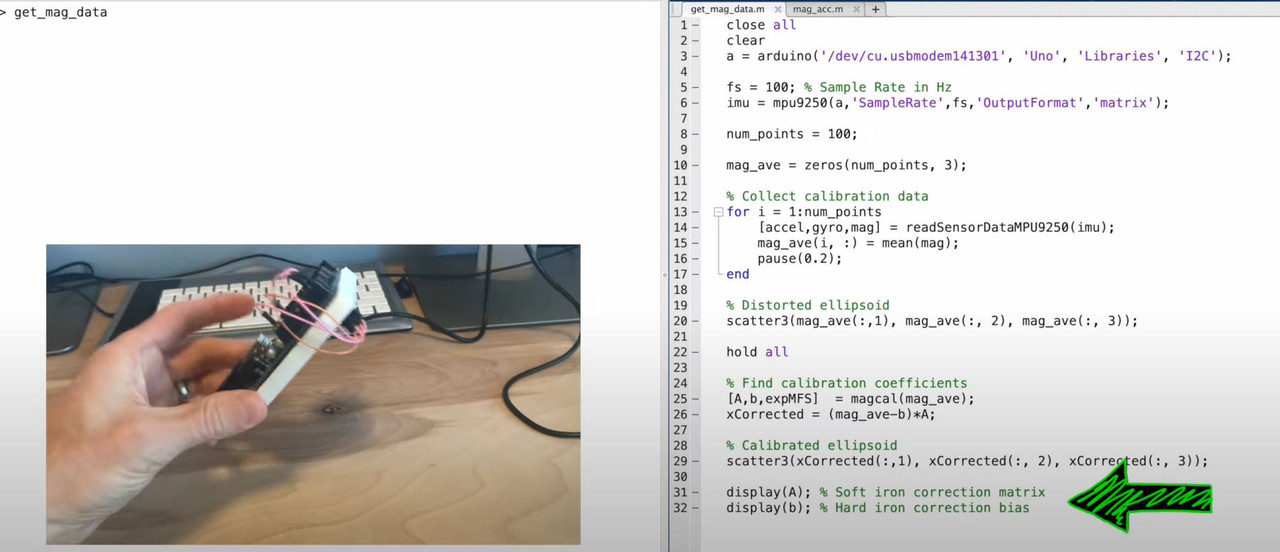
- first connect to the Arduino and IMU
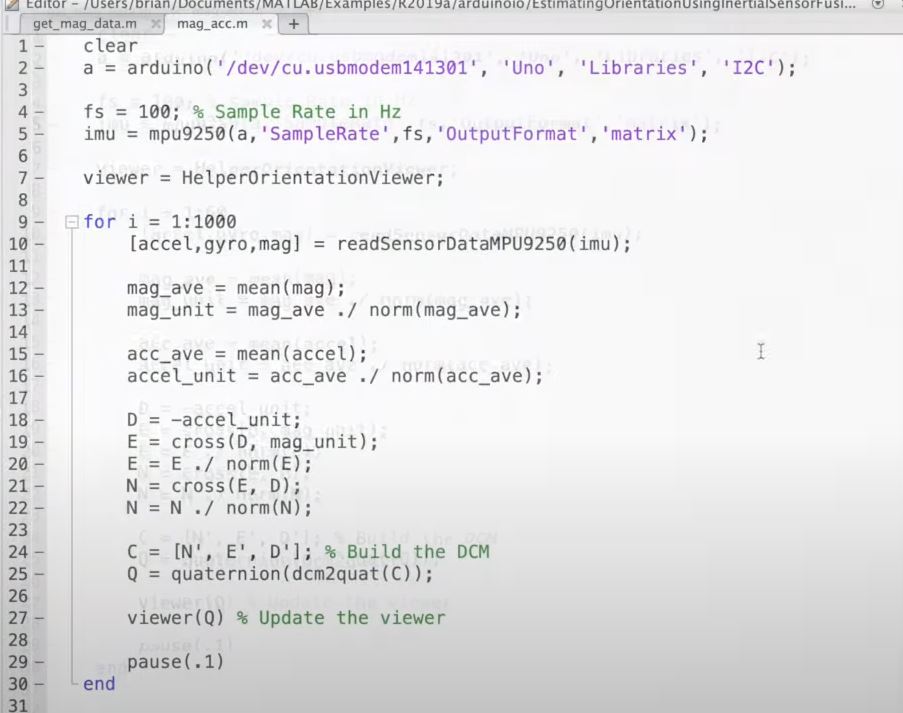
- and using a Matlab viewer to visualize the orientation
- update the view each time
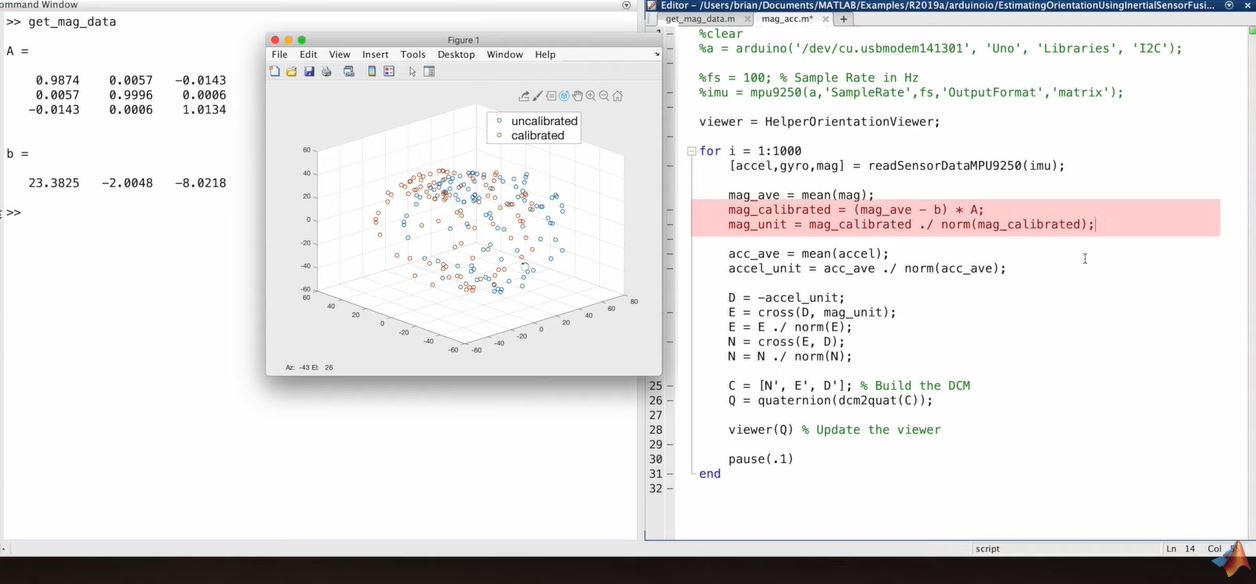
- from for 1 = 1:1000 to Q
- is a basically reading the sensors performing the cross products and building The DCM
- but the systme is linear, so if moving alot it’s estimate accurate down
- Accleration 센서는 오직 위아래 중력 값만 판단한다.
- Magnetic 물체가 있으면 orientation 값을 찾는데 방해를 받는다.
-
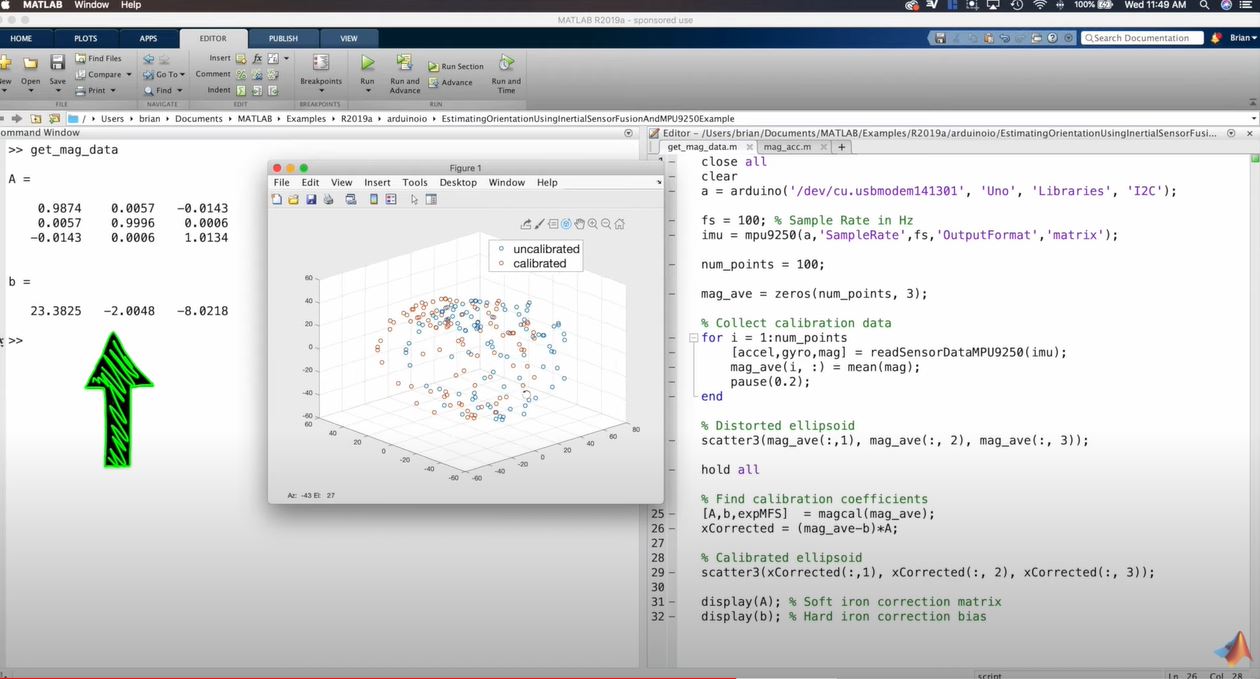
- 문제를 풀기 위해 Calibration 필요
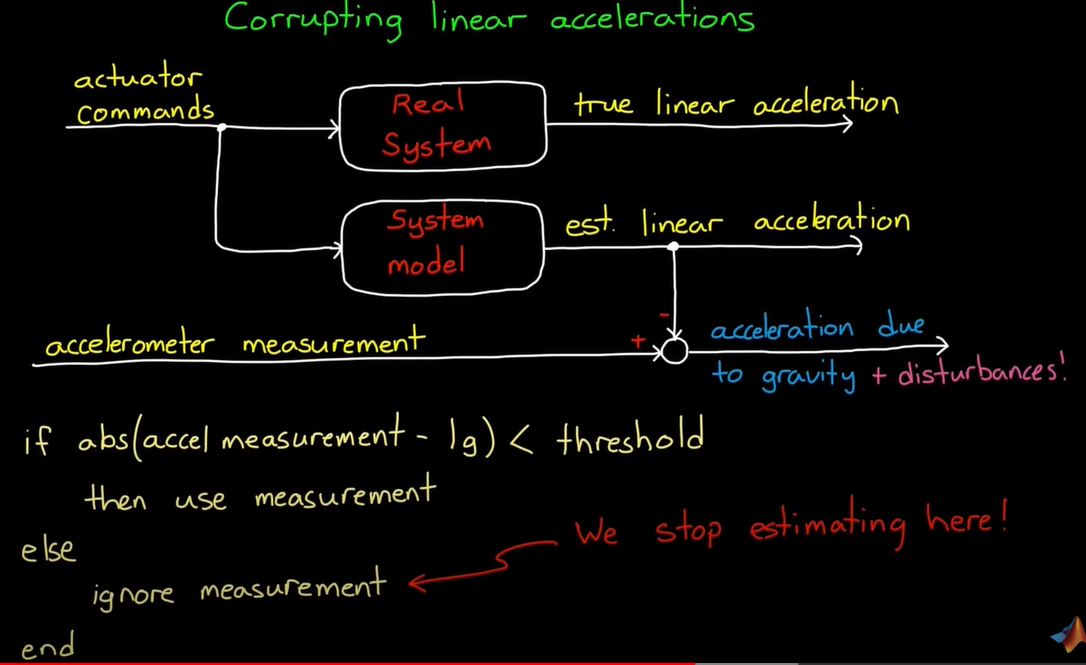
- 한가지 더 문제인 Corrupting linear accelrations
- take the commands that are sent to the actuators and play it through a model of the system to estimate the expected linear acceration and then subtract that value from the measurement
- this is something that is possible if say our system is drone and mine is flying it around by commanding the four propellers.
- if we can’t predict the linear acceleration or the external disturbances are too high, another option is to ignore accelerometer reading that are outside of some threshold from a 1g measurement. if magnitude of the reading is not close to the magnitude of gravity, then, clearly the sensor is picking up on other movement and it can’t be trusted.
- this keeps corrupted measuremens from getting into our fusion algorithm, but it is not a great solution because we stopped estimating orientation during these times and we lose track of the state of the system again
- it is not really problem if we trying to estimate orientation for a static object.
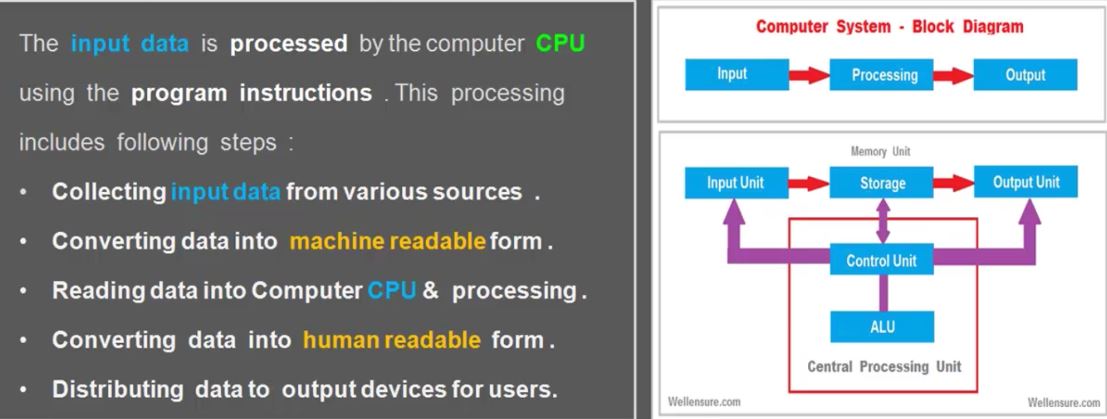
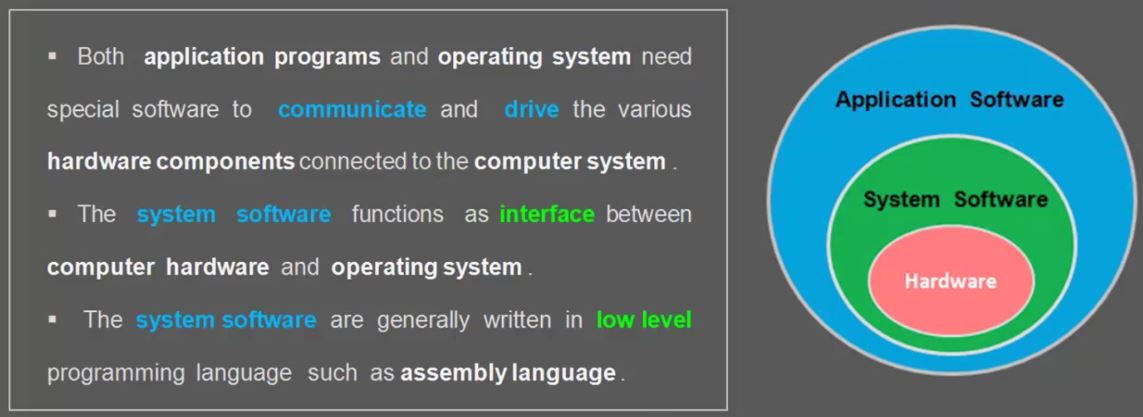
Solving to get orientation value problem
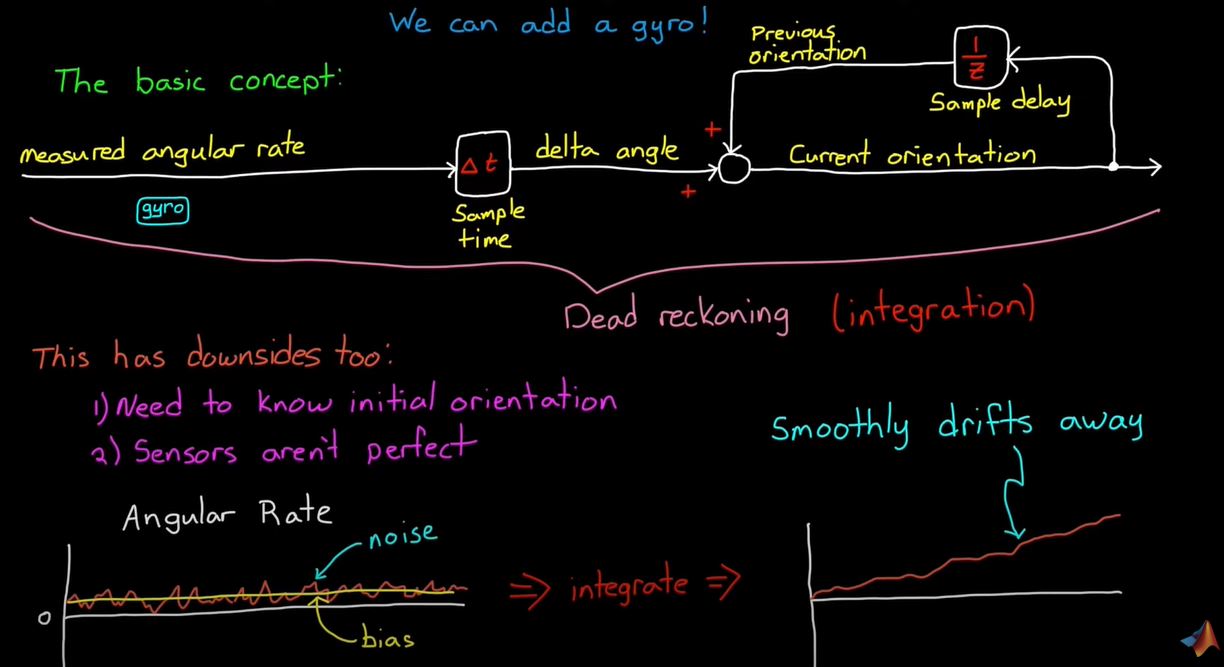
- add gyro !
- there are two method to find orientation
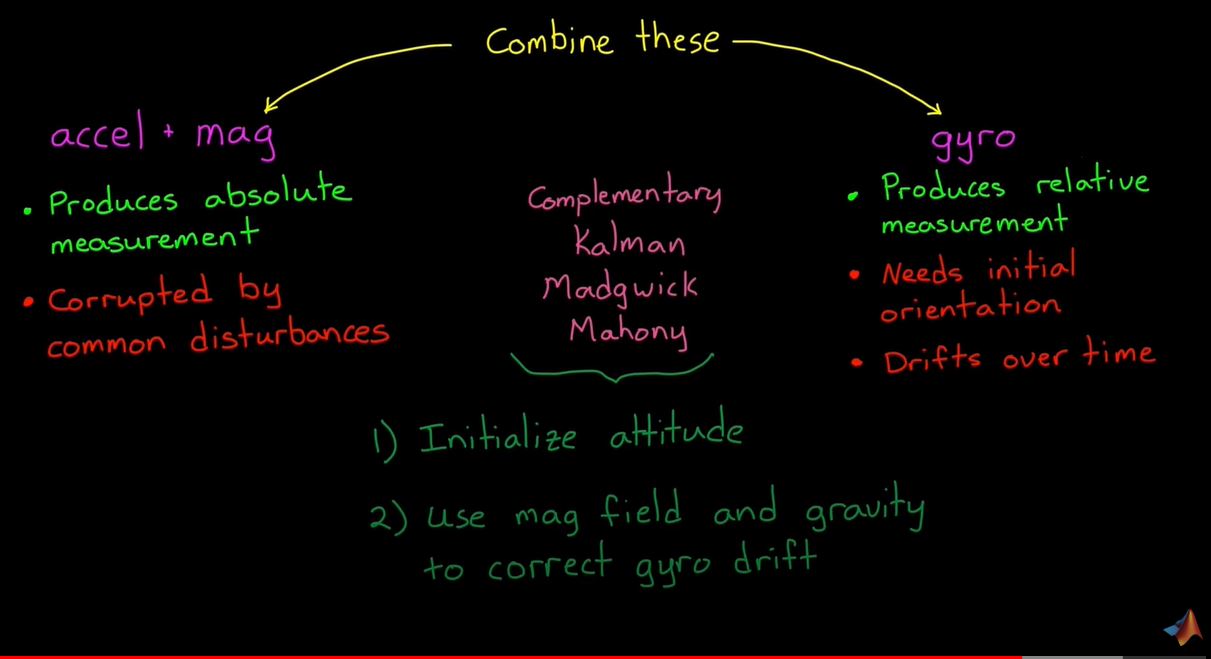
- accel + mag
- Gyro
- accel + mag 장단점과 Gyro의 장단점을 합하여 문제점 해결
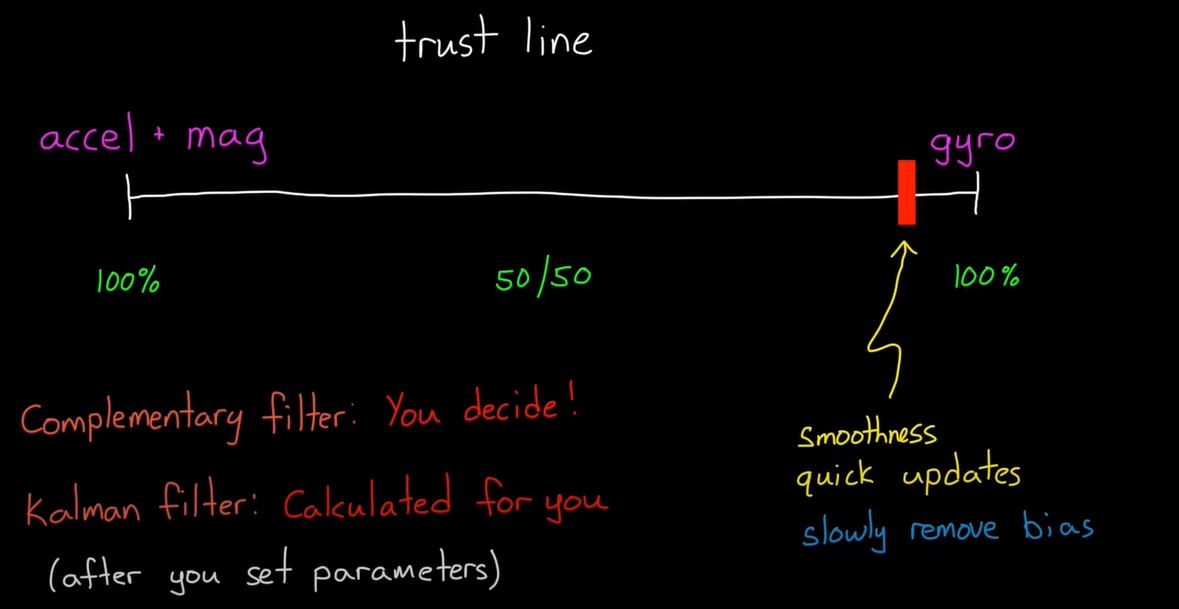
- Complementary(상호 보완) Filter
- Kalman Filter
- Madgwick
-
mahony
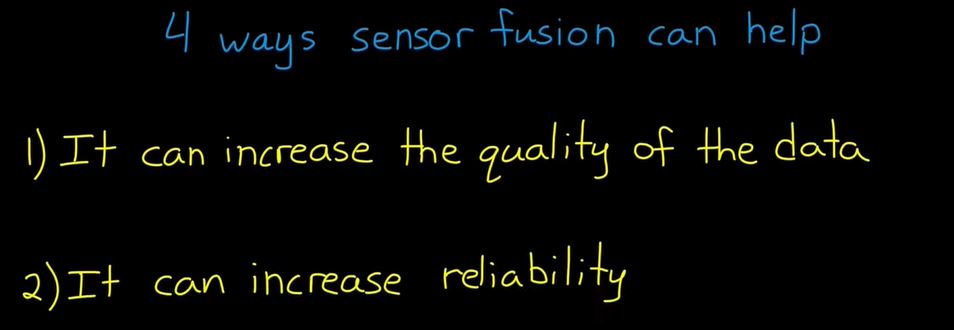
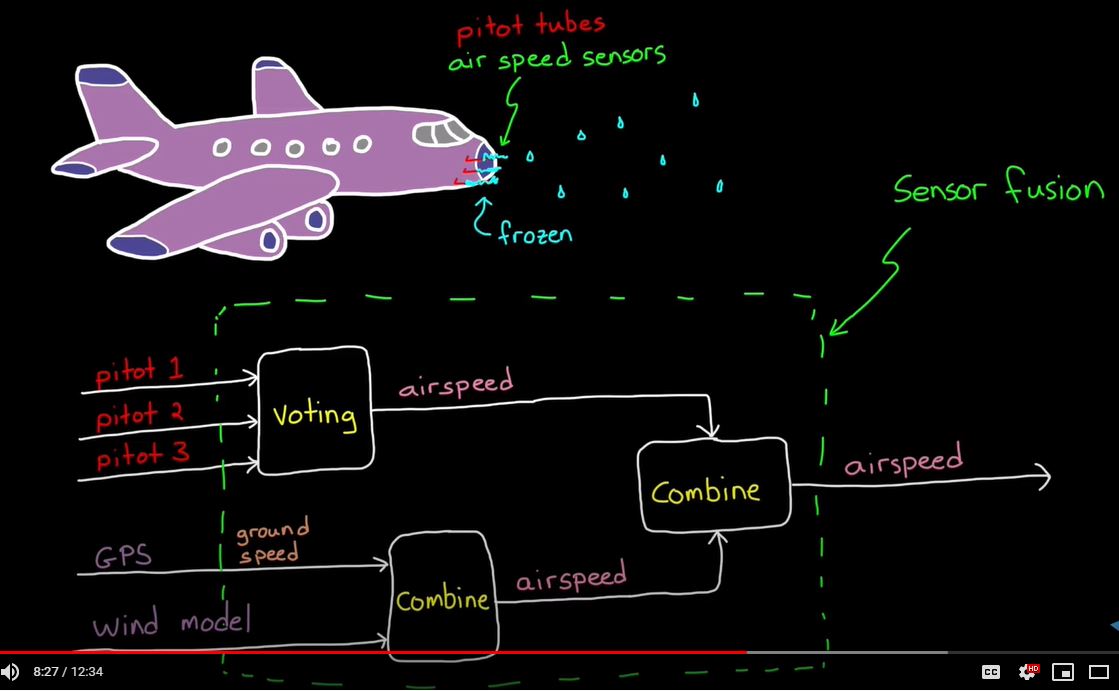
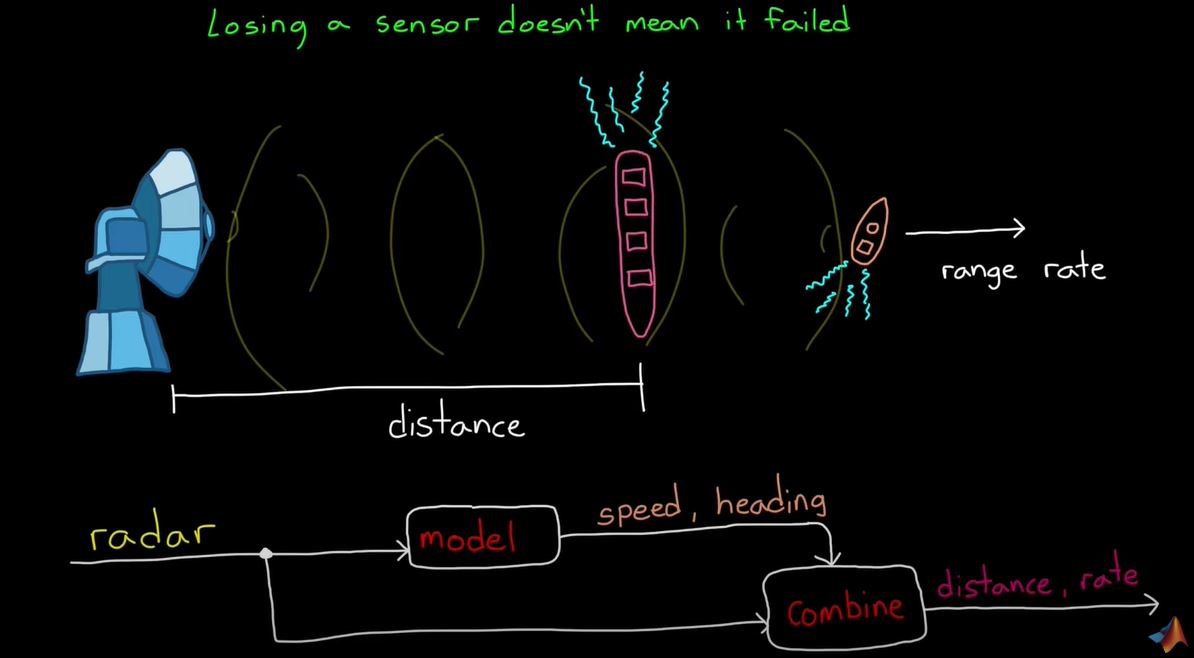
- 센서 퓨전을 하면서 어떤 센서를 더 믿을 것인지 결정하는 것이 중요하다.
Reference
Matlab Sensor Fusion.
Sensor Fusion to estimate orientation
- Attitude and Heading reference system(AHRM)
- 자력계 [magnetometer, 磁力計]
- we can find orientation using Magnetometer, Accelerometer, Gyro
- Accleromter : 중력 방향을 이용해서 orientation을 찾는다 (accleration은 오직 위아래 Gravity만 얻는다.)
- Magnetometer : 자기력을 이용하여 북쪽을 결정한다. (기준점을 이용한 orientation구한다, 만약 Magnetic 물체가 있으면 방해를 받는다.)
- 하지만 남반구인지 북반구인지에 따라 북쪽을 가르키는 방향이 다르다.
- 아래쪽은 가속도 벡터의 반대 방향( Measure accleration)
- East는 아래쪽과 Magnetic field의 외적이고
- 북쪽은 동쪽과 아래쪽의 외적이다.
- 따라서 본체의 방향은 본체 프레임과 NED(North, East, Down) 프레임 사이의 회전이다.
- 방금 계산한 NED 벡터에서 Direction Consine Matrix directly하게 구할 수 있다.
let’s check real device
- there is a physical IMU and Accelerometer.
- first connect to the Arduino and IMU
- and using a Matlab viewer to visualize the orientation
- update the view each time
- from for 1 = 1:1000 to Q
- is a basically reading the sensors performing the cross products and building The DCM
- but the systme is linear, so if moving alot it’s estimate accurate down
- Accleration 센서는 오직 위아래 중력 값만 판단한다.
- Magnetic 물체가 있으면 orientation 값을 찾는데 방해를 받는다.
- 문제를 풀기 위해 Calibration 필요
- 한가지 더 문제인 Corrupting linear accelrations
- take the commands that are sent to the actuators and play it through a model of the system to estimate the expected linear acceration and then subtract that value from the measurement
- this is something that is possible if say our system is drone and mine is flying it around by commanding the four propellers.
- if we can’t predict the linear acceleration or the external disturbances are too high, another option is to ignore accelerometer reading that are outside of some threshold from a 1g measurement. if magnitude of the reading is not close to the magnitude of gravity, then, clearly the sensor is picking up on other movement and it can’t be trusted.
- this keeps corrupted measuremens from getting into our fusion algorithm, but it is not a great solution because we stopped estimating orientation during these times and we lose track of the state of the system again
- it is not really problem if we trying to estimate orientation for a static object.
Solving to get orientation value problem
- add gyro !
- there are two method to find orientation
- accel + mag
- Gyro
- accel + mag 장단점과 Gyro의 장단점을 합하여 문제점 해결
- Complementary(상호 보완) Filter
- Kalman Filter
- Madgwick
-
mahony
- 센서 퓨전을 하면서 어떤 센서를 더 믿을 것인지 결정하는 것이 중요하다.
Reference
Matlab Sensor Fusion.