2. Cartoon Effect
02 Sep 2019 | Python
Create a Cartoon Image
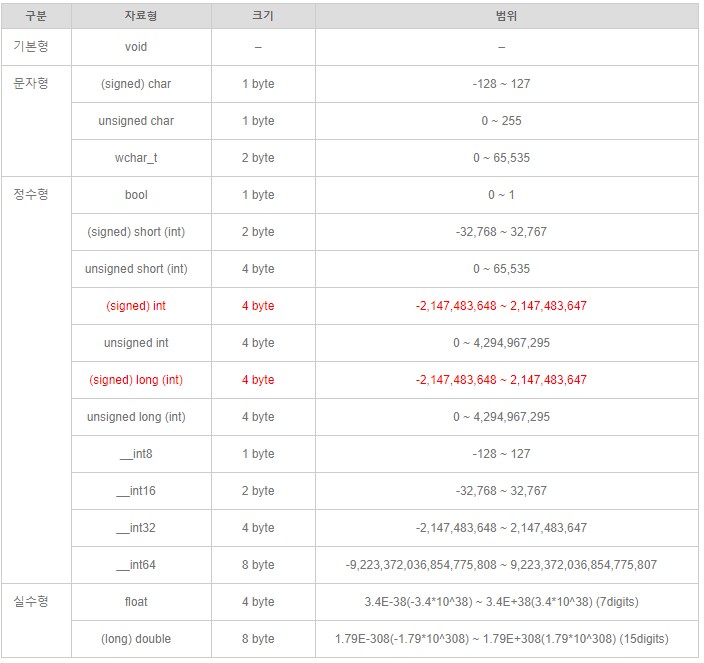
- Stylization aims to produce digital imagery with a wide variety of effects not focused on photorealism. Stylization can abstract regions of low contrast while preserving, or enhancing, high-contrast features.
- Parameters
- src Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
- dst Output image with the same size and type as src.
- sigma_s Range between 0 to 200.
- sigma_r Range between 0 to 1.
- Note
- sigma_s controls how much the image is smoothed - the larger its value, the more smoothed the image gets, but it’s also slower to compute.
- sigma_r is important if you want to preserve edges while smoothing the image. Small sigma_r results in only very similar colors to be averaged (i.e. smoothed), while colors that differ much will stay intact.
import cv2 #opencv library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #create a matplotlib
color_image = cv2.imread("trudeau.jpg") # reading image file by using cv2.imread("trudeau.jpg")
cartoon_image = cv2.stylization(color_image, sigma_s=100, sigma_r=0.1)
#cartoon_image, cartoon_image2 = cv2.pencilSketch(color_image, sigma_s=60, sigma_r=0.1)
cv2.imshow('cartoon', cartoon_image)
cv2.waitKey() #wating any key
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Example
import matplotlib.image as mpimg #had to perform many someting handy for us. image read function.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np # numerical analysis
import cv2
image_color = mpimg.imread("trudeau.jpg")
plt.imshow(image_color)
image_gray = cv2.cvtColor(image_color, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# our picture and color funtion.
plt.imshow(image_gray, cmap = 'gray') # 'gray' we have to give them color
image_gray.shape
# (569,800)
image_gray #each of pixel presenting in the color
# (569,800,3)
array([[ 19, 21, 22, ..., 159, 160, 161],
[ 18, 19, 21, ..., 159, 161, 162],
[ 17, 19, 20, ..., 160, 161, 162],
...,
[139, 140, 143, ..., 132, 132, 131],
[139, 140, 143, ..., 131, 130, 129],
[136, 140, 144, ..., 126, 126, 126]], dtype=uint8)
# Save the image in greyscale
cv2.imwrite("image_grayscale.jpg", image_gray)
# save the image. # specifiy the name of image when we save
# true means that actually save it
color_image = cv2.imread("trudeau.jpg")
# cartoon_image = cv2.stylization(color_image, sigma_s=200, sigma_r=0.3)
cartoon_image, cartoon_image2 = cv2.pencilSketch(color_image, sigma_s=60, sigma_r=0.1)
# pencilsketch has two return value. cartoon_image is not color, cartoon_image2 is the colorful by pencil
cv2.imshow('cartoon', cartoon_image2)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Create a Cartoon Image
- Stylization aims to produce digital imagery with a wide variety of effects not focused on photorealism. Stylization can abstract regions of low contrast while preserving, or enhancing, high-contrast features.
- Parameters
- src Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
- dst Output image with the same size and type as src.
- sigma_s Range between 0 to 200.
- sigma_r Range between 0 to 1.
- Note
- sigma_s controls how much the image is smoothed - the larger its value, the more smoothed the image gets, but it’s also slower to compute.
- sigma_r is important if you want to preserve edges while smoothing the image. Small sigma_r results in only very similar colors to be averaged (i.e. smoothed), while colors that differ much will stay intact.
import cv2 #opencv library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #create a matplotlib
color_image = cv2.imread("trudeau.jpg") # reading image file by using cv2.imread("trudeau.jpg")
cartoon_image = cv2.stylization(color_image, sigma_s=100, sigma_r=0.1)
#cartoon_image, cartoon_image2 = cv2.pencilSketch(color_image, sigma_s=60, sigma_r=0.1)
cv2.imshow('cartoon', cartoon_image)
cv2.waitKey() #wating any key
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Example
import matplotlib.image as mpimg #had to perform many someting handy for us. image read function.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np # numerical analysis
import cv2
image_color = mpimg.imread("trudeau.jpg")
plt.imshow(image_color)
image_gray = cv2.cvtColor(image_color, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# our picture and color funtion.
plt.imshow(image_gray, cmap = 'gray') # 'gray' we have to give them color
image_gray.shape
# (569,800)
image_gray #each of pixel presenting in the color
# (569,800,3)
array([[ 19, 21, 22, ..., 159, 160, 161],
[ 18, 19, 21, ..., 159, 161, 162],
[ 17, 19, 20, ..., 160, 161, 162],
...,
[139, 140, 143, ..., 132, 132, 131],
[139, 140, 143, ..., 131, 130, 129],
[136, 140, 144, ..., 126, 126, 126]], dtype=uint8)
# Save the image in greyscale
cv2.imwrite("image_grayscale.jpg", image_gray)
# save the image. # specifiy the name of image when we save
# true means that actually save it
color_image = cv2.imread("trudeau.jpg")
# cartoon_image = cv2.stylization(color_image, sigma_s=200, sigma_r=0.3)
cartoon_image, cartoon_image2 = cv2.pencilSketch(color_image, sigma_s=60, sigma_r=0.1)
# pencilsketch has two return value. cartoon_image is not color, cartoon_image2 is the colorful by pencil
cv2.imshow('cartoon', cartoon_image2)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()