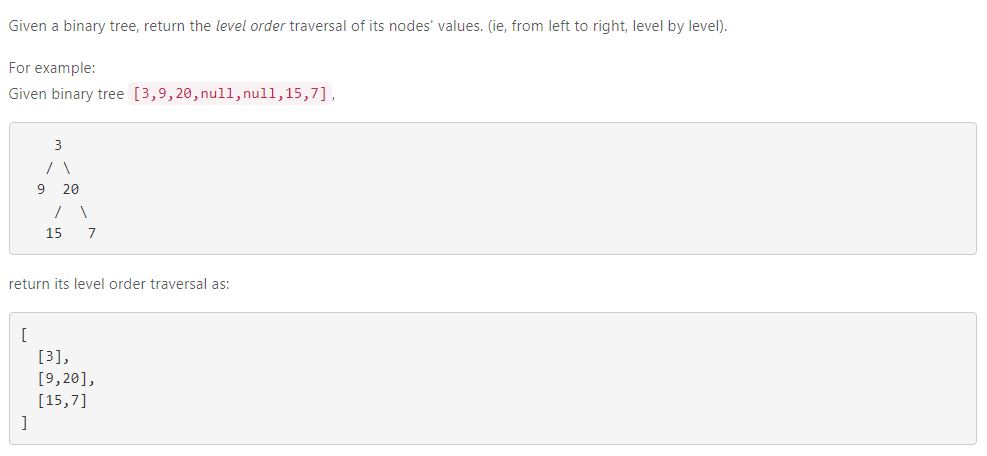
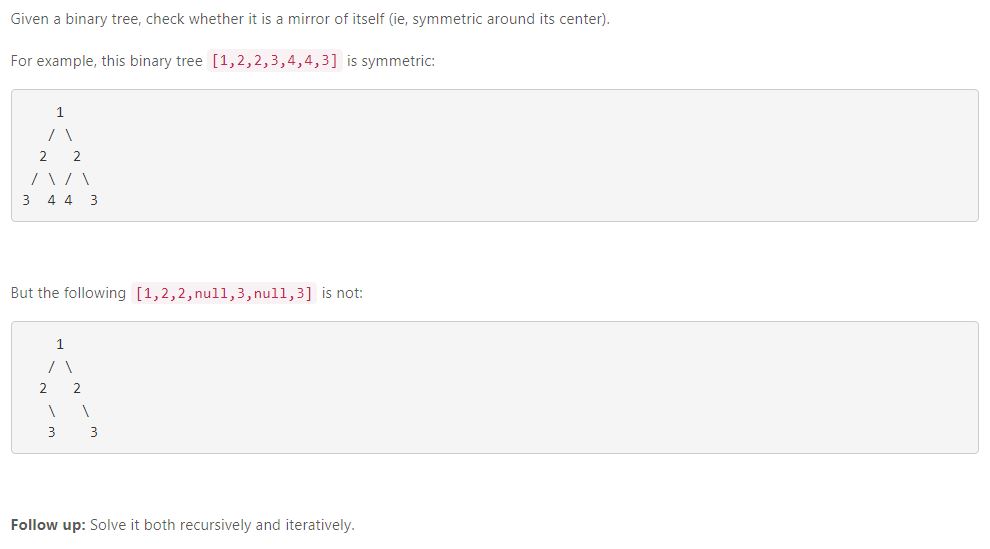
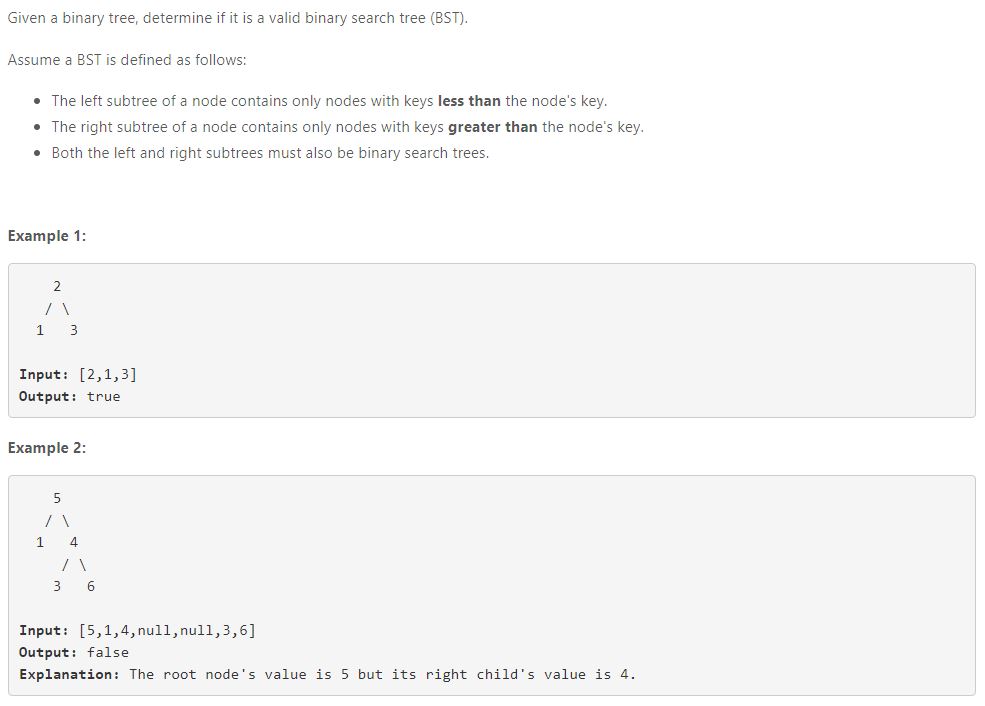
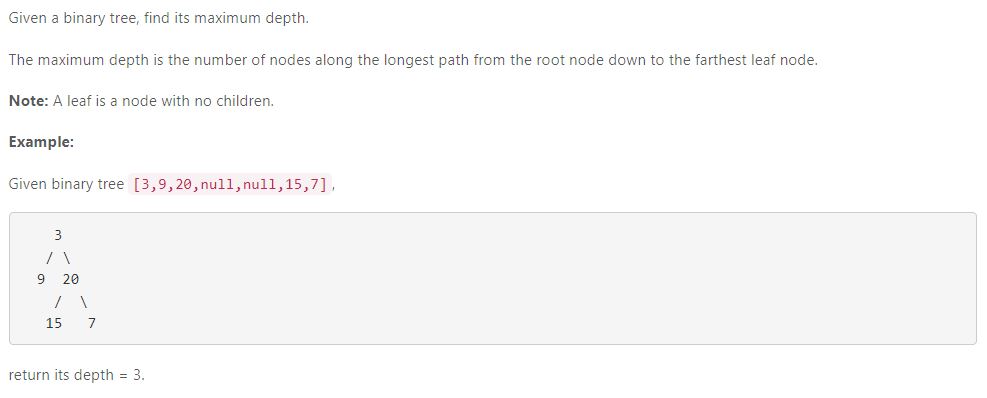
31. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree(我的缺点是TREE,以后有代码考试需要集中tree学习)
02 Jul 2020 | Daily Algorithms
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0, nums.size());
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end)
{
if(end<=start)
{
return NULL;
}
int mid = (start+end)/2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = sortedArrayToBST(nums,start, mid);
root->right = sortedArrayToBST(nums,mid+1, end);
return root;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {
return sortedArrayToBST(nums, 0, nums.size());
}
TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums, int start, int end)
{
if(end<=start)
{
return NULL;
}
int mid = (start+end)/2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root->left = sortedArrayToBST(nums,start, mid);
root->right = sortedArrayToBST(nums,mid+1, end);
return root;
}
};