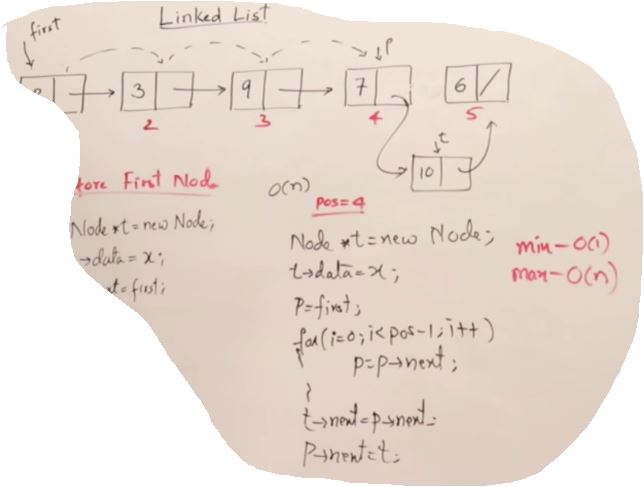
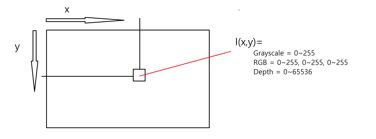
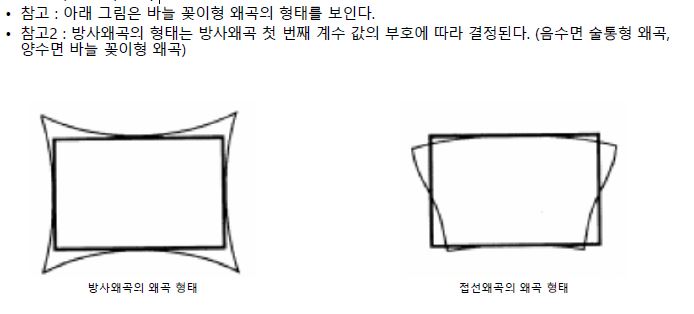
17. Linked List 2
16 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
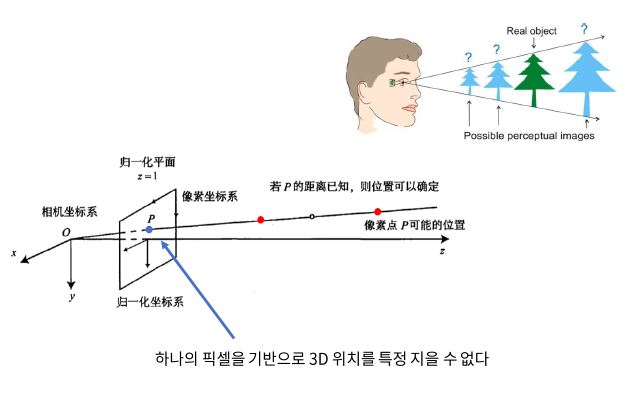
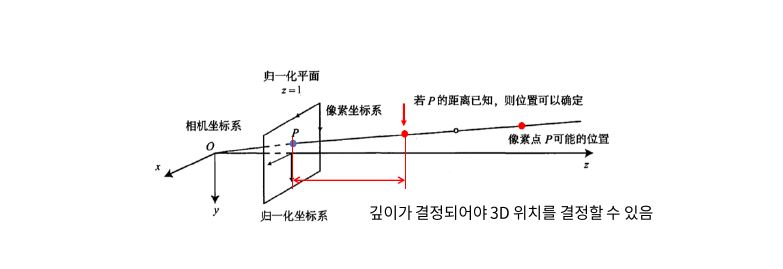
Searching in Linked list
Linear Search
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
Node* Lsearch(Node* p, int key)
{
Node* q;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if (key == p->data)
{
q->data = p->data;
return q;
}
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
return NULL;
}
Node* Rsearch(Node* p, int key)
{
if(p==NULL)
return NULL;
if(key==p->data)
return p;
return Rsearch(p->next,key);
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp; // 새로 new, heap에 생성할 필요없이 카피할 데이터는 포인터만 하면 된다.
Node* result;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
result = Lsearch(temp, 8);
cout<<result->data<<endl;
return 0;
}
Insert for Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
Node* insert_(Node* p, int index, int x)
{
Node* temp;
int i;
if(index<0 || index>8)
return p;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
if(index == 0)
{
temp->next = p;
p = temp;
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
p=p->next;
temp->next = p->next;
p->next = temp;
}
return p;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
insert_(temp,2,5);
Display(temp);
return 0;
}
- min O(1)
- max O(n)
Insert for Linked list (Last input)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void insert_(Node* p, int index, int x)
{
Node* temp;
int i;
if(index<0 || index>8)
return;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
if(index == 0)
{
temp->next = p->next;
p->next = temp;
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
p=p->next;
temp->next = p->next;
p->next = temp;
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head;
head = new Node;
insert_(head,0,15);
insert_(head,0,8);
insert_(head,0,9);
insert_(head,2,10);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
Sorted Input
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void sorted_insert(Node* p, int x)
{
Node* temp,*q=NULL;
Node* head;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
temp->next =NULL;
head = p;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=temp;
}
else
{
while(p&&p->data<x)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
if(p==head)
{
temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
else
{
temp->next = q->next;
q->next = temp;
}
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
sorted_insert(head,15);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
Remove Duplicates from linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void RemoveDuplicate(Node* p)
{
Node* q;
q = p->next;
while(q!=NULL)
{
if(p->data!=q->data)
{
p=q;
q=q->next;
}
else
{
//dupicated
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
q = p->next;
}
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,20,40,50,50,50,60};
Node* head;
head = create(A,8);
RemoveDuplicate(head);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
Searching in Linked list
Linear Search
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
Node* Lsearch(Node* p, int key)
{
Node* q;
while(p!=NULL)
{
if (key == p->data)
{
q->data = p->data;
return q;
}
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
return NULL;
}
Node* Rsearch(Node* p, int key)
{
if(p==NULL)
return NULL;
if(key==p->data)
return p;
return Rsearch(p->next,key);
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp; // 새로 new, heap에 생성할 필요없이 카피할 데이터는 포인터만 하면 된다.
Node* result;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
result = Lsearch(temp, 8);
cout<<result->data<<endl;
return 0;
}
Insert for Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
Node* insert_(Node* p, int index, int x)
{
Node* temp;
int i;
if(index<0 || index>8)
return p;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
if(index == 0)
{
temp->next = p;
p = temp;
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
p=p->next;
temp->next = p->next;
p->next = temp;
}
return p;
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={3,8,7,10,25,8,32,2};
Node* temp;
temp = create(A,sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
insert_(temp,2,5);
Display(temp);
return 0;
}
- min O(1)
- max O(n)
Insert for Linked list (Last input)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void insert_(Node* p, int index, int x)
{
Node* temp;
int i;
if(index<0 || index>8)
return;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
if(index == 0)
{
temp->next = p->next;
p->next = temp;
}
else
{
for(i=0;i<index-1;i++)
p=p->next;
temp->next = p->next;
p->next = temp;
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head;
head = new Node;
insert_(head,0,15);
insert_(head,0,8);
insert_(head,0,9);
insert_(head,2,10);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
Sorted Input
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void sorted_insert(Node* p, int x)
{
Node* temp,*q=NULL;
Node* head;
temp = new Node;
temp->data = x;
temp->next =NULL;
head = p;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=temp;
}
else
{
while(p&&p->data<x)
{
q=p;
p=p->next;
}
if(p==head)
{
temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
else
{
temp->next = q->next;
q->next = temp;
}
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,30,40,50};
Node* head;
head = create(A,5);
sorted_insert(head,15);
Display(head);
return 0;
}
Remove Duplicates from linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node* create(int A[],int n)
{
int i;
Node* t, *last;
Node* head;
head = new Node;
head->data = A[0];
head->next = NULL;
last = head;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
t = new Node;
t->data = A[i];
t->next =NULL;
last->next = t;
last = t;
}
return head;
}
void RemoveDuplicate(Node* p)
{
Node* q;
q = p->next;
while(q!=NULL)
{
if(p->data!=q->data)
{
p=q;
q=q->next;
}
else
{
//dupicated
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
q = p->next;
}
}
}
void Display(Node* p)
{
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p=p->next;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[]={10,20,20,40,50,50,50,60};
Node* head;
head = create(A,8);
RemoveDuplicate(head);
Display(head);
return 0;
}