13.majority element(가장 많은 수)
22 May 2020 | STL Programming Practice_1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*
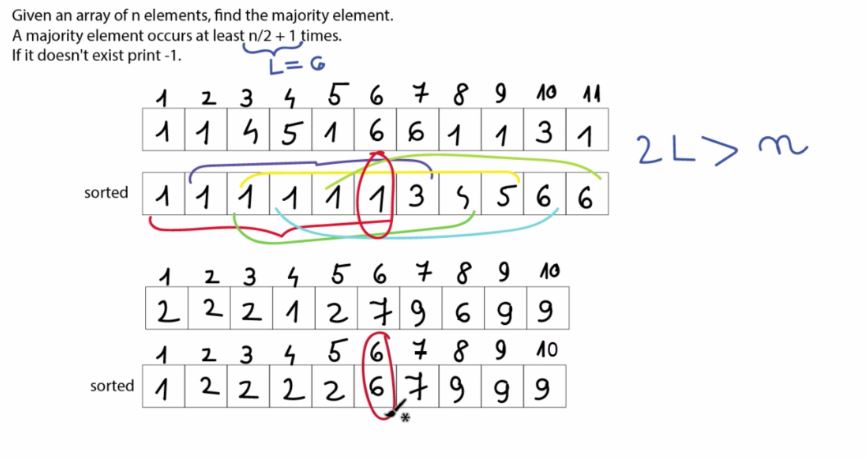
Given an array of n elements, find the majority element.
A majority element occurs at least n/2 + 1 times
if it doesn't exist print -1
*/
int A[]= {0,1,1,4,5,1,6,6,1,1,3,1};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
sort(A+0,A+n);
// A[n/2+1] can be the majority element
int majorityElement=A[n/2+1];
int nOccurrences = 0;
for(int i=0; i<=n; ++i)
if ((A[i])==majorityElement) ++nOccurrences;
if (nOccurrences >= n/2+1)
{
cout<<"the majority element is "<<majorityElement;
cout<<"and it appears "<<nOccurrences<<"time";
}
else
{
cout<<"-1/n";
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*
Given an array of n elements, find the majority element.
A majority element occurs at least n/2 + 1 times
if it doesn't exist print -1
*/
int A[]= {0,1,1,4,5,1,6,6,1,1,3,1};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
sort(A+0,A+n);
// A[n/2+1] can be the majority element
int majorityElement=A[n/2+1];
int nOccurrences = 0;
for(int i=0; i<=n; ++i)
if ((A[i])==majorityElement) ++nOccurrences;
if (nOccurrences >= n/2+1)
{
cout<<"the majority element is "<<majorityElement;
cout<<"and it appears "<<nOccurrences<<"time";
}
else
{
cout<<"-1/n";
}
return 0;
}