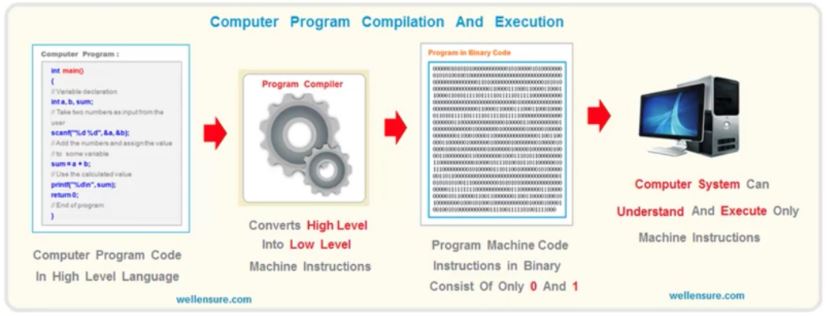
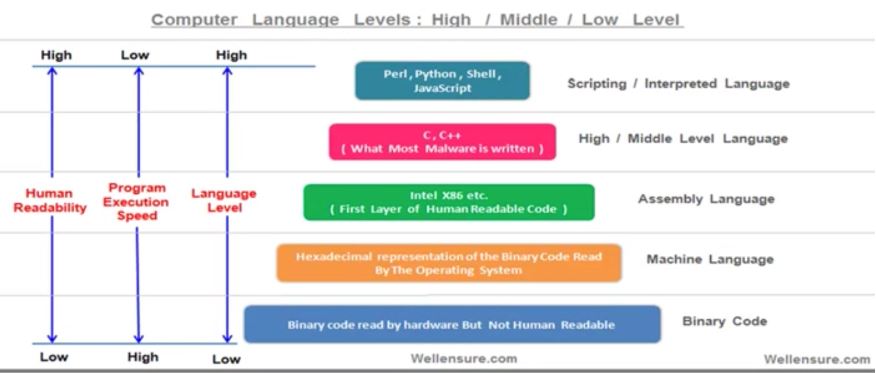
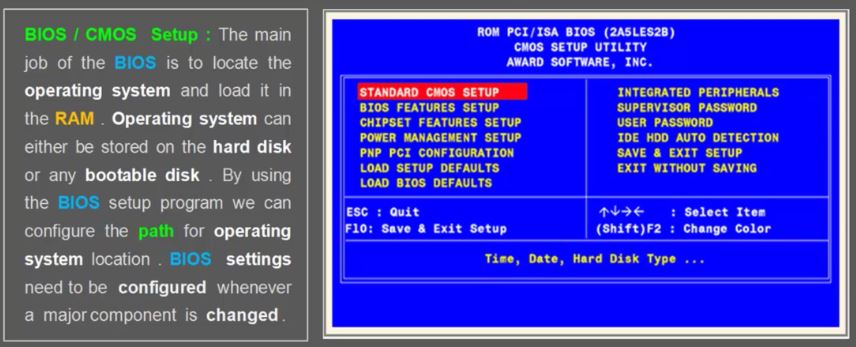
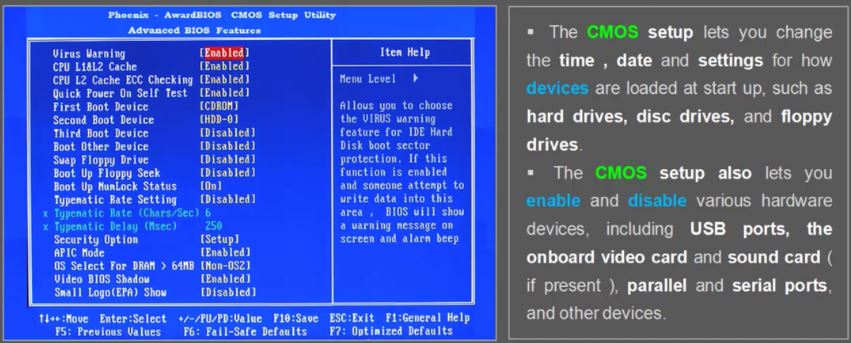
33. Algorithm
20 May 2020 | CS
Computer Programming and program instructions
-
An Algorithm is a step by step procedure for solving a program and finding a programming solution is essentially a way of expressing algorithms.
-
An algorithms are systematic methodical approach in which a program is first clearly defined and a solution is expressed in terms of series of computational steps required and when implemented leads to the program solution.
-
AN algorithm is a collection of instructions to solve a problem and when these instructions are executed in a specific sequence will produce the correct result. the study of algorithm is at the heart of computer science.
-
we can express an algorithm with the help of pseudocode and flowcharts. we can have more have one algorithm for the same problem definition and thus we need to figure out the algorithm, best suitable for a particular problem in terms of execution speed and memory space required.
-
A program is an implementation of an algorithm to be run on a specific computer and operating system.
-
an algorithm is more abstract - it is not a machine specific and independent of any programming language.
-
the measure of performance /efficiency for any algorithm is assessed on two parameters
- Time : algorithm should take minimum time to execute
- Space : algorithm should use less memory.
Pseudocode
-
A pseudocode is a detailed but readable step by step description of what a computer program or algorithm must do
-
A pseudocode is a simple way of writing programming code in English. A pseudocode is not a actual program written in programming language which can be executed by a computer.
-
As the name suggest a pseudo code can be written in any language such as English language.
Flow chart
-
the Large programs with complex logic can be visually quite intimidating. sometimes it’s more effective to visualize the complex algorithms graphically than to express in form of program code. that is the essence of what flowcharts are meant for.
-
the flowcharts explain a program algorithm clearly through symbols and text. moreover, flowcharts give the gist of the program flow in a single glance. the flowchart make use of different shapes, each indicating specific program element.
Computer Programming and program instructions
-
An Algorithm is a step by step procedure for solving a program and finding a programming solution is essentially a way of expressing algorithms.
-
An algorithms are systematic methodical approach in which a program is first clearly defined and a solution is expressed in terms of series of computational steps required and when implemented leads to the program solution.
-
AN algorithm is a collection of instructions to solve a problem and when these instructions are executed in a specific sequence will produce the correct result. the study of algorithm is at the heart of computer science.
-
we can express an algorithm with the help of pseudocode and flowcharts. we can have more have one algorithm for the same problem definition and thus we need to figure out the algorithm, best suitable for a particular problem in terms of execution speed and memory space required.
-
A program is an implementation of an algorithm to be run on a specific computer and operating system.
-
an algorithm is more abstract - it is not a machine specific and independent of any programming language.
-
the measure of performance /efficiency for any algorithm is assessed on two parameters
- Time : algorithm should take minimum time to execute
- Space : algorithm should use less memory.
Pseudocode
-
A pseudocode is a detailed but readable step by step description of what a computer program or algorithm must do
-
A pseudocode is a simple way of writing programming code in English. A pseudocode is not a actual program written in programming language which can be executed by a computer.
-
As the name suggest a pseudo code can be written in any language such as English language.
Flow chart
-
the Large programs with complex logic can be visually quite intimidating. sometimes it’s more effective to visualize the complex algorithms graphically than to express in form of program code. that is the essence of what flowcharts are meant for.
-
the flowcharts explain a program algorithm clearly through symbols and text. moreover, flowcharts give the gist of the program flow in a single glance. the flowchart make use of different shapes, each indicating specific program element.