12. Class
12 Sep 2019 | C++
Class
- Class는 파이썬과 마찬가지로 프로젝트를 함에 있어 알고리즘을 나누는 역할을 한다.
- 예로 어떤 클래스는 더하기를, 어떤 클래스를 곱하기를 역할을 나눠주고 Main Class에다가 합쳐 Main클래스를 간결하게 해준다.
Exercise 1
Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "people.h"
using namespace std;
/* classes */
void test()
{
PersonalData *pointer = new PersonalData[5];
delete []pointer;
}
int main()
{
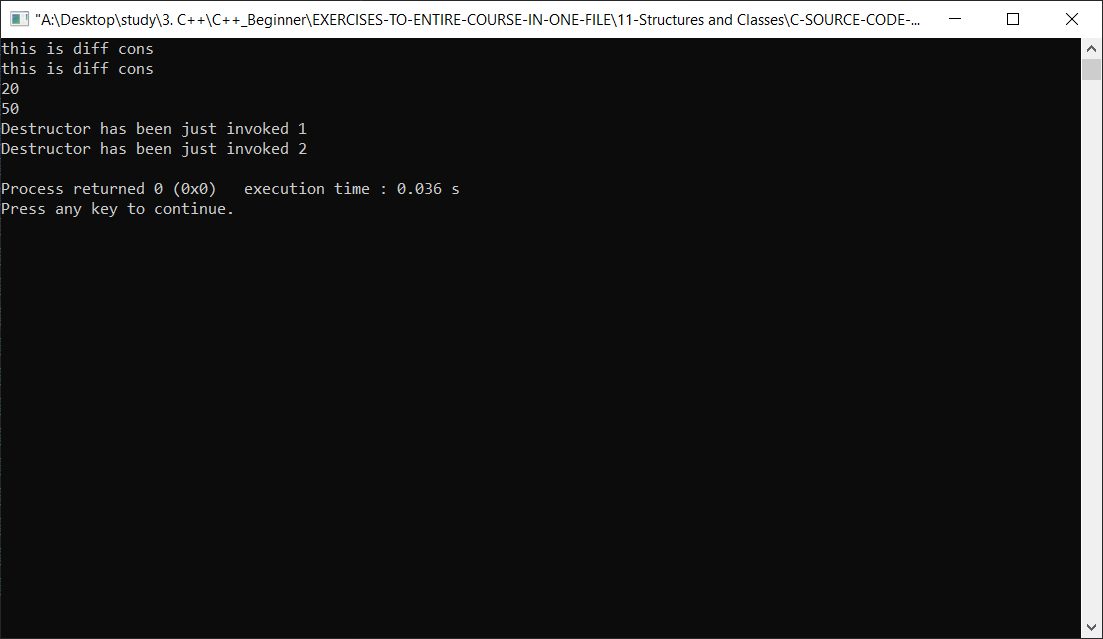
PersonalData person(20);
PersonalData person2(50);
cout << person.getAge()<< endl;
cout << person2.getAge() << endl;
// test();
return 0;
}
people.h
#ifndef PEOPLE_H_INCLUDED
#define PEOPLE_H_INCLUDED
class PersonalData
{
private:
short age; // the first argument taken
int *p;
public:
PersonalData(); // 인수가 없으면 이 클래스로 가고 있으면 아래 클래스로 간다.
PersonalData(short);
~PersonalData();
/**
This function is setting age. If age is lower than 0, then age = 10.
*/
void setAge(int);
short getAge() {return age;}
};
#endif // PEOPLE_H_INCLUDED
people.cpp
#include "people.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void PersonalData::setAge(int age)
{
if (age < 0)
this->age = 0;
else
this->age = age;
}
PersonalData::PersonalData()
{
static int i = 0;
cout << "Constructor has been just invoked " << ++i << endl;
age = 10;
p = new int[5];
}
PersonalData::PersonalData(short age)
{
cout <<"this is diff cons" << endl;
this->age = age;
}
PersonalData::~PersonalData()
{
static int j = 0;
cout << "Destructor has been just invoked " << ++j << endl;
delete [] p;
}
Exercise 2
Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "position.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Position dog(10, 50);
dog.getPosition();
dog.setPosition(50, 100);
dog.getPosition();
const Position house(100, 200);
house.getPosition();
// house.setPosition(444, 444);
//house.getPosition();
return 0;
}
Position.h
#ifndef POSITION_H_INCLUDED
#define POSITION_H_INCLUDED
class Position
{
int x, y;
public:
Position(int,int);
~Position();
void getPosition() const;
void setPosition(int, int);
};
#endif // POSITION_H_INCLUDED
position.cpp
#include "position.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Position::Position(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
Position::~Position()
{
}
void Position::getPosition() const
{
cout << "x : " << x << endl;
cout << "y : " << y << endl;
}
void Position::setPosition(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
(operator)[http://algamza.blogspot.com/2016/03/c-operator-overloading.html]
- 사용자 정의 클래스 를 사용할 때 연산자에 특별한 의미를 부여할 수 있다는 점은 C++의 멋진 기능 중 하나입니다.
- 이 기능을 연산자 오버로딩(operator overloading) 이라고 합니다. C++의 연산자 오버로딩은 클래스에 특별 멤버 함수를 다음과 같은 명명 규칙에 따라서 작성해 구현할 수 있습니다.
Operator 종류
- = (할당 연산자, assignment operator)
-
-
-
- (이진 산술 연산자, binary arithmetic operators)
- += -= = (복합 할당 연산자, compound assignment operators)
- == != (비교 연산자, comparison operators)
예제
class MyClass {
public:
...
MyClass & operator=(const MyClass &rhs);
...
}
MyClass a, b;
...
b = a; // b.operator=(a); 와 동일함
MyClass& MyClass::operator=(const MyClass &rhs) {
// 자기 할당을 확인합니다.
if (this == &rhs) // 동일 객체?
return *this; // 맞네요. 그럼 할당을 건너뛰고 *this를 반환합니다.
... // 할당 해제, 새 공간을 할당하고 값을 복사합니다...
return *this;
}
Example 3
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "integer.h"
using namespace std;
/* CONVERT constructor - overloading operators */
int main()
{
Integer a(50);
int b = a;
a = 100;
cout << a.getNr() << endl; //100
cout << b << endl; // 50
cout << a + b << endl; //150
b += a; // a = a + b;
cout << b << endl; // 150
cout << a << endl; // 100
return 0;
}
interger.h
#ifndef INTEGER_H_INCLUDED
#define INTEGER_H_INCLUDED
class Integer
{
int nr;
public:
Integer() { };
Integer(int);
operator int();
int operator+=(Integer);
int getNr() { return nr; };
};
#endif // INTEGER_H_INCLUDED
interger.cpp
#include "integer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Integer::Integer(int nr)
{
this->nr = nr;
}
Integer::operator int()
{
return this->nr;
}
int Integer::operator+=(Integer o)
{
this->nr = o.getNr() + this->nr; //this는 오퍼레이터에서 받아지는 인수값이다. 그리고 o 는 그 뒤에 받아지는 값
return this->nr; // 여로 들면 a+=b라고 했을떄 a값이 this이고 b값이 integer o라고 보면 된다.
}
Class
- Class는 파이썬과 마찬가지로 프로젝트를 함에 있어 알고리즘을 나누는 역할을 한다.
- 예로 어떤 클래스는 더하기를, 어떤 클래스를 곱하기를 역할을 나눠주고 Main Class에다가 합쳐 Main클래스를 간결하게 해준다.
Exercise 1
Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "people.h"
using namespace std;
/* classes */
void test()
{
PersonalData *pointer = new PersonalData[5];
delete []pointer;
}
int main()
{
PersonalData person(20);
PersonalData person2(50);
cout << person.getAge()<< endl;
cout << person2.getAge() << endl;
// test();
return 0;
}
people.h
#ifndef PEOPLE_H_INCLUDED
#define PEOPLE_H_INCLUDED
class PersonalData
{
private:
short age; // the first argument taken
int *p;
public:
PersonalData(); // 인수가 없으면 이 클래스로 가고 있으면 아래 클래스로 간다.
PersonalData(short);
~PersonalData();
/**
This function is setting age. If age is lower than 0, then age = 10.
*/
void setAge(int);
short getAge() {return age;}
};
#endif // PEOPLE_H_INCLUDED
people.cpp
#include "people.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void PersonalData::setAge(int age)
{
if (age < 0)
this->age = 0;
else
this->age = age;
}
PersonalData::PersonalData()
{
static int i = 0;
cout << "Constructor has been just invoked " << ++i << endl;
age = 10;
p = new int[5];
}
PersonalData::PersonalData(short age)
{
cout <<"this is diff cons" << endl;
this->age = age;
}
PersonalData::~PersonalData()
{
static int j = 0;
cout << "Destructor has been just invoked " << ++j << endl;
delete [] p;
}
Exercise 2
Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "position.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Position dog(10, 50);
dog.getPosition();
dog.setPosition(50, 100);
dog.getPosition();
const Position house(100, 200);
house.getPosition();
// house.setPosition(444, 444);
//house.getPosition();
return 0;
}
Position.h
#ifndef POSITION_H_INCLUDED
#define POSITION_H_INCLUDED
class Position
{
int x, y;
public:
Position(int,int);
~Position();
void getPosition() const;
void setPosition(int, int);
};
#endif // POSITION_H_INCLUDED
position.cpp
#include "position.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Position::Position(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
Position::~Position()
{
}
void Position::getPosition() const
{
cout << "x : " << x << endl;
cout << "y : " << y << endl;
}
void Position::setPosition(int x, int y)
{
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
}
(operator)[http://algamza.blogspot.com/2016/03/c-operator-overloading.html]
- 사용자 정의 클래스 를 사용할 때 연산자에 특별한 의미를 부여할 수 있다는 점은 C++의 멋진 기능 중 하나입니다.
- 이 기능을 연산자 오버로딩(operator overloading) 이라고 합니다. C++의 연산자 오버로딩은 클래스에 특별 멤버 함수를 다음과 같은 명명 규칙에 따라서 작성해 구현할 수 있습니다.
Operator 종류
- = (할당 연산자, assignment operator)
-
-
-
- (이진 산술 연산자, binary arithmetic operators)
-
-
- += -= = (복합 할당 연산자, compound assignment operators)
- == != (비교 연산자, comparison operators)
예제
class MyClass {
public:
...
MyClass & operator=(const MyClass &rhs);
...
}
MyClass a, b;
...
b = a; // b.operator=(a); 와 동일함
MyClass& MyClass::operator=(const MyClass &rhs) {
// 자기 할당을 확인합니다.
if (this == &rhs) // 동일 객체?
return *this; // 맞네요. 그럼 할당을 건너뛰고 *this를 반환합니다.
... // 할당 해제, 새 공간을 할당하고 값을 복사합니다...
return *this;
}
Example 3
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "integer.h"
using namespace std;
/* CONVERT constructor - overloading operators */
int main()
{
Integer a(50);
int b = a;
a = 100;
cout << a.getNr() << endl; //100
cout << b << endl; // 50
cout << a + b << endl; //150
b += a; // a = a + b;
cout << b << endl; // 150
cout << a << endl; // 100
return 0;
}
interger.h
#ifndef INTEGER_H_INCLUDED
#define INTEGER_H_INCLUDED
class Integer
{
int nr;
public:
Integer() { };
Integer(int);
operator int();
int operator+=(Integer);
int getNr() { return nr; };
};
#endif // INTEGER_H_INCLUDED
interger.cpp
#include "integer.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Integer::Integer(int nr)
{
this->nr = nr;
}
Integer::operator int()
{
return this->nr;
}
int Integer::operator+=(Integer o)
{
this->nr = o.getNr() + this->nr; //this는 오퍼레이터에서 받아지는 인수값이다. 그리고 o 는 그 뒤에 받아지는 값
return this->nr; // 여로 들면 a+=b라고 했을떄 a값이 this이고 b값이 integer o라고 보면 된다.
}

Comments