28. Standard Template library(STL) - Map
28 Sep 2019 | C++
Maps
- 기본형태
- map<key,value> : key와 value를 pair 형태로 선언합니다.
- iterator(반복자)
- begin() : beginning iterator를 반환
- end() : end iterator를 반환
- 추가 및 삭제
- insert( make_pair(key,value) ) : 맵에 원소를 pair 형태로 추가
- erase(key) : 맵에서 key(키값)에 해당하는 원소 삭제
- clear() : 맵의 원소들 모두 삭제
- 조회
- find(key) : key(키값)에 해당하는 iterator를 반환
- count(key) : key(키값)에 해당하는 원소들(value들)의 개수를 반환
- 기타
- empty() : 맵이 비어있으면 true 아니면 false를 반환
- size() : 맵 원소들의 수를 반환
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> ages;
ages["Mike"] = 40;
ages["Raj"] = 20;
ages["Vicky"] = 30;
ages["Mike"] = 70;
//
ages.insert(make_pair("Peter", 100));
//pair<string, int> addToMap("peter",100);
//ages.insert(addToMap);
cout << ages["Raj"] << endl;
// to find the techinical
if(ages.find("Vicky") != ages.end()) {
cout << "Found Vicky" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Key not found." << endl;
}
for(map<string, int>::iterator it = ages.begin(); it != ages.end(); it++) {
pair<string, int> age = *it;
cout << age.first << ": " << age.second << endl;
// first and second the function in the map library
}
for(map<string, int>::iterator it = ages.begin(); it != ages.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
// first and second is valuable the value of the ages by key and value.
}
return 0;
}
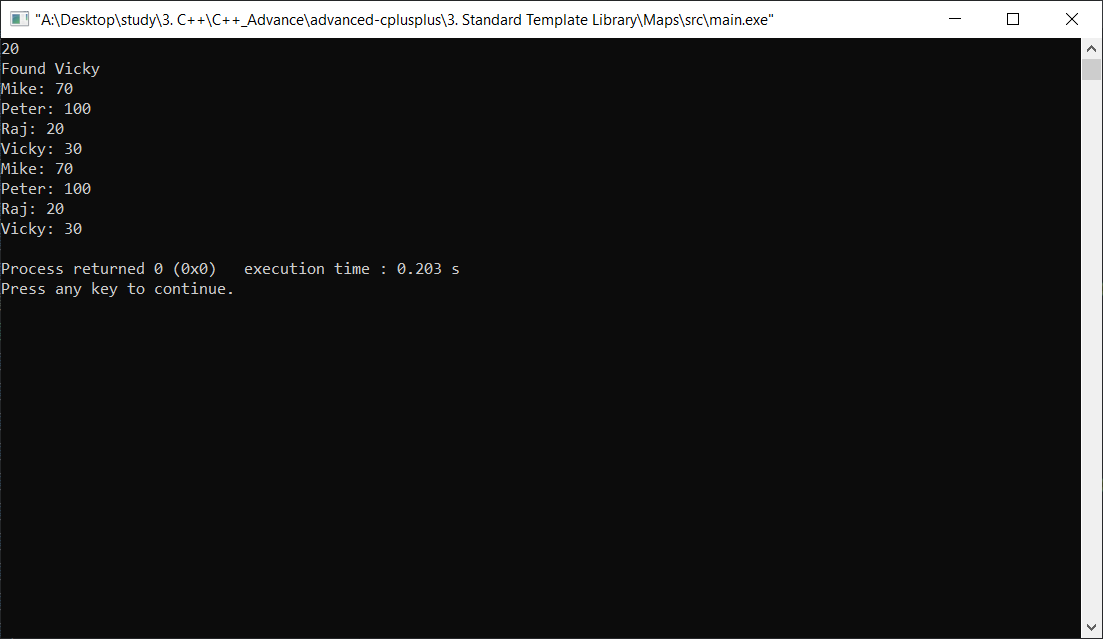
Result
Custom Objects as map Keys
Flush
- 개발 된 Microsoft C/c + + 응용 프로그램에서는 cout 스트림 버퍼링 됩니다.
- 즉, 버퍼를 플러시할 때까지 cout 스트림에 보낼 정보가 화면에 나타나지 않습니다.
- 이 동작은 Visual C++ 4.2 및 이후 버전의 경우 이전 iostream 라이브러리를 사용할 때만 발생 합니다.
- 네 가지 방법을 다음과 같이 cout 버퍼를 플러시할 수 있습니다.
- Endl 조작자를 사용 하 여 줄 바꿈 문자를 출력 스트림에 삽입 버퍼를 플러시합니다. Endl 조작자를 사용 하 여 삽입 연산자를 다음과 같이 사용.
- cout « … « endl;
- Ostream 클래스 또는 플러시 조작자에 플러시 멤버 함수를 사용 합니다.
- 플러시 조작자 버퍼를 플러시합니다 전에 스트림에 줄 바꿈 문자가 삽입 되지는 않습니다. 플러시 멤버 함수를 호출 하려면 다음과 유사한 코드를 사용.
- cout.flush();
- 플러시 조작자를 사용 하 여 삽입 연산자를 다음과 같이 사용.
- cout « … « flush;
First and Second 함수
- 구조체 템플릿 std::pair 는 두 가지 유형의 정확히 두 개의 반환 값을 함께 묶을 수 있습니다
#include <utility>
std::pair<int, int> foo(int a, int b) {
return std::make_pair(a+b, a-b);
}
- C ++ 11 이후 버전에서는 std::make_pair 대신에 초기화리스트를 사용할 수 있습니다 :
#include <utility>
std::pair<int, int> foo(int a, int b) {
return {a+b, a-b};
}
- 쌍의 first 및 second 구성원 개체를 사용하여 반환 된 std::pair 의 개별 값을 검색 할 수 있습니다.
std::pair<int, int> mrvs = foo(5, 12);
std::cout << mrvs.first + mrvs.second << std::endl;
Example
- Map<person, int> people
- Person first map and value is second map
- Ex) [Person1, value1] [person2,value2]…
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() :
name(""), age(0) {
}
Person(string name, int age) :
name(name), age(age) {
}
// 상속
//constructor need to initialize this
//so thats why we use to initilaze the actual instance(기억장치 할당) variables in above
//we dont have to provide any more implementation(실행)
Person(const Person& other) {
name = other.name;
age = other.age;
}
//copy constoctur.
void print() const {
cout << name << ": " << age << flush;
}
//operator is just like +,-,<,>,!= 지정해주는
// 리퍼런스 other에 대신 데이터를 받아 가동을 시켜준다.
bool operator<(const Person &other) const {
if (name == other.name) {
return age < other.age;
} else {
return name < other.name;
}
}
};
int main() {
map<Person, int> people;
//map<key,value>
people[Person("Mike", 40)] = 40;
people[Person("Mike", 444)] = 123;
people[Person("Sue", 30)] = 30;
people[Person("Raj", 40)] = 20;
for (map<Person, int>::iterator it = people.begin(); it != people.end();
it++) {
cout << it->second << ": " << flush;
it->first.print();
cout << endl;
}
// it need to bool operation becuase
return 0;
}
Example 2
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() :
name(""), age(0) {
}
// this is the default parameter of constructor.
// this is the keep
// member-wise <- in terms of(관해서) members(item associated with class instances)
Person(string name, int age) :
name(name), age(age) {
}
// this is necassary for 기억할당 in map function
Person(const Person &other){
cout << "Copy constructor running!" << endl;
name = other.name; // 얕은복사
age = other.age; //깊은 복사
}
// copy constructor is a member function which initialize an obeject using another object of the same class
// 복사생성자의 값을 복사 구성체에다가 받는다
// 인트매인에서 객체에 주어진 값이 같지만 주소가 바뀌거나 생성자 호출을 하지 않기 떄문에 이와 같이
// 새로운 공간 할당.
void print() {
cout << name << ": " << age << endl;
}
};
int main() {
map<int, Person> people;
people[50] = Person("Mike", 40);
people[32] = Person("Vicky", 30);
people[1] = Person("Raj", 20);
people.insert(make_pair(55, Person("Bob", 45 )));
people.insert(make_pair(55, Person("Sue", 24 )));
// copy constructor is called heres
for (map<int, Person>::iterator it = people.begin(); it != people.end();
it++) {
cout << it->first << ": " << flush;
it->second.print();
}
// flush is sending a content and cleaning up the buffer
return 0;
}
REFERENCE
Maps
- 기본형태
- map<key,value> : key와 value를 pair 형태로 선언합니다.
- iterator(반복자)
- begin() : beginning iterator를 반환
- end() : end iterator를 반환
- begin() : beginning iterator를 반환
- 추가 및 삭제
- insert( make_pair(key,value) ) : 맵에 원소를 pair 형태로 추가
- erase(key) : 맵에서 key(키값)에 해당하는 원소 삭제
- clear() : 맵의 원소들 모두 삭제
- insert( make_pair(key,value) ) : 맵에 원소를 pair 형태로 추가
- 조회
- find(key) : key(키값)에 해당하는 iterator를 반환
- count(key) : key(키값)에 해당하는 원소들(value들)의 개수를 반환
- find(key) : key(키값)에 해당하는 iterator를 반환
- 기타
- empty() : 맵이 비어있으면 true 아니면 false를 반환
- size() : 맵 원소들의 수를 반환
- empty() : 맵이 비어있으면 true 아니면 false를 반환
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<string, int> ages;
ages["Mike"] = 40;
ages["Raj"] = 20;
ages["Vicky"] = 30;
ages["Mike"] = 70;
//
ages.insert(make_pair("Peter", 100));
//pair<string, int> addToMap("peter",100);
//ages.insert(addToMap);
cout << ages["Raj"] << endl;
// to find the techinical
if(ages.find("Vicky") != ages.end()) {
cout << "Found Vicky" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "Key not found." << endl;
}
for(map<string, int>::iterator it = ages.begin(); it != ages.end(); it++) {
pair<string, int> age = *it;
cout << age.first << ": " << age.second << endl;
// first and second the function in the map library
}
for(map<string, int>::iterator it = ages.begin(); it != ages.end(); it++) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
// first and second is valuable the value of the ages by key and value.
}
return 0;
}
Result
Custom Objects as map Keys
Flush
- 개발 된 Microsoft C/c + + 응용 프로그램에서는 cout 스트림 버퍼링 됩니다.
- 즉, 버퍼를 플러시할 때까지 cout 스트림에 보낼 정보가 화면에 나타나지 않습니다.
- 이 동작은 Visual C++ 4.2 및 이후 버전의 경우 이전 iostream 라이브러리를 사용할 때만 발생 합니다.
- 네 가지 방법을 다음과 같이 cout 버퍼를 플러시할 수 있습니다.
- Endl 조작자를 사용 하 여 줄 바꿈 문자를 출력 스트림에 삽입 버퍼를 플러시합니다. Endl 조작자를 사용 하 여 삽입 연산자를 다음과 같이 사용.
- cout « … « endl;
- Ostream 클래스 또는 플러시 조작자에 플러시 멤버 함수를 사용 합니다.
- 플러시 조작자 버퍼를 플러시합니다 전에 스트림에 줄 바꿈 문자가 삽입 되지는 않습니다. 플러시 멤버 함수를 호출 하려면 다음과 유사한 코드를 사용.
- cout.flush();
- 플러시 조작자를 사용 하 여 삽입 연산자를 다음과 같이 사용.
- cout « … « flush;
- Endl 조작자를 사용 하 여 줄 바꿈 문자를 출력 스트림에 삽입 버퍼를 플러시합니다. Endl 조작자를 사용 하 여 삽입 연산자를 다음과 같이 사용.
First and Second 함수
- 구조체 템플릿 std::pair 는 두 가지 유형의 정확히 두 개의 반환 값을 함께 묶을 수 있습니다
#include <utility>
std::pair<int, int> foo(int a, int b) {
return std::make_pair(a+b, a-b);
}
- C ++ 11 이후 버전에서는 std::make_pair 대신에 초기화리스트를 사용할 수 있습니다 :
#include <utility>
std::pair<int, int> foo(int a, int b) {
return {a+b, a-b};
}
- 쌍의 first 및 second 구성원 개체를 사용하여 반환 된 std::pair 의 개별 값을 검색 할 수 있습니다.
std::pair<int, int> mrvs = foo(5, 12);
std::cout << mrvs.first + mrvs.second << std::endl;
Example
- Map<person, int> people
- Person first map and value is second map
- Ex) [Person1, value1] [person2,value2]…
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() :
name(""), age(0) {
}
Person(string name, int age) :
name(name), age(age) {
}
// 상속
//constructor need to initialize this
//so thats why we use to initilaze the actual instance(기억장치 할당) variables in above
//we dont have to provide any more implementation(실행)
Person(const Person& other) {
name = other.name;
age = other.age;
}
//copy constoctur.
void print() const {
cout << name << ": " << age << flush;
}
//operator is just like +,-,<,>,!= 지정해주는
// 리퍼런스 other에 대신 데이터를 받아 가동을 시켜준다.
bool operator<(const Person &other) const {
if (name == other.name) {
return age < other.age;
} else {
return name < other.name;
}
}
};
int main() {
map<Person, int> people;
//map<key,value>
people[Person("Mike", 40)] = 40;
people[Person("Mike", 444)] = 123;
people[Person("Sue", 30)] = 30;
people[Person("Raj", 40)] = 20;
for (map<Person, int>::iterator it = people.begin(); it != people.end();
it++) {
cout << it->second << ": " << flush;
it->first.print();
cout << endl;
}
// it need to bool operation becuase
return 0;
}
Example 2
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
Person() :
name(""), age(0) {
}
// this is the default parameter of constructor.
// this is the keep
// member-wise <- in terms of(관해서) members(item associated with class instances)
Person(string name, int age) :
name(name), age(age) {
}
// this is necassary for 기억할당 in map function
Person(const Person &other){
cout << "Copy constructor running!" << endl;
name = other.name; // 얕은복사
age = other.age; //깊은 복사
}
// copy constructor is a member function which initialize an obeject using another object of the same class
// 복사생성자의 값을 복사 구성체에다가 받는다
// 인트매인에서 객체에 주어진 값이 같지만 주소가 바뀌거나 생성자 호출을 하지 않기 떄문에 이와 같이
// 새로운 공간 할당.
void print() {
cout << name << ": " << age << endl;
}
};
int main() {
map<int, Person> people;
people[50] = Person("Mike", 40);
people[32] = Person("Vicky", 30);
people[1] = Person("Raj", 20);
people.insert(make_pair(55, Person("Bob", 45 )));
people.insert(make_pair(55, Person("Sue", 24 )));
// copy constructor is called heres
for (map<int, Person>::iterator it = people.begin(); it != people.end();
it++) {
cout << it->first << ": " << flush;
it->second.print();
}
// flush is sending a content and cleaning up the buffer
return 0;
}
REFERENCE

Comments