Deep Understanding of Reference LRValue and Pointer Relationship
13 Feb 2022 | C++
- Concepts of left and right values
-
The left value is a value that can be assigned on the left side of the assignment number; the left value must have an entity in memory;
-
Right values are assigned to other variables on the right side of the assignment number; right values can be in memory or in CPU registers.
-
When an object is used as a right value, its content (value) is used, and when it is used as a left value, its address is used.
- citation
Reference is optimized by C++ grammar, and the essence of reference is realized by pointer. Reference to an alias equivalent to a variable.
References can change the pointer’s direction and the value pointed to by the pointer.
The basic rules cited are:
When declaring a reference, it must be initialized, and once bound, it cannot be bound to other objects; that is, the reference must be initialized, and the reference cannot be redefined;
All operations on references are equivalent to operations on the original object.
- Explain it with Example.
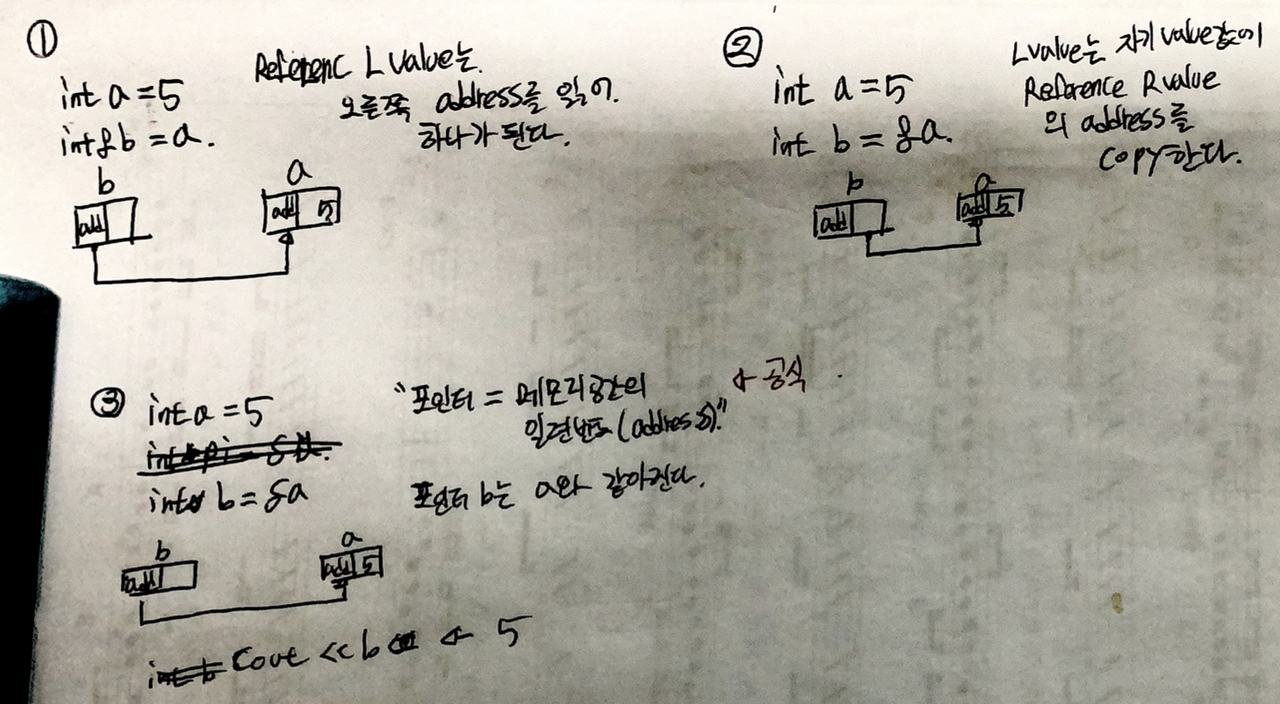
(1) case
L Value는 R Value값을 읽는다.
Reference L Value는 R Value의 Address를 읽는다.
(2) case
L Value는 R Value값을 읽는다.
Reference R Value일 경우, L Value는 순수하게 Address를 읽는다.
(3) case
Pointer = 메모리공간의 일련번호(address) 그렇기 때문에 Pointer는 Address를 가르켜야 한다.
NOTE : 예제 3번에 마지막 cout에 b앞에 “*“를 넣어줘야 한다.
포인터는 어드레스를 읽지만, 표현할때(RValue로 사용할 때에는)에는 어드레이스에 있는 밸류를 표현하기 때문이다.
만약 RVALUE로 사용할때 앞에 “*” 붙여주지 않는다면, pointer의 address로 표현이 될것이다.
또한 만약 Pointer가 Initialize가 되었다면(Pointing some address)면
int i = 5;
int* p = &i;
*p = 2;
// 이런식으로 표혀할 수도 있고,
int*p = nullptr; //initialize 하여서
int i = 5;
*p = i; // 이런식으로 바로 사용할 수 있다.
// 이미 이니셜라이즈가 되었는데 address를 새로 주려고 한다면 error 가 생긴다
int i = 5;
int* p = nullptr;
*p = &i; // 컴파일 에러! 에러! 에러! 에러! 이미 이니셜라이즈 했는데 address를 받는 것이므로
아래식으로 compile에러 없이 pointer에 밸류를 바꿀 수 있다. 이는 i의 값도 바뀌게 된다.
이는 포인터가 initialize가 되었을때에 value값을 바꾸는 방법이다.
void text(int& j)
{
cout << j << endl;
}
void text(int* j)
{
cout << *j << endl;
}
// those are samething
int i = 5;
test(i)
int i = 5;
test(&i)
REFERENCE
- Concepts of left and right values
-
The left value is a value that can be assigned on the left side of the assignment number; the left value must have an entity in memory;
-
Right values are assigned to other variables on the right side of the assignment number; right values can be in memory or in CPU registers.
-
When an object is used as a right value, its content (value) is used, and when it is used as a left value, its address is used.
- citation
Reference is optimized by C++ grammar, and the essence of reference is realized by pointer. Reference to an alias equivalent to a variable.
References can change the pointer’s direction and the value pointed to by the pointer. The basic rules cited are:
When declaring a reference, it must be initialized, and once bound, it cannot be bound to other objects; that is, the reference must be initialized, and the reference cannot be redefined;
All operations on references are equivalent to operations on the original object.
- Explain it with Example.
(1) case L Value는 R Value값을 읽는다. Reference L Value는 R Value의 Address를 읽는다.
(2) case L Value는 R Value값을 읽는다. Reference R Value일 경우, L Value는 순수하게 Address를 읽는다.
(3) case
Pointer = 메모리공간의 일련번호(address) 그렇기 때문에 Pointer는 Address를 가르켜야 한다.
NOTE : 예제 3번에 마지막 cout에 b앞에 “*“를 넣어줘야 한다.
포인터는 어드레스를 읽지만, 표현할때(RValue로 사용할 때에는)에는 어드레이스에 있는 밸류를 표현하기 때문이다.
만약 RVALUE로 사용할때 앞에 “*” 붙여주지 않는다면, pointer의 address로 표현이 될것이다.
또한 만약 Pointer가 Initialize가 되었다면(Pointing some address)면
int i = 5;
int* p = &i;
*p = 2;
// 이런식으로 표혀할 수도 있고,
int*p = nullptr; //initialize 하여서
int i = 5;
*p = i; // 이런식으로 바로 사용할 수 있다.
// 이미 이니셜라이즈가 되었는데 address를 새로 주려고 한다면 error 가 생긴다
int i = 5;
int* p = nullptr;
*p = &i; // 컴파일 에러! 에러! 에러! 에러! 이미 이니셜라이즈 했는데 address를 받는 것이므로
아래식으로 compile에러 없이 pointer에 밸류를 바꿀 수 있다. 이는 i의 값도 바뀌게 된다. 이는 포인터가 initialize가 되었을때에 value값을 바꾸는 방법이다.
void text(int& j)
{
cout << j << endl;
}
void text(int* j)
{
cout << *j << endl;
}
// those are samething
int i = 5;
test(i)
int i = 5;
test(&i)

Comments