9. Computer Architecture
17 May 2020 | CS
Computer Architecture
- the bit size of the CPU dictates(强行规定) the maximum permissible(许可的) size of the RAM. for a 32bit CPU and 32bit OS the maximum RAM supported is 4GB and a 64bit CPU and 64bit OS can support any size of main memory RAM.
-
in computer Architecture, the CPU is responsbile to process the data sa per the program instruction. the CPU can execute the program instruction at a very high speed. A gigahertz, the most common measure of processor speed and it means that one billion clock cycles can be completed per second.
-
however, the permanent memory(disk memory/ hard disk) of the system cannot transfer the data to the cpu to match the processing speed of the cpu. this slows down the processor speed and therefore we need intermidiate memory such as RAM, cache where the access speed is relatively much faster as compared to the disk memory.
-
therefore, in computer Architecture, in order to optimize on the cpu performance different types of memories are placed between the CPU and the disk memory. thses memories are placed in a hierachical order depending upon the data access speed, size and distance from the cpu. this significantly improves the system performance.
Memory Hierarchy
-
the hierarchical arrangement of the various memory storages in computer architecture is called the memory hierachy(하이러키). the memory hierachy in a computer system is designed to optimize on the CPU performance.
-
the hierachical arrangement of memories is based on the access speed, distance of the memory from cpu, memory size required and the cost consideration.
-
as we go up in the hierachy, each level of the memory hierachy is of higher speed, lower latency (潜伏) and is of smaller size than lower level.
-
the registers are the fastest in access speed, closest to the cpu, smallest in size and also expensive. the disk memory is slowest in access speed, farthest from the cpu, largest in size and relatively inepxensive.
-
the CPU doesn’t directly access the main memory and the dist memory.
-
the CPU will first look for the data from the cache memory. thus the data is copied from disk memory to RAM(main memory) and from RAM to the cache memory where CPU can quickly access.
types of Memory in Computer System
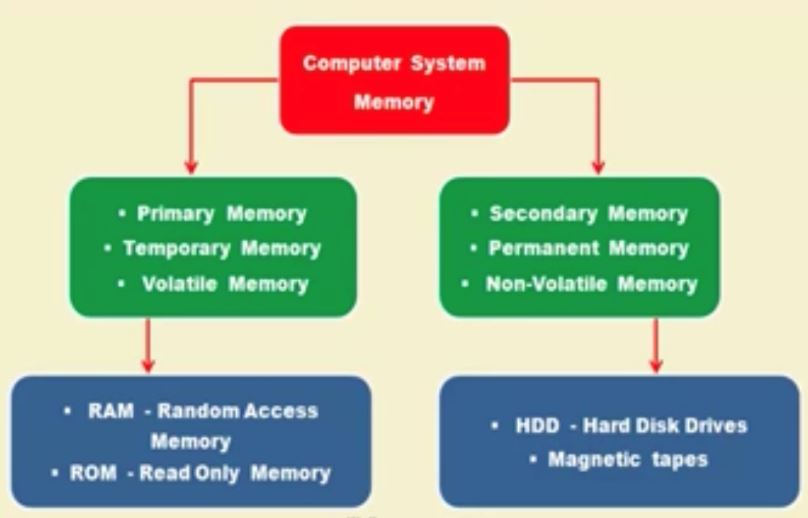
- the computer memory is mainly devided in to two types based on the data retention(保持) by the computer when power is switched off to the system:
- primary(volatile(易变的)(휘발성)(벌러타일)) Memory
- Temporary Memory or voltatile memory or main system memory.
- Secondary(Non-Volatile(비 휘발성)) Memory
- permanent memory or Non Volatile Memory
- Primary Memory
- the primary memory in computer system in also called as main memory(RAM- Random Access Memory) of the system which is volatile memory.
- every program first must be loaded in the RAM to start its execution by the processor.
- the primary memory(RAM) is a volatile memory and it can retain data only till the time the system is powererd on.
- the data stored in the RAM will be lost once the system is switched off. therefore, data to be retained must be copied to the permanent storage(disk memory/ secondary memory)
-
the CPU can process the data and instructions at very high speed as compared to the speed of the data that can be accessed by the CPU from the disk(permanent/secondary) memory which limits the CPU performance. therefore intermidiate high speed memories are placed in between the CPU and the disk memory
-
the data / instruction are copied from disk memory to RAM(Main Memory) and from RAM to the Cache memory(L3->L2->L1) where CPU can access relatively at high speed.
Secondary memory(permanent Memory) in computer system
-
the secondary memory is known as non-voltatile or permanent memory because it can retain the data when the computer system power is switched off
-
the secondary memory is also known as permanent memory it can retain the data even if the power supply is switched off. the data is stored in to the permanent storage devices can retain the data without any power supply to the system.
-
the secondary memory is also alternately referred as permanent memory/ Non Volatile memory/ disk memory is used to store the program and data on a long-term basis. Common secondary storage devices are the hard disk and optical disks.
-
the storage capacity of the hard disk is very high as compared to the RAM. the common size of the RAM is generally 4GB to 16GB where as the common hard disk size is 250 GB to 1(1024GB) TB. However, the access speed of the disk memory is vary slow as compared to the RAM speed.
-
during the program execution, large blocks of data are copied from disk memory into main memory(RAM). this operation is slow but lots of data is copied. throughout the program execution, the processor is continously read and write small sections of the data in main memory. when it is done, a large block of data is written to the disk memory for permanent storage
-
the operation system is responsbile to mange the memory operation and optimially use the RAM.
-
Optical storage devices are any sotrage methods that use a laser to store and retrieve data from optical media.
-
Optical storage media includes CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, DVD-RAM, WORM cartridges, erasble optical catridges and removeable mass storage media, which includes flash drives and removeable disks.
Computer Architecture
- the bit size of the CPU dictates(强行规定) the maximum permissible(许可的) size of the RAM. for a 32bit CPU and 32bit OS the maximum RAM supported is 4GB and a 64bit CPU and 64bit OS can support any size of main memory RAM.
-
in computer Architecture, the CPU is responsbile to process the data sa per the program instruction. the CPU can execute the program instruction at a very high speed. A gigahertz, the most common measure of processor speed and it means that one billion clock cycles can be completed per second.
-
however, the permanent memory(disk memory/ hard disk) of the system cannot transfer the data to the cpu to match the processing speed of the cpu. this slows down the processor speed and therefore we need intermidiate memory such as RAM, cache where the access speed is relatively much faster as compared to the disk memory.
-
therefore, in computer Architecture, in order to optimize on the cpu performance different types of memories are placed between the CPU and the disk memory. thses memories are placed in a hierachical order depending upon the data access speed, size and distance from the cpu. this significantly improves the system performance.
Memory Hierarchy
-
the hierarchical arrangement of the various memory storages in computer architecture is called the memory hierachy(하이러키). the memory hierachy in a computer system is designed to optimize on the CPU performance.
-
the hierachical arrangement of memories is based on the access speed, distance of the memory from cpu, memory size required and the cost consideration.
-
as we go up in the hierachy, each level of the memory hierachy is of higher speed, lower latency (潜伏) and is of smaller size than lower level.
-
the registers are the fastest in access speed, closest to the cpu, smallest in size and also expensive. the disk memory is slowest in access speed, farthest from the cpu, largest in size and relatively inepxensive.
-
the CPU doesn’t directly access the main memory and the dist memory.
-
the CPU will first look for the data from the cache memory. thus the data is copied from disk memory to RAM(main memory) and from RAM to the cache memory where CPU can quickly access.
types of Memory in Computer System
- the computer memory is mainly devided in to two types based on the data retention(保持) by the computer when power is switched off to the system:
- primary(volatile(易变的)(휘발성)(벌러타일)) Memory
- Temporary Memory or voltatile memory or main system memory.
- Secondary(Non-Volatile(비 휘발성)) Memory
- permanent memory or Non Volatile Memory
- primary(volatile(易变的)(휘발성)(벌러타일)) Memory
- Primary Memory
- the primary memory in computer system in also called as main memory(RAM- Random Access Memory) of the system which is volatile memory.
- every program first must be loaded in the RAM to start its execution by the processor.
- the primary memory(RAM) is a volatile memory and it can retain data only till the time the system is powererd on.
- the data stored in the RAM will be lost once the system is switched off. therefore, data to be retained must be copied to the permanent storage(disk memory/ secondary memory)
-
the CPU can process the data and instructions at very high speed as compared to the speed of the data that can be accessed by the CPU from the disk(permanent/secondary) memory which limits the CPU performance. therefore intermidiate high speed memories are placed in between the CPU and the disk memory
-
the data / instruction are copied from disk memory to RAM(Main Memory) and from RAM to the Cache memory(L3->L2->L1) where CPU can access relatively at high speed.
Secondary memory(permanent Memory) in computer system
-
the secondary memory is known as non-voltatile or permanent memory because it can retain the data when the computer system power is switched off
-
the secondary memory is also known as permanent memory it can retain the data even if the power supply is switched off. the data is stored in to the permanent storage devices can retain the data without any power supply to the system.
-
the secondary memory is also alternately referred as permanent memory/ Non Volatile memory/ disk memory is used to store the program and data on a long-term basis. Common secondary storage devices are the hard disk and optical disks.
-
the storage capacity of the hard disk is very high as compared to the RAM. the common size of the RAM is generally 4GB to 16GB where as the common hard disk size is 250 GB to 1(1024GB) TB. However, the access speed of the disk memory is vary slow as compared to the RAM speed.
-
during the program execution, large blocks of data are copied from disk memory into main memory(RAM). this operation is slow but lots of data is copied. throughout the program execution, the processor is continously read and write small sections of the data in main memory. when it is done, a large block of data is written to the disk memory for permanent storage
-
the operation system is responsbile to mange the memory operation and optimially use the RAM.
-
Optical storage devices are any sotrage methods that use a laser to store and retrieve data from optical media.
-
Optical storage media includes CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, DVD-RAM, WORM cartridges, erasble optical catridges and removeable mass storage media, which includes flash drives and removeable disks.












Comments