12. Random Access Memory(RAM)
18 May 2020 | CS
RAM - Random Access Memory
-
the RAM is a temporay storage area for programs being executed by the CPU. the data may not be stored in a contagious(感染力) memory locations inside the RAM
-
the memory consist number of addressable memory units(bytes) where the data is stored. depending upon the data type, the operating system allocates the memory.
-
RAM is essential component of every computer system which plays a crucial role in functioning of a computer system. the random-access memory(RAM) is a type of temporay storage(volatie) for computer systems that make it possible for CPU to access the data very quickly in random order.
-
RAM is a vital resource and it is managed by the operating system by allocating and de-allocating the RAM to the different program being executed.
-
the size of the RAM available in a computer system plays a very crucial role in the over all system performance and adequate RAM size is critical for optimizing the CPU performance.
-
inadequate(不充分的) Ram size can adversely(反对地) affect overall system performance resulting a very slow program execution.
-
the RAM size is measured in terms of “Bytes” and the usual size of the RAM modules is 512MB or 1GB(1024). the PC RAM size can suitably modified by adding more RAM modules placed in slots available on the motherboard.
-
the RAM modul consist of number of Memory IC chips placed on a PCB strip which effectively function as RAM modules.
- Byte = 8 bits
- 1025 bytes = 1KB
- 1025 Kb = 512Mb
- 1024 MB = 1GB
- RAM is the tpye of memory installed inside a computer and fitted in to slots provided on the mother board. we can increase the RAM memory size of our computer by adding more RAM chip circuits depending upon the operating system(32bits/ 64bits) limits.
-
As the technology progressed, the RAM chips have become faster with the advent of new technology. However, the RAM compatibility must be checked before its installation to a compatible motherboard.
-
the maximum size of the RAM supported by a computer system also depending upon the type of the operating system(32bits/64bits). for example the maximum addressable RAM supported by a 32 bit operating system is 4GB whereas 64bit OS can support very high RAM size.
-
in computer architecture, a computer system makes the use of different types of memories and these memories can be classified depending upon the proximity to the CPU, access speed, memory size and cost of the memory.
- the CPU in a computer system essentially performs two types of operations
- reading from the memory
- writing to the memory.
-
the user commands the operating system to run a specific program by double clikcing with mouse on the program executable file which instructs the operating system to initiate the program exeuction.
- Every program must be first loaeded in the RAM in order to execute the program. the operating system loaeds the program’s exeuctable file from a source drive (CDROM/Hard Disk) to the RAM and allocates the required memeory for program exeuction.
-
the program execution starts with the program code in binary machine code is copied from permanent disk memory to the volatile main memory RAM.
-
this consist of machine code instructions directly exeuctable by the CPU
- THe comtrol unit inside the CPU initiates the process of program execution by loading these instructions one by one from RAM to the CPU with instruction cycle consisting of steps
- Fetch -> decode -> Execute -> store
-
the operating ststem(OS) splits the program into number of manageable units called processes. the operating system manages these processes by allocating the CPU processing time which is known as process management. the CPU can execute many processes simultaneously.
-
the data is again sent to the RAM after being processed by the CPU. however the RAM being volatile memory cannot permanently retain the data. the data in the ram is lost if the system is turned off.
- therefore, the data present inside the RAM must be stored in any permanent storage device such as hard dist else the data will be lost if program is terminated without saving the data.
Types of RAM
- there are two basic types of RAM:
- Dynamic RAM(DRAM)
- Dynamic RAM is the more common and needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second.
- Static RAM(SRAM)
- Static RAM does not need to be refreshed making it a lot faster but also much more expensive as compared to DRAM.
- the computer system makes use of both static RAM and dynamic RAM at the same time, but it uses them for different reasons because of the cost and size difference between the two types.
DRAM
-
DRAM is more commonly used for personal computer memory and SRAM chips are preffered when energy efficieny is a concern, such as in cars, household appliances, and handheld electornics devices.
- the Dynamic RAM(DRAM) is the most common type of memory in use today. inside a dynamic RAM chip, each memory cell holds one bit of inoramtion and is made up of two parts
- a transistor and a capacitor.
- these are extremely small transistors and capacitors so that millions of them can fit on a single memory chip.
-
the capacitor holds the bit of inoframtion(0 or 1). the transisotr acts as a switch that lets the control circuitry on the memory chip read the capacitor or change its state.
-
the problem with dynamic RAM chipes is that the capacitor leaks enery very quickly and can hold a charge for only a fraction of a second. A refresh circuit is needed to maintain the charge in a capacitor and retain the information.
-
this refreshing process takes place hundreds of times every second and requires that all cells must be accessed, even if the information is not needed.
- As each line of cells is read, the computer’s CPU re-writes each bit of information and recharge the capacitor as needed.
SRAM
- The static RAM chips, on the other hand use a different technology by using flip flop which doesn’t need refreshing to retain data.
- the biggest drawback to SRAM is space. each transistor on a dynamic RAM chip can store one bit of information, but four to six transisotrs are required to store a bit using SRAM.
- this means that a dynamic RAM chip will hold at least four times as much memory as a static RAM chip of the samze size, making SRAM much more expensive.
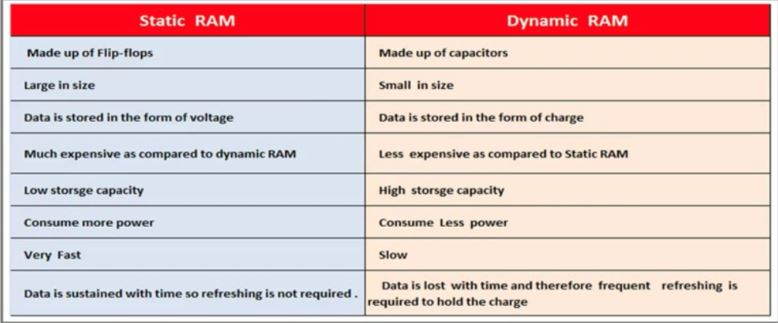
difference between SRAM and DRAM
insturction cycle and Main Memory - RAM
- An insturction cycle ( also called a fetch-decode-execute-store cycle) is the baisc operational process of a computer.
-
it is the process by which a computer retrieves a program instruction from its memory, determines what actions the instruction dictates (强行规定) and carries out those actions.
- this cycle is repreated continously by a computer’s CPU, from boot-up to when the computer is shut down.
-
the operating system loads the executable copy of the program from disk memory into the RAM for cput to initiate execution. the program consist of machine code instructions directly executed by the CPU.
-
the program instructions are typically arranged sequentially in memory.
-
each instruction occupies one or more memory words(memory location).
- to execute any program, the CPU has to contentiously perform instruction cycle which consist of for steps
- Fetch - Decode - Execute - Store
-
the CPU executes the progam by fetching program insturction one by one from the main system memory RAM.
- the CPU stores the data and instructions in to the various CPU registers which are Temporary internal storage memory areas. the out put is again sent to the RAM.
RAM - Random Access Memory
-
the RAM is a temporay storage area for programs being executed by the CPU. the data may not be stored in a contagious(感染力) memory locations inside the RAM
-
the memory consist number of addressable memory units(bytes) where the data is stored. depending upon the data type, the operating system allocates the memory.
-
RAM is essential component of every computer system which plays a crucial role in functioning of a computer system. the random-access memory(RAM) is a type of temporay storage(volatie) for computer systems that make it possible for CPU to access the data very quickly in random order.
-
RAM is a vital resource and it is managed by the operating system by allocating and de-allocating the RAM to the different program being executed.
-
the size of the RAM available in a computer system plays a very crucial role in the over all system performance and adequate RAM size is critical for optimizing the CPU performance.
-
inadequate(不充分的) Ram size can adversely(反对地) affect overall system performance resulting a very slow program execution.
-
the RAM size is measured in terms of “Bytes” and the usual size of the RAM modules is 512MB or 1GB(1024). the PC RAM size can suitably modified by adding more RAM modules placed in slots available on the motherboard.
-
the RAM modul consist of number of Memory IC chips placed on a PCB strip which effectively function as RAM modules.
- Byte = 8 bits
- 1025 bytes = 1KB
- 1025 Kb = 512Mb
- 1024 MB = 1GB
- RAM is the tpye of memory installed inside a computer and fitted in to slots provided on the mother board. we can increase the RAM memory size of our computer by adding more RAM chip circuits depending upon the operating system(32bits/ 64bits) limits.
-
As the technology progressed, the RAM chips have become faster with the advent of new technology. However, the RAM compatibility must be checked before its installation to a compatible motherboard.
-
the maximum size of the RAM supported by a computer system also depending upon the type of the operating system(32bits/64bits). for example the maximum addressable RAM supported by a 32 bit operating system is 4GB whereas 64bit OS can support very high RAM size.
-
in computer architecture, a computer system makes the use of different types of memories and these memories can be classified depending upon the proximity to the CPU, access speed, memory size and cost of the memory.
- the CPU in a computer system essentially performs two types of operations
- reading from the memory
- writing to the memory.
-
the user commands the operating system to run a specific program by double clikcing with mouse on the program executable file which instructs the operating system to initiate the program exeuction.
- Every program must be first loaeded in the RAM in order to execute the program. the operating system loaeds the program’s exeuctable file from a source drive (CDROM/Hard Disk) to the RAM and allocates the required memeory for program exeuction.
-
the program execution starts with the program code in binary machine code is copied from permanent disk memory to the volatile main memory RAM.
-
this consist of machine code instructions directly exeuctable by the CPU
- THe comtrol unit inside the CPU initiates the process of program execution by loading these instructions one by one from RAM to the CPU with instruction cycle consisting of steps
- Fetch -> decode -> Execute -> store
-
the operating ststem(OS) splits the program into number of manageable units called processes. the operating system manages these processes by allocating the CPU processing time which is known as process management. the CPU can execute many processes simultaneously.
-
the data is again sent to the RAM after being processed by the CPU. however the RAM being volatile memory cannot permanently retain the data. the data in the ram is lost if the system is turned off.
- therefore, the data present inside the RAM must be stored in any permanent storage device such as hard dist else the data will be lost if program is terminated without saving the data.
Types of RAM
- there are two basic types of RAM:
- Dynamic RAM(DRAM)
- Dynamic RAM is the more common and needs to be refreshed thousands of times per second.
- Static RAM(SRAM)
- Static RAM does not need to be refreshed making it a lot faster but also much more expensive as compared to DRAM.
- Dynamic RAM(DRAM)
- the computer system makes use of both static RAM and dynamic RAM at the same time, but it uses them for different reasons because of the cost and size difference between the two types.
DRAM
-
DRAM is more commonly used for personal computer memory and SRAM chips are preffered when energy efficieny is a concern, such as in cars, household appliances, and handheld electornics devices.
- the Dynamic RAM(DRAM) is the most common type of memory in use today. inside a dynamic RAM chip, each memory cell holds one bit of inoramtion and is made up of two parts
- a transistor and a capacitor.
- these are extremely small transistors and capacitors so that millions of them can fit on a single memory chip.
-
the capacitor holds the bit of inoframtion(0 or 1). the transisotr acts as a switch that lets the control circuitry on the memory chip read the capacitor or change its state.
-
the problem with dynamic RAM chipes is that the capacitor leaks enery very quickly and can hold a charge for only a fraction of a second. A refresh circuit is needed to maintain the charge in a capacitor and retain the information.
-
this refreshing process takes place hundreds of times every second and requires that all cells must be accessed, even if the information is not needed.
- As each line of cells is read, the computer’s CPU re-writes each bit of information and recharge the capacitor as needed.
SRAM
- The static RAM chips, on the other hand use a different technology by using flip flop which doesn’t need refreshing to retain data.
- the biggest drawback to SRAM is space. each transistor on a dynamic RAM chip can store one bit of information, but four to six transisotrs are required to store a bit using SRAM.
- this means that a dynamic RAM chip will hold at least four times as much memory as a static RAM chip of the samze size, making SRAM much more expensive.
difference between SRAM and DRAM
insturction cycle and Main Memory - RAM
- An insturction cycle ( also called a fetch-decode-execute-store cycle) is the baisc operational process of a computer.
-
it is the process by which a computer retrieves a program instruction from its memory, determines what actions the instruction dictates (强行规定) and carries out those actions.
- this cycle is repreated continously by a computer’s CPU, from boot-up to when the computer is shut down.
-
the operating system loads the executable copy of the program from disk memory into the RAM for cput to initiate execution. the program consist of machine code instructions directly executed by the CPU.
-
the program instructions are typically arranged sequentially in memory.
-
each instruction occupies one or more memory words(memory location).
- to execute any program, the CPU has to contentiously perform instruction cycle which consist of for steps
- Fetch - Decode - Execute - Store
-
the CPU executes the progam by fetching program insturction one by one from the main system memory RAM.
- the CPU stores the data and instructions in to the various CPU registers which are Temporary internal storage memory areas. the out put is again sent to the RAM.










Comments