13. Virtual Memory
19 May 2020 | CS
Virtual Memory
- the performance of the computer system primarily depends upon three factors:
- size of the main Memory(RAM)
- 32 bit OS -> 4GB
- 64 bit OS -> more than 4GB
- the CPU processing speed.
- Type of the operating system(32bit/64bit)
-
Out of these three factors the size of the maximum permissible RAM depends upon the type of the operating system(32bit/64bit) which defines the maxium addressable memory locations.
-
A platform is a runtime evnvironment provided by the CPU and compatible operating system on which various process can run
-
the choice of platform also affect the maximum permissible addressable RAM that can be supported by the computer system
-
today, the most common size of RAM available generally ranges between 4GB to 16GB depending upon the operating system installed on a laptops and desktop computer.
-
However, the size of the software have grown significantly and it is very common to find a software especially some of the graphics design, video editing and video games where required RAM size exceeds more than 10GB
-
then, how come we can run these programs which exceeds the available RAM in the computer system?
Review of Memory characteristic
Memory
- the memory of a computer is a large indexed set of memory cells.
- by “large” we could mean anywhere from 256 cells to 32 million cells.
- by “indexed” we mean that each individual memory cell has its very own index number(aka identification number). this index number is usually called an address and can be through of as “stamped” on the “edge “of the memmory
- memory supports these operation
- selecting
- reading
- writing.
Memory Cell
- A memory cell is the smallest part of a computer memory that can be changed in a signle operation
- A memory cell records a number writeen in binary - this number is called the content of the memory cell. the cell pictured to the right has content 11010011 = D3
- A RAM(random access memory) cell can have different numbers recorded in it at different times.
- it is like a cassette tape that can be recorded with different songs. However, when a ne number is recorded in a RAM memory cell, the old number is FOREVER LOST.
- A ROM(read only memory) cell has a number permanctly recorded in it. it is like a message chiseled in stone. it cannot be lost, even if the power is turned off.
- All the numbers recorded in a memory cell always have the same bumber of bits
back to Virual Memory
-
the computer main memory(RAM) is organized into number of addressable units with each unit of a 1 byte(8 bits) size and each of this memory location has a unique memory address
-
for a computer system, the RAM will always be a limited resource due to ever increasing size of the software and number of programs simultaneusly running on the system
-
the operating system can handle number of programs running simultaneously on the system. however sometimes the program/process size exceeds the main system memory RAM.
-
A computer system can crash if the main memory - RAM available falls short of memory required to run the procsses being executed by the CPU.
-
the virtual memory solves this problem by treating each computer as if it has a large size of RAM which is not being shared with any other programs.
-
the operating system, such as Microsoft Windos or Apple’s OS, creates a set of virtual addresses for each program. the operating system translate virutal addresses into phsysical addresses, dynamically fitting programs into the RAM as it becomes available.
-
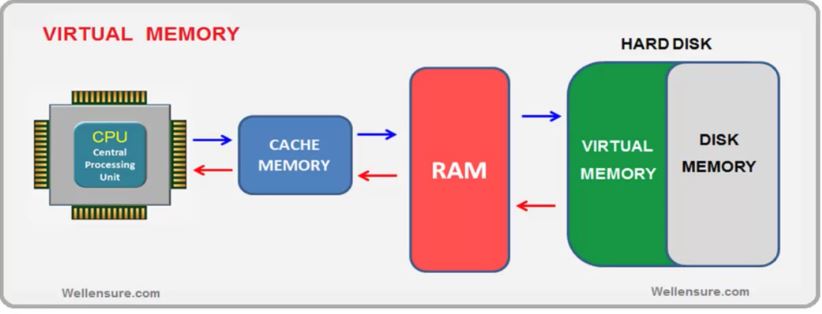
the virtual memory is an important mechanism provided within the operating system which makse use of some portion of the secondary memory such as Hard Dist which is also referred as disk memory.
-
the virtual memory is an logical extension of the computer system’s main memory RAM which is also referred as primary memory Or phsysical memory
-
in a situation when the size of the various processes (program) being executed by the CPU exceeds the size of the available physical memory RAM. the virual memory creates illusion of unlimited main memory RAM by using some part of hard dist as virtual memmory.
How operating system implements the virtual Memory?
- the operating system implementation of the virtual memory consist of number of steps which includes both hardware and software side.
- hardware side deals with the physical RAM and the software side deals with the process management.
-
the virtual memory is an important mechanism/feature provided within the operating system which allows user to run multiple programs simultaneusly which exceeds the size of the RAM available to the computer system.
- the operating system splits the RAM in to equal size partitions called page frames/pags. the general size of the page frame for intel processors is 4kb which could vary on a higher side for some recent processors.
- each page frame size = 4Kb
-
A process is a instance of the program. the operating system initiates the program execution by allocating the required memory from the main memory RAM.
- Similarly, the operating system also splits the procss into equal size partitions called block. the operating system splits the process in such a manner that the process block size equal to the size of the RAM page frame
- RAM pageFrame size = Process block size.
-
the operating system also maintains “Page Frame Table” for each process which is being executed by the CPU. the page frame table is also stored in the RAM
-
the page frame table contains the details of the mapping for the process block to corresponding page frame in the RAM.
-
the operating system allocates the RAM to different processs being executed simultaneously by the CPU. the operating system neeed not store the process block in to contagious memory locations
-
therefore, the CPU has to each time first look into the page frame table to find the memory location of a block for a given process after converting the virtual addresses with the physical RAM address.
-
the number of processes can share the RAM without conflicting with each other due to active page frame table.
-
the operating system creates a page frame table for each process being executed by the CPU. the page frame table is used by the MMU(Memory Management Unit) of the CPU to generate the physical RAM addresses for each process block.
-
the processor(CPU) executes only one process at a time and during this period the associated page frame table will be a active page frame table. the CPU will access the memory addresses only from the page frame table which is currently active.
-
the operating system does not load all the block associated with process but loads only those block which being used by user.
-
the OS allocates some portion of secondary storage (HardDIst) as swap space.
-
this swap space will have all the blocks/pages belonging to a processs.
-
the pages from swap area are loaded by the OS on demand as required during process execution by the CPU.
-
the present bin in the process page table indicates if that block is present in the RAM or not present in the RAM
-
if the present Bit =1 then block is present in the RAM. if the present Bit=0 then block is not present in the RAM
-
The CPU use page fault interrupt to load the blocks.
-
in demand paging only a part of the program(blocks/pages) are loaded in to the RAM. if the program access the page whicn not present in the RAM then processor issue a page fault interrupt which is a trigger for the operating system to loade the page from swap space in to the RAM and update the process page table present bit from 0 to 1.
-
if there is no free page frame available in the RAM for new pages to be loaded then the OS has to remove some pages from the RAM.
- the OS take this decision based on the replacement algorithm
- First in Frist out
- least recently used.
- least Frequently used.
-
SWAP OUT : the OS removes the pages from RAM which are not in use by the process and copies back to swap space on the secondary storage(hard disk)
- SWAP IN : the OS loads the required pages by the program from secondary storage swap space to the RAM. the present bit status is updated in process page table from 0 to 1.
-
present bit : the present bit indicates the status of the process page/block presence in RAM.
-
Dirty bit : the pages already present in the RAM modified by the program and need to swapped out and copied back to the swap space so that the swap area on the secondary storage will have the updated copy. the process page table also need to be modified to track this change.
-
Dirty Bit : the process page/block modified by program inside RAM must be written back to the swap area. the operating system keeps the track of such pages with the help of dirty bit satus inside the process page table.
- if the Dirty bit = 1 then the page needs to be written back to the swap area on the secondary storage
- if the Dirty bit = 0 then page has not changed & swap out is not required
- protection bit : the process page table has one additional column as protection bit in addition to P and D columns. the PB column is used by the operating system to assign some additional attributes to the process page/blcok, such as executable code, read only OR some other code.
Virtual Memory
- the performance of the computer system primarily depends upon three factors:
- size of the main Memory(RAM)
- 32 bit OS -> 4GB
- 64 bit OS -> more than 4GB
- the CPU processing speed.
- Type of the operating system(32bit/64bit)
-
Out of these three factors the size of the maximum permissible RAM depends upon the type of the operating system(32bit/64bit) which defines the maxium addressable memory locations.
-
A platform is a runtime evnvironment provided by the CPU and compatible operating system on which various process can run
-
the choice of platform also affect the maximum permissible addressable RAM that can be supported by the computer system
-
today, the most common size of RAM available generally ranges between 4GB to 16GB depending upon the operating system installed on a laptops and desktop computer.
-
However, the size of the software have grown significantly and it is very common to find a software especially some of the graphics design, video editing and video games where required RAM size exceeds more than 10GB
-
then, how come we can run these programs which exceeds the available RAM in the computer system?
Review of Memory characteristic
Memory
- the memory of a computer is a large indexed set of memory cells.
- by “large” we could mean anywhere from 256 cells to 32 million cells.
- by “indexed” we mean that each individual memory cell has its very own index number(aka identification number). this index number is usually called an address and can be through of as “stamped” on the “edge “of the memmory
- memory supports these operation
- selecting
- reading
- writing.
Memory Cell
- A memory cell is the smallest part of a computer memory that can be changed in a signle operation
- A memory cell records a number writeen in binary - this number is called the content of the memory cell. the cell pictured to the right has content 11010011 = D3
- A RAM(random access memory) cell can have different numbers recorded in it at different times.
- it is like a cassette tape that can be recorded with different songs. However, when a ne number is recorded in a RAM memory cell, the old number is FOREVER LOST.
- A ROM(read only memory) cell has a number permanctly recorded in it. it is like a message chiseled in stone. it cannot be lost, even if the power is turned off.
- All the numbers recorded in a memory cell always have the same bumber of bits
back to Virual Memory
-
the computer main memory(RAM) is organized into number of addressable units with each unit of a 1 byte(8 bits) size and each of this memory location has a unique memory address
-
for a computer system, the RAM will always be a limited resource due to ever increasing size of the software and number of programs simultaneusly running on the system
-
the operating system can handle number of programs running simultaneously on the system. however sometimes the program/process size exceeds the main system memory RAM.
-
A computer system can crash if the main memory - RAM available falls short of memory required to run the procsses being executed by the CPU.
-
the virtual memory solves this problem by treating each computer as if it has a large size of RAM which is not being shared with any other programs.
-
the operating system, such as Microsoft Windos or Apple’s OS, creates a set of virtual addresses for each program. the operating system translate virutal addresses into phsysical addresses, dynamically fitting programs into the RAM as it becomes available.
-
the virtual memory is an important mechanism provided within the operating system which makse use of some portion of the secondary memory such as Hard Dist which is also referred as disk memory.
-
the virtual memory is an logical extension of the computer system’s main memory RAM which is also referred as primary memory Or phsysical memory
-
in a situation when the size of the various processes (program) being executed by the CPU exceeds the size of the available physical memory RAM. the virual memory creates illusion of unlimited main memory RAM by using some part of hard dist as virtual memmory.
How operating system implements the virtual Memory?
- the operating system implementation of the virtual memory consist of number of steps which includes both hardware and software side.
- hardware side deals with the physical RAM and the software side deals with the process management.
-
the virtual memory is an important mechanism/feature provided within the operating system which allows user to run multiple programs simultaneusly which exceeds the size of the RAM available to the computer system.
- the operating system splits the RAM in to equal size partitions called page frames/pags. the general size of the page frame for intel processors is 4kb which could vary on a higher side for some recent processors.
- each page frame size = 4Kb
-
A process is a instance of the program. the operating system initiates the program execution by allocating the required memory from the main memory RAM.
- Similarly, the operating system also splits the procss into equal size partitions called block. the operating system splits the process in such a manner that the process block size equal to the size of the RAM page frame
- RAM pageFrame size = Process block size.
-
the operating system also maintains “Page Frame Table” for each process which is being executed by the CPU. the page frame table is also stored in the RAM
-
the page frame table contains the details of the mapping for the process block to corresponding page frame in the RAM.
-
the operating system allocates the RAM to different processs being executed simultaneously by the CPU. the operating system neeed not store the process block in to contagious memory locations
-
therefore, the CPU has to each time first look into the page frame table to find the memory location of a block for a given process after converting the virtual addresses with the physical RAM address.
-
the number of processes can share the RAM without conflicting with each other due to active page frame table.
-
the operating system creates a page frame table for each process being executed by the CPU. the page frame table is used by the MMU(Memory Management Unit) of the CPU to generate the physical RAM addresses for each process block.
-
the processor(CPU) executes only one process at a time and during this period the associated page frame table will be a active page frame table. the CPU will access the memory addresses only from the page frame table which is currently active.
-
the operating system does not load all the block associated with process but loads only those block which being used by user.
-
the OS allocates some portion of secondary storage (HardDIst) as swap space.
-
this swap space will have all the blocks/pages belonging to a processs.
-
the pages from swap area are loaded by the OS on demand as required during process execution by the CPU.
-
the present bin in the process page table indicates if that block is present in the RAM or not present in the RAM
-
if the present Bit =1 then block is present in the RAM. if the present Bit=0 then block is not present in the RAM
-
The CPU use page fault interrupt to load the blocks.
-
in demand paging only a part of the program(blocks/pages) are loaded in to the RAM. if the program access the page whicn not present in the RAM then processor issue a page fault interrupt which is a trigger for the operating system to loade the page from swap space in to the RAM and update the process page table present bit from 0 to 1.
-
if there is no free page frame available in the RAM for new pages to be loaded then the OS has to remove some pages from the RAM.
- the OS take this decision based on the replacement algorithm
- First in Frist out
- least recently used.
- least Frequently used.
-
SWAP OUT : the OS removes the pages from RAM which are not in use by the process and copies back to swap space on the secondary storage(hard disk)
- SWAP IN : the OS loads the required pages by the program from secondary storage swap space to the RAM. the present bit status is updated in process page table from 0 to 1.
-
present bit : the present bit indicates the status of the process page/block presence in RAM.
-
Dirty bit : the pages already present in the RAM modified by the program and need to swapped out and copied back to the swap space so that the swap area on the secondary storage will have the updated copy. the process page table also need to be modified to track this change.
-
Dirty Bit : the process page/block modified by program inside RAM must be written back to the swap area. the operating system keeps the track of such pages with the help of dirty bit satus inside the process page table.
- if the Dirty bit = 1 then the page needs to be written back to the swap area on the secondary storage
- if the Dirty bit = 0 then page has not changed & swap out is not required
- protection bit : the process page table has one additional column as protection bit in addition to P and D columns. the PB column is used by the operating system to assign some additional attributes to the process page/blcok, such as executable code, read only OR some other code.











Comments