16.How CPU executes a Program
19 May 2020 | CS
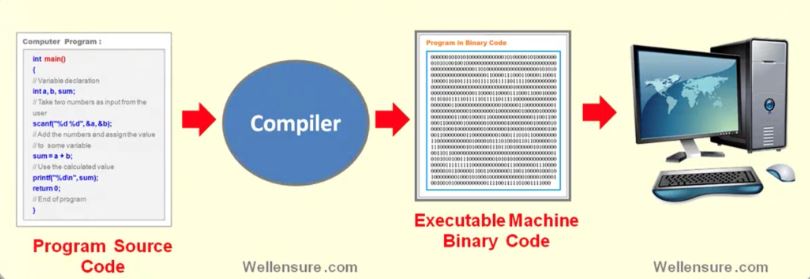
program compilation
-
A computer understands only machine language instruction (low level) that is a code written in binary code and execute the operation as per its instruction set.
-
A compiler is a special program which translate human readable code written in any high level programming launguage into a equivalent machine readable machine code in binary code.
-
A computer Program source code is generally written in a human readable high level language such as C, C++, python and many more. the high level program is then converted to machine readable binary code by using a special program called compiler.
-
An executable copy(machine Code) of the program consist of set of low level binary code instructions that can be direcly decoded and then executed by the computer’s processor.
-
the operating system allocates the required memory and processor time to initiate the program execution. the computer program(set of machine/ binary code instructions) is first loaded by the operating system from computer hard disk(secondary memory) to the RAM(main memory)
-
the CPU retrieves these instructions one by one from the main memory RAM and initiates the program execution process.
-
the program exectuion starts with the program instructions in binary machine code is copied from permanent disk memory to the volatile man Memory RAM. thses program instruction consist of binary machine code instructions directly executable by the CPU.
-
the constrol unit inside the CPU initiates the process of program execution by loading these instructions one by one from RAM to the CPU’s internal memory unit which consist of high speed memory(Registers and CACHE L1 memory).
-
the CPU makes use of differnt types of high speed internal memory registers during the various stages of program execution.
-
The CPU’s decode unit interprets these program instruction as per the processor’s instruction set architecture and performs the required operations on the data. the result is then sent to the main memory for further action.
-
the processed data(result) from the main memory RAM can be either sent to the output device(printer) OR could be sent to the permanent storage device
what is a program instruction?
-
A computer program is basically a list of instruction or statements that directs the computer hardware to perform a specific task as specified in the program instructions.
-
there are many programming languages available to a programmer but the computer basically understands only a program in machine code binary. therefore all the computer programs are eventually must be translated to machine code instructions which computer CPU can interprets and execute.
-
Machine code(binary code) is only form of program instruction that the computer hardware can understand and execute directly. all other forms of computer program written in different language must be first translated into machine code in order to be executed by the Hardware(CPU)
-
the Compiler is a special program used to convert high level program to low level machine code. thses machine code instructions are fetched from the memory and executed by the CPU.
-
Each CPU’s internal design is based on some standard micro architecture which is implemented by the CPU manufacuring companies which is knwon as “ISA(instruction Set architecture)”
-
an instruction is a binary pattern designed inside a CPU to perform a specific operation
-
the entire group of instructions that is implemented and supported by the microprocessor is called as “instruction Set”. for Example ISA 8085 has 246 instructions.
-
the program instruction can be classidied in to five broad categories
- Data transfer Instruction
- Arithmetic Instructions
- Logicl instructions
- branching instructions
- control instruction
-
an instruction set is a list of all the instructions that a processor can decode and execute. such instructions include arithmetic operations such as add and substract, logical operaions such as AND or OR and NOT, data instruction such as move, input and output and control instructions such as goto, call, and return.
-
the instruction set specifies the opcodes(machine language operation codes) that are used to identify each instruction.
-
ISC generally break down into two main approaches
- RISC
- CISC
-
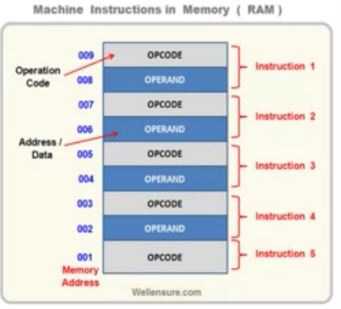
A single instruction can take more than one memory location to store. for example as shown in the diagram instruction 1,2,3,4 needs two memory locations each to store a part of the instruction in the main memory (RAM). whereas the instruction 5 will need only one memory location as it has only opcode
-
the computer program loaded by the operating system in to the RAM. the executable file of the program consist of number of instructions and each instruction has unique address in the memory which CPU can refer to while fetching the instructions.
-
Each instruction is represented by 8 bits binary value. this 8 bits binary value is called OPCODE or instruction byte.
-
the Machine instructions to be stored in the RAM must be encoded in binary as a sequence of 0’s and 1’s because all storage devices consist of a set of locations that can have one of two possible states(0,1). these instructions are fetched by the CPU one by one to execute the program.
-
the machine instruction is a binary representation of the instruction for the CPU in machine language (0 and 1) to perform a specific taks such as Add, divide, increment etc
- Each Machine instruction has tow parts
- OPCODE : Operation Code
- OPERAND : Address of DATA / DATA
- the OPCODE portion of the machine instruction specifies the operation to be performed by the ALU on the OPERAND as per instruction set of the CPU.
-
An OPCODE is a single instruction that can be executed by the CPU. in machine language it is a bianry or hexadecimal value such as “B6” loaded into the instruction register.
-
a simple example of a machine instruction ADD# 45 that we can give to a computer. this is called machine code instructions.
-
the machine code allows computers to perform the most basic, but essential tasks. the CPU makes use of the Accumulator Register which is used to stroe the intermediate results of all our calculations
program compilation
-
A computer understands only machine language instruction (low level) that is a code written in binary code and execute the operation as per its instruction set.
-
A compiler is a special program which translate human readable code written in any high level programming launguage into a equivalent machine readable machine code in binary code.
-
A computer Program source code is generally written in a human readable high level language such as C, C++, python and many more. the high level program is then converted to machine readable binary code by using a special program called compiler.
-
An executable copy(machine Code) of the program consist of set of low level binary code instructions that can be direcly decoded and then executed by the computer’s processor.
-
the operating system allocates the required memory and processor time to initiate the program execution. the computer program(set of machine/ binary code instructions) is first loaded by the operating system from computer hard disk(secondary memory) to the RAM(main memory)
-
the CPU retrieves these instructions one by one from the main memory RAM and initiates the program execution process.
-
the program exectuion starts with the program instructions in binary machine code is copied from permanent disk memory to the volatile man Memory RAM. thses program instruction consist of binary machine code instructions directly executable by the CPU.
-
the constrol unit inside the CPU initiates the process of program execution by loading these instructions one by one from RAM to the CPU’s internal memory unit which consist of high speed memory(Registers and CACHE L1 memory).
-
the CPU makes use of differnt types of high speed internal memory registers during the various stages of program execution.
-
The CPU’s decode unit interprets these program instruction as per the processor’s instruction set architecture and performs the required operations on the data. the result is then sent to the main memory for further action.
-
the processed data(result) from the main memory RAM can be either sent to the output device(printer) OR could be sent to the permanent storage device
what is a program instruction?
-
A computer program is basically a list of instruction or statements that directs the computer hardware to perform a specific task as specified in the program instructions.
-
there are many programming languages available to a programmer but the computer basically understands only a program in machine code binary. therefore all the computer programs are eventually must be translated to machine code instructions which computer CPU can interprets and execute.
-
Machine code(binary code) is only form of program instruction that the computer hardware can understand and execute directly. all other forms of computer program written in different language must be first translated into machine code in order to be executed by the Hardware(CPU)
-
the Compiler is a special program used to convert high level program to low level machine code. thses machine code instructions are fetched from the memory and executed by the CPU.
-
Each CPU’s internal design is based on some standard micro architecture which is implemented by the CPU manufacuring companies which is knwon as “ISA(instruction Set architecture)”
-
an instruction is a binary pattern designed inside a CPU to perform a specific operation
-
the entire group of instructions that is implemented and supported by the microprocessor is called as “instruction Set”. for Example ISA 8085 has 246 instructions.
-
the program instruction can be classidied in to five broad categories
- Data transfer Instruction
- Arithmetic Instructions
- Logicl instructions
- branching instructions
- control instruction
-
an instruction set is a list of all the instructions that a processor can decode and execute. such instructions include arithmetic operations such as add and substract, logical operaions such as AND or OR and NOT, data instruction such as move, input and output and control instructions such as goto, call, and return.
-
the instruction set specifies the opcodes(machine language operation codes) that are used to identify each instruction.
-
ISC generally break down into two main approaches
- RISC
- CISC
-
A single instruction can take more than one memory location to store. for example as shown in the diagram instruction 1,2,3,4 needs two memory locations each to store a part of the instruction in the main memory (RAM). whereas the instruction 5 will need only one memory location as it has only opcode
-
the computer program loaded by the operating system in to the RAM. the executable file of the program consist of number of instructions and each instruction has unique address in the memory which CPU can refer to while fetching the instructions.
-
Each instruction is represented by 8 bits binary value. this 8 bits binary value is called OPCODE or instruction byte.
-
the Machine instructions to be stored in the RAM must be encoded in binary as a sequence of 0’s and 1’s because all storage devices consist of a set of locations that can have one of two possible states(0,1). these instructions are fetched by the CPU one by one to execute the program.
-
the machine instruction is a binary representation of the instruction for the CPU in machine language (0 and 1) to perform a specific taks such as Add, divide, increment etc
- Each Machine instruction has tow parts
- OPCODE : Operation Code
- OPERAND : Address of DATA / DATA
- the OPCODE portion of the machine instruction specifies the operation to be performed by the ALU on the OPERAND as per instruction set of the CPU.
-
An OPCODE is a single instruction that can be executed by the CPU. in machine language it is a bianry or hexadecimal value such as “B6” loaded into the instruction register.
-
a simple example of a machine instruction ADD# 45 that we can give to a computer. this is called machine code instructions.
-
the machine code allows computers to perform the most basic, but essential tasks. the CPU makes use of the Accumulator Register which is used to stroe the intermediate results of all our calculations






Comments