22. Compose of Motherboard
19 May 2020 | CS
Motherboard
-
the motherboard is a largest PCB(printed CIrcuit board) in a computer system where some of most imporatant components(such as Processor and RAM modules) are connected with each other. motherboard also acts as junction(汇合处) for all other components.
-
the list of the number of components on the motherboard is pretty long and also depends upon the motherboard architecture. however, some components are vital(必不可少的) to the functioning of the system and will be present on all the motherboard
- Clock generator
- the instructions(Fetch->decode->execute->store:machine cycle) executed by the CPU are carried out in a given number of clock cycles and therefore the overall processing speed of the CPU(i.e the speed with which it can execute programs) will be directly related to the number of clock cycles per second. in other words, all other factors being equal, the faster the clock speed, the faster the CPU will operate. this also results considerable amount of heat and thus CPU needs an efficient cooling system.
- CPU socket
- A CPU socket or CPU slot is mechanical component that provide mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board(PCB). this allows the CPU to be replaced without soldering.
- the CPU sockets have retention(保持) clips that apply a constant force and retain the CPU firmly inside the socket. for Processor with a large number of pins, either zero insertion force(ZIP) sockets or lang grid array(LGA) sockets are used instead
- the Processor sockets use a pin grid array(PGA) where pins on the underside of the processor chip connect to holes in the processor socket.
- RAM - Memory Sockets
- RAM is considered to be the main memory for a computer system and each program must be first loaded into the RAM for CPU to initiate its execution.
- the RAM memory is available in modules of standard sizes(500MB, 1GB) and these modules are fitted on the motherboard of a system in slots which has a locking mechanism.
- RAM module must be supported by the motherboard. the maximum RAM supported also depends upon the CPU(32bit OR 64 bit) and the type of the operating system installed on the computer system.
- ROM BIOS
-
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System which is a system software and it is the first start-up program executed by the CPU when computer system is switch on
-
the main purpose of the BIOS program is to provide the bare minimum essential resources(hardware check, initial set of drivers) to the CPU during computer system booting(starting) process till the main operating system is loaded and the system is ready for other Application to run.
- CMOS RAM & Battery
- the CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) is a RAM chip on the MotherBoard which is a Battery powered Semiconductor chip inside computer that stores system information and user preferences.
- the CMOS chip is used to retain the user settings when system is turned off. this information range from the system time and data to system hardware settings preferred by the user.
-
A CMOS/Real-time CLock(RTC) is a computer clock(most often in the form of an integrated circuit) that keeps track of the current time and date
-
Although the term RTC often refers to the devices in personal computers, severs and embedded system. RTC are present in almost any electronic device which needs to keep accurate time.
- Black panel connectors.
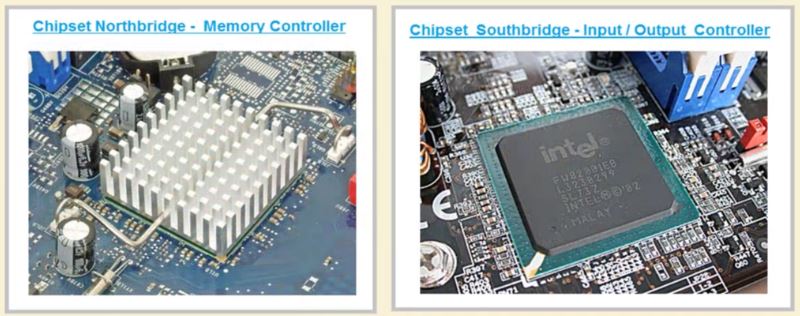
- Chipset(North & South Bridge)
- the Northbridge is an IC(Intergrated Circuit) placed near CPU on the motherboard. the Northbridge is responsible ofr communications between the CPU interface, AGP slot and the main memory(RAM slots)
- when the CPU needs data from RAM, a request is sent to the Northbridge(memory controller). After the request has been recieved, it responds with how long the processor need to wait to fread the memory over the fornt side bus(FSB)
- the CPU can process the instructions at very high rate which is known as CPU speed. However the various internal and extenrnal hardwar components cannot match the CPU speed and therefore we need an intermediate device controller which acts as an interface between the CPU and the varius hardware components.
-
the CPU communicates with different hardware components through the device controller chips installed on the motherboard.
- the southbridge is one of the chipset present on the motherboard which is connected to the processor through NorthBridge. the Southbridge mainly handles the communication ports on the motherboard which are used to connect peripheral devices. therefore, the Southbridge is also commonly referred as Input-Output COntroller.
the Southbridge is connected to the Northbridge through a high speed bus and the Northbridge is connected to CPU through FSB - Front side bus.
- Motherboard Buses
-
the “buses” are group wires on the motherboard that connect the CPU to other components. there are many buses on the motherboard. A bus move instructions, data and the control signals around the system.
-
the speed of a bus is measured in Mhz, the faster the bus, the faster data is communicated the speed of the mother board in defined by the bus speed.
- Expansion slots.
- the expansion card has an edge connectors on the lower edge of the card that precisely fits into the expansion slot on the motherboard. each expansion card has row of electrical contacts on the lower edge that is designed to establish an electrical connection between the motherboard and the electronic on the card which consist of mostly intergrate circuits(IC) chips.
- there are three types of expansion slots found in modern computers
- PCI(peripheral(周边的) component interconnect)
- PCle stands for PCI expresss. PCI express is a new technology that is slowly replacing AGP. PCI express x16 slots can transfer data at 4GBs per seconds, which is about twise faster than AGP 8x slot
- PCI Express slots come in five different sizes and speeds
- PCIe x1,PCIe x2, PCIe x4,PCIe x8,PCIe x16.
- PCIe x16 slots are used for graphics card.
- AGP(Accelerated Graphics Port)
- the AGP stands for Accelerated Graphics Port.
- AGP is an advanced port designed for video cards and 3D accelerators. Designed by intel and introudced in August of 1997. today, AGP slots has been replaced by PCI express slots.
- ISA(Industry Standard architecture)
- they differ primarily in how fast they transfer information between the microprocessor and the expansion board.
Motherboard
Motherboard
-
the motherboard is a largest PCB(printed CIrcuit board) in a computer system where some of most imporatant components(such as Processor and RAM modules) are connected with each other. motherboard also acts as junction(汇合处) for all other components.
-
the list of the number of components on the motherboard is pretty long and also depends upon the motherboard architecture. however, some components are vital(必不可少的) to the functioning of the system and will be present on all the motherboard
- Clock generator
- the instructions(Fetch->decode->execute->store:machine cycle) executed by the CPU are carried out in a given number of clock cycles and therefore the overall processing speed of the CPU(i.e the speed with which it can execute programs) will be directly related to the number of clock cycles per second. in other words, all other factors being equal, the faster the clock speed, the faster the CPU will operate. this also results considerable amount of heat and thus CPU needs an efficient cooling system.
- CPU socket
- A CPU socket or CPU slot is mechanical component that provide mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board(PCB). this allows the CPU to be replaced without soldering.
- the CPU sockets have retention(保持) clips that apply a constant force and retain the CPU firmly inside the socket. for Processor with a large number of pins, either zero insertion force(ZIP) sockets or lang grid array(LGA) sockets are used instead
- the Processor sockets use a pin grid array(PGA) where pins on the underside of the processor chip connect to holes in the processor socket.
- RAM - Memory Sockets
- RAM is considered to be the main memory for a computer system and each program must be first loaded into the RAM for CPU to initiate its execution.
- the RAM memory is available in modules of standard sizes(500MB, 1GB) and these modules are fitted on the motherboard of a system in slots which has a locking mechanism.
- RAM module must be supported by the motherboard. the maximum RAM supported also depends upon the CPU(32bit OR 64 bit) and the type of the operating system installed on the computer system.
- ROM BIOS
-
BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System which is a system software and it is the first start-up program executed by the CPU when computer system is switch on
-
the main purpose of the BIOS program is to provide the bare minimum essential resources(hardware check, initial set of drivers) to the CPU during computer system booting(starting) process till the main operating system is loaded and the system is ready for other Application to run.
- CMOS RAM & Battery
- the CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) is a RAM chip on the MotherBoard which is a Battery powered Semiconductor chip inside computer that stores system information and user preferences.
- the CMOS chip is used to retain the user settings when system is turned off. this information range from the system time and data to system hardware settings preferred by the user.
-
A CMOS/Real-time CLock(RTC) is a computer clock(most often in the form of an integrated circuit) that keeps track of the current time and date
-
Although the term RTC often refers to the devices in personal computers, severs and embedded system. RTC are present in almost any electronic device which needs to keep accurate time.
- Black panel connectors.
- Chipset(North & South Bridge)
- the Northbridge is an IC(Intergrated Circuit) placed near CPU on the motherboard. the Northbridge is responsible ofr communications between the CPU interface, AGP slot and the main memory(RAM slots)
- when the CPU needs data from RAM, a request is sent to the Northbridge(memory controller). After the request has been recieved, it responds with how long the processor need to wait to fread the memory over the fornt side bus(FSB)
- the CPU can process the instructions at very high rate which is known as CPU speed. However the various internal and extenrnal hardwar components cannot match the CPU speed and therefore we need an intermediate device controller which acts as an interface between the CPU and the varius hardware components.
-
the CPU communicates with different hardware components through the device controller chips installed on the motherboard.
- the southbridge is one of the chipset present on the motherboard which is connected to the processor through NorthBridge. the Southbridge mainly handles the communication ports on the motherboard which are used to connect peripheral devices. therefore, the Southbridge is also commonly referred as Input-Output COntroller. the Southbridge is connected to the Northbridge through a high speed bus and the Northbridge is connected to CPU through FSB - Front side bus.
- Motherboard Buses
-
the “buses” are group wires on the motherboard that connect the CPU to other components. there are many buses on the motherboard. A bus move instructions, data and the control signals around the system.
-
the speed of a bus is measured in Mhz, the faster the bus, the faster data is communicated the speed of the mother board in defined by the bus speed.
- Expansion slots.
- the expansion card has an edge connectors on the lower edge of the card that precisely fits into the expansion slot on the motherboard. each expansion card has row of electrical contacts on the lower edge that is designed to establish an electrical connection between the motherboard and the electronic on the card which consist of mostly intergrate circuits(IC) chips.
- there are three types of expansion slots found in modern computers
- PCI(peripheral(周边的) component interconnect)
- PCle stands for PCI expresss. PCI express is a new technology that is slowly replacing AGP. PCI express x16 slots can transfer data at 4GBs per seconds, which is about twise faster than AGP 8x slot
- PCI Express slots come in five different sizes and speeds
- PCIe x1,PCIe x2, PCIe x4,PCIe x8,PCIe x16.
- PCIe x16 slots are used for graphics card.
- AGP(Accelerated Graphics Port)
- the AGP stands for Accelerated Graphics Port.
- AGP is an advanced port designed for video cards and 3D accelerators. Designed by intel and introudced in August of 1997. today, AGP slots has been replaced by PCI express slots.
- ISA(Industry Standard architecture)
- PCI(peripheral(周边的) component interconnect)
- they differ primarily in how fast they transfer information between the microprocessor and the expansion board.











Comments