23. MotherBoard Buses
19 May 2020 | CS
Motherboard BUS
-
all these components are connected to the system with a network of wires and these wires are known as computer buses.
-
A bus is a common communication pathway through which information flows from one computer component to another.
-
the computer bus system is a network of thses buses which physically connect all the components with wires(actual bus wires OR circuit wires on the motherboard). the bus system consist of different types of buses based on the component being connected and function assigned to the bus.
-
A bus can consist of set of wires grouped together as connection wire or a printed circuit boards which carry the data and other commands(instructions) from the CPU to the memory and to various other components connected to the system. the bus performance is an important parameter to access the system performance.
-
All the internal components of a computer system are connected with each other with a network of group of cables. the various system components communicate with each other through this network of group of cables called bus system.
-
the bus consist of group of cables and each of these cable can carry 1Bit(0 or 1) at a time. therefore a bus consist of a group cables so that a group of bits can be sent through the bus.
-
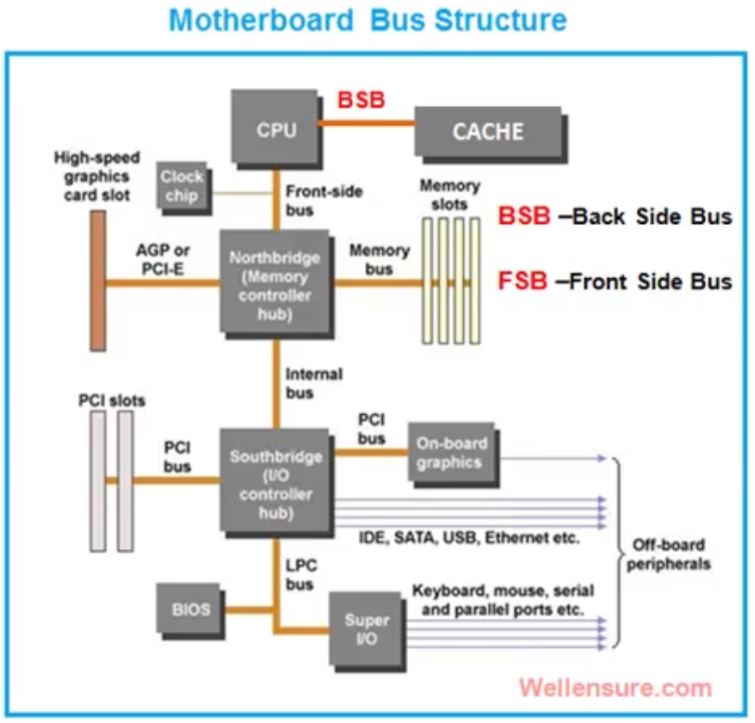
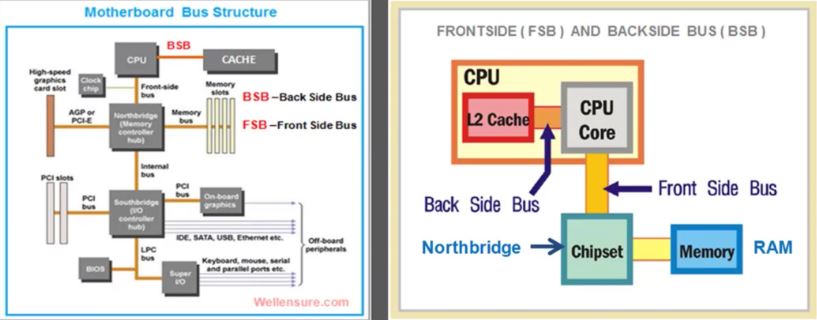
A CPU is connected to internal components such as RAM and external peripheral device by using device controller circuits all put on only two controller chips called chipset. the chipset consist of NorthBridge and Southbridge placed on the motherboard
-
the memory controller NorthBridge and input/out controller Southbridge circuits on the MotherBoard are connected to the main memory RAM and other peripheral devices by uisng system bus wires which carres three type of information
- Memory addresses
- Control Instruction
- Data
-
A bus is a information highway over which information flows and wider the bus, the more information can flow over channel. therefore, a compatible bus width and bus speed is important for the optimal CPU and RAM performance.
-
this is similar to a multi lane wider highway that can carry more cars due to more number of lanes available for traffic. whereas, a single lane road can carry less number of cars are compared to a multi lane road.
- the computer system buses essentially carries three different types of information
- Address Bus - Carries memory location addresses
- Conrtol Bus - Device control instructions from CPU
- Data Bust - Carries data from and to the CPU
- the computer bus consist of group of wires and each wire carry one bit of data(0 or 1). the bus width is the total number of wires present in the bus which indicates total number of bits that the bus can transfer at a time.
-
the size of a bus is known as its bus width, is important because it determines how much data(in bits) can be transmitted at one time. the Larger system bus width significantly improves the processor performance.
-
For example
- A 64 bit bus has 64 cables thus can transmit 64 bits of data at a time
-
the bus speed is another important measure of the bus performance. the bus speed is defined by its frequency expressed in Hz. the bus frequency is the number of data packets sent or received per second. Each time that data is sent or recieved, it is called as one cycle.
-
the bus speed is generally referred to the FSB-Front Side Bus speed which connects the CPU to the memory controller chip NorthBridge.
-
most buses tranmit one bit of data per line, per clock cycle, although newer high-performance buses like AGP may actually move two bits of data per clock cycle, doubling performance. similary older Buses like the ISA bus may take two clock cycles to move on bit which is a significant reduction in the performance
-
the bus bandwidth which is also called as throughput, refers to the total amount of data that can theoretically be transferred on the bus in a given unit of time
-
using the highway analogy, if the bus width is the number of lanes, and the bus speed is how fast the cars are driving, then the bandwidth is the product of these two and reflects the amount of traffic that the channel can concy per second.
-
the Buses are limited by their width in bits. they are usually 8, 16, 32 or 64-bits wide. the bit size of the bus tells us how many bits can be sent by the bus at any one time. Example: A 32-bit bus can send 32bits at once.
-
the system bus that connects the CPU to the memory is called the Front-side bus(FSB). CPU cores share level 2 and level 3 cache memory across the FSB. they will usually connect to Level2 cache through the back-side bus(BSB). the BSB is much faster than the FSB
Motherboard BUS
-
all these components are connected to the system with a network of wires and these wires are known as computer buses.
-
A bus is a common communication pathway through which information flows from one computer component to another.
-
the computer bus system is a network of thses buses which physically connect all the components with wires(actual bus wires OR circuit wires on the motherboard). the bus system consist of different types of buses based on the component being connected and function assigned to the bus.
-
A bus can consist of set of wires grouped together as connection wire or a printed circuit boards which carry the data and other commands(instructions) from the CPU to the memory and to various other components connected to the system. the bus performance is an important parameter to access the system performance.
-
All the internal components of a computer system are connected with each other with a network of group of cables. the various system components communicate with each other through this network of group of cables called bus system.
-
the bus consist of group of cables and each of these cable can carry 1Bit(0 or 1) at a time. therefore a bus consist of a group cables so that a group of bits can be sent through the bus.
-
A CPU is connected to internal components such as RAM and external peripheral device by using device controller circuits all put on only two controller chips called chipset. the chipset consist of NorthBridge and Southbridge placed on the motherboard
-
the memory controller NorthBridge and input/out controller Southbridge circuits on the MotherBoard are connected to the main memory RAM and other peripheral devices by uisng system bus wires which carres three type of information
- Memory addresses
- Control Instruction
- Data
-
A bus is a information highway over which information flows and wider the bus, the more information can flow over channel. therefore, a compatible bus width and bus speed is important for the optimal CPU and RAM performance.
-
this is similar to a multi lane wider highway that can carry more cars due to more number of lanes available for traffic. whereas, a single lane road can carry less number of cars are compared to a multi lane road.
- the computer system buses essentially carries three different types of information
- Address Bus - Carries memory location addresses
- Conrtol Bus - Device control instructions from CPU
- Data Bust - Carries data from and to the CPU
- the computer bus consist of group of wires and each wire carry one bit of data(0 or 1). the bus width is the total number of wires present in the bus which indicates total number of bits that the bus can transfer at a time.
-
the size of a bus is known as its bus width, is important because it determines how much data(in bits) can be transmitted at one time. the Larger system bus width significantly improves the processor performance.
-
For example
- A 64 bit bus has 64 cables thus can transmit 64 bits of data at a time
-
the bus speed is another important measure of the bus performance. the bus speed is defined by its frequency expressed in Hz. the bus frequency is the number of data packets sent or received per second. Each time that data is sent or recieved, it is called as one cycle.
-
the bus speed is generally referred to the FSB-Front Side Bus speed which connects the CPU to the memory controller chip NorthBridge.
-
most buses tranmit one bit of data per line, per clock cycle, although newer high-performance buses like AGP may actually move two bits of data per clock cycle, doubling performance. similary older Buses like the ISA bus may take two clock cycles to move on bit which is a significant reduction in the performance
-
the bus bandwidth which is also called as throughput, refers to the total amount of data that can theoretically be transferred on the bus in a given unit of time
-
using the highway analogy, if the bus width is the number of lanes, and the bus speed is how fast the cars are driving, then the bandwidth is the product of these two and reflects the amount of traffic that the channel can concy per second.
-
the Buses are limited by their width in bits. they are usually 8, 16, 32 or 64-bits wide. the bit size of the bus tells us how many bits can be sent by the bus at any one time. Example: A 32-bit bus can send 32bits at once.
-
the system bus that connects the CPU to the memory is called the Front-side bus(FSB). CPU cores share level 2 and level 3 cache memory across the FSB. they will usually connect to Level2 cache through the back-side bus(BSB). the BSB is much faster than the FSB








Comments