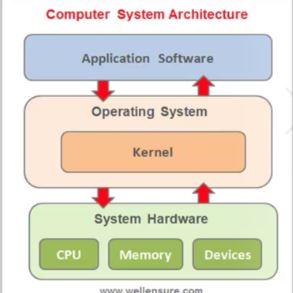
26. Operating System architecture
20 May 2020 | CS
Operating System architecture
-
An operating system structure(OS design approach/architecture) can be classified based on the design approach and implementation by the operating system.
- simple structure OS
- layered approach OS
- Monolithic Approach OS
- Microkernel Approach OS
Monolithic((组织或体系) 庞大而僵化的) Kernel Design
-
A kernel is the central part of an operating system with unrestricted access to all system recourses. it manages the tasks of the computer software and the hardware(most notably(特别) Memory RAM and CPU processing time).
-
there are two types of kernels:
- A Microkernel : which contains only basic functionality
- A Monolithic Kernel : which contains many drivers
-
A computer user never interacts directly with the kernel. the kernel run behind the scenes and user interact with OS GUI interface OR through a command line.
-
The kernel is the most fundamental part and core an operating system. we can think of kernel as the system program which controls all other application program running on the computer system.
-
when the computer starts, it goes through some initialization(booting) function, such as checking memory. the kernel handles all the system recourses such as main memory RAM and CPU processing time. the kernel is responsible for allocating and reallocating the system memory which allows application programs to run.
- the early kernel designs were based on monolithic architecture in which each component of the operating system was contained within the kernel. Applications could communicate directly with any internal component of the operating system and had unrestricted system access. this kind of layered design was perceived(注意到) to be efficient but prone(易于遭受) for crash.
-
the core software components of an operating system are collectively known as the kernel. the kernel has unrestricted access to all the system resources of a computer system.
-
in monolithic architecture, each layer communicates only with the layer immediately above and below it. the lower-level layers provide services to higher-level ones using an interface that hide their implementation
-
although from efficiency point of view the monolithic kernel will perform very well as such operating systems implementing monolithic kernel will be very efficient.
-
the most important drawback of the monolithic kernel is the inability(无能) to isolate the other components in the event if one such component crashes endangering the entire system to crash. thus there was a high risk of damage due to erroneous of malicious(恶毒的) code
-
the summarize, the core components of the operating system are collectively referred as kernel. the kernel has unrestricted access to all the system resources. the kernel also handles all the crucial tasks performed by the operating system.
-
in computer endangering, computer architecture is a set of rules and methods that describes the functionality, system design specifications, organization and implementation details of a computer systems.
-
A computer architecture is a design specifications detailing how a set of software and hardware technology standards interact to form a computer system or a platform. in short, computer architecture refers to how a computer system is designed and what technologies it is compatible with.
-
An operating system is an essential component of the computer system. it is a system program which provides services, resources and runtime environment for application programs running on the computer system.
-
An operating system architecture is a term that specifies the overall structure of the operating system, its logical components and the logical interrelationships of various components that constitute an operating system.
Microkernel Design
-
A Microkernel architecture includes only a very small number of bare minimum essential services within the kernel area as an attempt to keep it small, protected and scalable.
-
the services within Microkernel area typically include the low-level memory management, inter-processes communication and basic process synchronisation to enable processes to cooperate.
-
as compared to a typical kernel, a Microkernel is designed to be compact and performing only the basic functions universal to all computer systems.
-
the Microkernel are designed to be intergraded into different operating systems. therefore, Microkernel are highly modular which makes them protected, extensible, portable and scalable.
-
in Microkernel designs, most operating system components such as process management and device management are placed outside kernel area which execute outside the kernel within a user area with lower level of system access.
-
the Microkernel design OS is considered to be more stable as the device drivers are moved out to the user space so that OS crash could be avoided in the event of faulty drivers.
-
in a Microkernel operating system, the OS kernel deals only with the critical activities such as controlling the memory allocation and CPU processing time and nothing else.
-
Drivers and other functions that monolithic kernels would normally do within the kernel area are moved outside the kernel area to the user area, where they are under control.
-
in Microkernel architecture, the operating system components placed outside the kernel area can fail without causing the entire operating system to crash.
-
however placing operating system components outside the kernel area affects the performance and the downside is an increased level of inter-module communication which can degrade system performance
-
to summarize, the core components of the operating system are collectively referred as kernel. the kernel has unrestricted access to all the system resources. the kernel also handles all the crucial tasks performed by the operating system.
Operating System architecture
-
An operating system structure(OS design approach/architecture) can be classified based on the design approach and implementation by the operating system.
- simple structure OS
- layered approach OS
- Monolithic Approach OS
- Microkernel Approach OS
Monolithic((组织或体系) 庞大而僵化的) Kernel Design
-
A kernel is the central part of an operating system with unrestricted access to all system recourses. it manages the tasks of the computer software and the hardware(most notably(特别) Memory RAM and CPU processing time).
-
there are two types of kernels:
- A Microkernel : which contains only basic functionality
- A Monolithic Kernel : which contains many drivers
-
A computer user never interacts directly with the kernel. the kernel run behind the scenes and user interact with OS GUI interface OR through a command line.
-
The kernel is the most fundamental part and core an operating system. we can think of kernel as the system program which controls all other application program running on the computer system.
-
when the computer starts, it goes through some initialization(booting) function, such as checking memory. the kernel handles all the system recourses such as main memory RAM and CPU processing time. the kernel is responsible for allocating and reallocating the system memory which allows application programs to run.
- the early kernel designs were based on monolithic architecture in which each component of the operating system was contained within the kernel. Applications could communicate directly with any internal component of the operating system and had unrestricted system access. this kind of layered design was perceived(注意到) to be efficient but prone(易于遭受) for crash.
-
the core software components of an operating system are collectively known as the kernel. the kernel has unrestricted access to all the system resources of a computer system.
-
in monolithic architecture, each layer communicates only with the layer immediately above and below it. the lower-level layers provide services to higher-level ones using an interface that hide their implementation
-
although from efficiency point of view the monolithic kernel will perform very well as such operating systems implementing monolithic kernel will be very efficient.
-
the most important drawback of the monolithic kernel is the inability(无能) to isolate the other components in the event if one such component crashes endangering the entire system to crash. thus there was a high risk of damage due to erroneous of malicious(恶毒的) code
-
the summarize, the core components of the operating system are collectively referred as kernel. the kernel has unrestricted access to all the system resources. the kernel also handles all the crucial tasks performed by the operating system.
-
in computer endangering, computer architecture is a set of rules and methods that describes the functionality, system design specifications, organization and implementation details of a computer systems.
-
A computer architecture is a design specifications detailing how a set of software and hardware technology standards interact to form a computer system or a platform. in short, computer architecture refers to how a computer system is designed and what technologies it is compatible with.
-
An operating system is an essential component of the computer system. it is a system program which provides services, resources and runtime environment for application programs running on the computer system.
-
An operating system architecture is a term that specifies the overall structure of the operating system, its logical components and the logical interrelationships of various components that constitute an operating system.
Microkernel Design
-
A Microkernel architecture includes only a very small number of bare minimum essential services within the kernel area as an attempt to keep it small, protected and scalable.
-
the services within Microkernel area typically include the low-level memory management, inter-processes communication and basic process synchronisation to enable processes to cooperate.
-
as compared to a typical kernel, a Microkernel is designed to be compact and performing only the basic functions universal to all computer systems.
-
the Microkernel are designed to be intergraded into different operating systems. therefore, Microkernel are highly modular which makes them protected, extensible, portable and scalable.
-
in Microkernel designs, most operating system components such as process management and device management are placed outside kernel area which execute outside the kernel within a user area with lower level of system access.
-
the Microkernel design OS is considered to be more stable as the device drivers are moved out to the user space so that OS crash could be avoided in the event of faulty drivers.
-
in a Microkernel operating system, the OS kernel deals only with the critical activities such as controlling the memory allocation and CPU processing time and nothing else.
-
Drivers and other functions that monolithic kernels would normally do within the kernel area are moved outside the kernel area to the user area, where they are under control.
-
in Microkernel architecture, the operating system components placed outside the kernel area can fail without causing the entire operating system to crash.
-
however placing operating system components outside the kernel area affects the performance and the downside is an increased level of inter-module communication which can degrade system performance
-
to summarize, the core components of the operating system are collectively referred as kernel. the kernel has unrestricted access to all the system resources. the kernel also handles all the crucial tasks performed by the operating system.





Comments