30. Computer system - BIOS
20 May 2020 | CS
Introduction to Computer system - BIOS
-
the BIOS is a start up program. the main function of the BIOS program is to load the operating system into the system main memory RAM. this process is referred as computer system booting.
-
therefore the CPU’s first job is to locate and initiate the process of loading the operating system when system is switched on. this is done with the help of system utility program BIOS(Basic Input Output System)
-
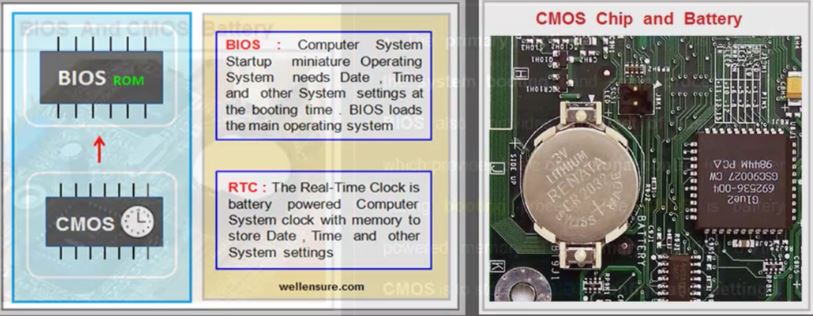
the BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System which is a system software that is placed in a ROM chip(Read Only) on the computer system motherboard as a firmware.
-
the BIOS is the first start-up program executed by the CPU when computer system is switched on. the main job of the BIOS is to locate and load the operating system into the main memory RAM.
-
the operating system is an essential component of the computer system. the main purpose of the BIOS program is to provide the bare minimum essential resources(hardware check, initial set of drivers) to the CPU during computer system booting(starting) process till the main operating system is loaded and the system is read for other applications to run.
-
the BIOS is placed inside a ROM(Read Only Memory) chip as a firmware by the BIOS chip manufacture. the BIOS chip is also known as ROM BIOS. A firmware is a program that is tied to a specific hardware.
-
the BIOS software is hardwired in to the ROM chip and because of this, the contents of the BIOS chip cannot be easily modified OR fail
-
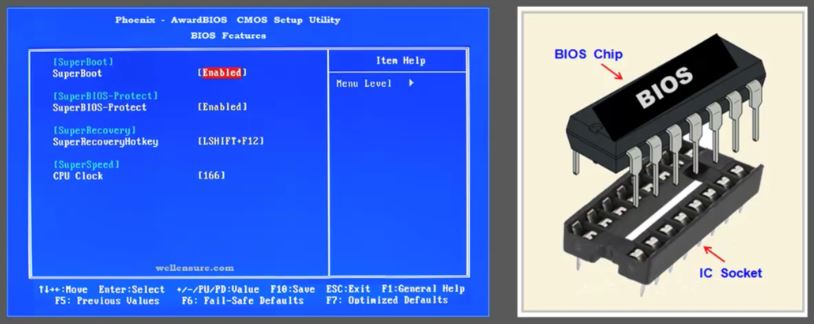
The BIOS chips can be easily spotted on the motherboard because they usually have “BIOS” written on them as part of a manufacture’s label.
- the BIOS chip is usually inserted in a IC socket on the motherboard. the IC socket allows the replacement of faulty BIOS chip which can easily be removed and replaced with new BIOS chip.
-
the main function of the BIOS is to locate and load the operating system. during the booting process the BIOS needs information such as data, time and other information about user system settings preferences. this information provided by CMOS.
-
the CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) and BIOS together handle an essential process of loading the operating system into the RAM. the BIOS and CMOS together set up and boot the computer system.
-
the primary functions of the BIOS is to handle the system booting and setup process. the BIOS also provides initial set of basic drivers which provides basic operational control to user during booting process. the CMOS is battery powered memory. the primary function of the CMOS is to store the BIOS configuration settings.
-
the BIOS performs following important functions during the computer system booting process
- to check power supply to the computer system.
- to check that essential internal components such as RAM and external peripheral devices are connected and working.
- to initiate the computer system booting sequence.
- to prove initial basic set of drivers.
- to locate the operation system and load into the RAM
- to handover the system control to the operating system once the OS is fully loaded and operational
-
POST : the “Power on self test” tests the computer systems internal hardware for compatibility, connection and ensures that no errors exist before loading the operating systems. only after successful completion of the POST, the bootstrap loader routine on the BIOS chip is invoked to load the operating system. if the POST fails then the computer system will beep different beep codes. After successfully completing the POST, the BIOS then attempt to loads the operating system into the main system memory RAM. the OS is located either on the internal hard disk attached to the computer system or from bootable OS disk in the CD ROM drive. the BIOS will pass the control to the operating system once the it is fully loaded.
-
Bootstrap Loader : locate the operating system. if a capable operating system is located then BIOS will load & pass control it.
- BIOS driver :
- All the external devices attached to the computer system are driven by a special system software called device driver. the operating system communicates with the hardware devices through these drivers whenever application program sends any request to use the device. it is the device driver which is a special system software which actually interacts with the device and get required job done. each device must have a driver to operate the device.
- during the computer system booting process when the operating system is still not loaded, it is the BIOS drivers which provides the initial set of drivers that give the computer basic operational control over your computer’s hardware.
- however, the BIOS handover the control to the operating system once it is loaded.
- the operating system has its own set of device drivers through which the operating system communicates with the devices attached to the computer system.
- some device drivers are required to be installed separately.
- after the operating system is loaded, more elaborate set drivers which are part of the operating system are loaded, which replace the bios basic routines. the BIOS also supports internal services such as the real-time clock
- on start-up, the Bios tests the system and prepares the computer for operation based on the installed hardware and the configuration settings from the manufacturer and user.
- BIOS/CMOS setup :
- configuration program that allows user to configure hardware settings including system settings such as computer passwords, time and date.
- this configuration utility program can be accessed just before the booting process is initiated by the CPU by pressing specific key such as escape key or predefined function key depending upon the computer system.
- the BIOS need to be configured when the new internal hardware components is added to the computer system.
- RTC CMOS
-
A real-time clock(RTC) is a battery-powered clock that is included in a microchip on a computer motherboard. this microchip is usually sperate from the microprocessor and other chips. the RTC is often simply referred to as “The CMOS”
-
A small memory on this microchip stores system description or setup values which includes current time values stored by the real-time clock.
-
when the computer is turned on, the BIOS that is stored in the computer’s read-only memory (ROM) microchip reads the current time from the memory in the chip with the real-time clock
-
the CMOS is also a computer chip on the motherboard, but more specifically, it is a RAM chip. this is a type of memory chip which stores information about the computer components and configuration settings for these components.
-
However, the normal RAM chips lose the information stored in them when power is disconnected once the system is switched off. in order to retain the information in the CMOS chip, a CMOS battery on the motherboard supplies constant power to the CMOS chip
Introduction to Computer system - BIOS
-
the BIOS is a start up program. the main function of the BIOS program is to load the operating system into the system main memory RAM. this process is referred as computer system booting.
-
therefore the CPU’s first job is to locate and initiate the process of loading the operating system when system is switched on. this is done with the help of system utility program BIOS(Basic Input Output System)
-
the BIOS stands for Basic Input Output System which is a system software that is placed in a ROM chip(Read Only) on the computer system motherboard as a firmware.
-
the BIOS is the first start-up program executed by the CPU when computer system is switched on. the main job of the BIOS is to locate and load the operating system into the main memory RAM.
-
the operating system is an essential component of the computer system. the main purpose of the BIOS program is to provide the bare minimum essential resources(hardware check, initial set of drivers) to the CPU during computer system booting(starting) process till the main operating system is loaded and the system is read for other applications to run.
-
the BIOS is placed inside a ROM(Read Only Memory) chip as a firmware by the BIOS chip manufacture. the BIOS chip is also known as ROM BIOS. A firmware is a program that is tied to a specific hardware.
-
the BIOS software is hardwired in to the ROM chip and because of this, the contents of the BIOS chip cannot be easily modified OR fail
-
The BIOS chips can be easily spotted on the motherboard because they usually have “BIOS” written on them as part of a manufacture’s label.
- the BIOS chip is usually inserted in a IC socket on the motherboard. the IC socket allows the replacement of faulty BIOS chip which can easily be removed and replaced with new BIOS chip.
-
the main function of the BIOS is to locate and load the operating system. during the booting process the BIOS needs information such as data, time and other information about user system settings preferences. this information provided by CMOS.
-
the CMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor) and BIOS together handle an essential process of loading the operating system into the RAM. the BIOS and CMOS together set up and boot the computer system.
-
the primary functions of the BIOS is to handle the system booting and setup process. the BIOS also provides initial set of basic drivers which provides basic operational control to user during booting process. the CMOS is battery powered memory. the primary function of the CMOS is to store the BIOS configuration settings.
-
the BIOS performs following important functions during the computer system booting process
- to check power supply to the computer system.
- to check that essential internal components such as RAM and external peripheral devices are connected and working.
- to initiate the computer system booting sequence.
- to prove initial basic set of drivers.
- to locate the operation system and load into the RAM
- to handover the system control to the operating system once the OS is fully loaded and operational
-
POST : the “Power on self test” tests the computer systems internal hardware for compatibility, connection and ensures that no errors exist before loading the operating systems. only after successful completion of the POST, the bootstrap loader routine on the BIOS chip is invoked to load the operating system. if the POST fails then the computer system will beep different beep codes. After successfully completing the POST, the BIOS then attempt to loads the operating system into the main system memory RAM. the OS is located either on the internal hard disk attached to the computer system or from bootable OS disk in the CD ROM drive. the BIOS will pass the control to the operating system once the it is fully loaded.
-
Bootstrap Loader : locate the operating system. if a capable operating system is located then BIOS will load & pass control it.
- BIOS driver :
- All the external devices attached to the computer system are driven by a special system software called device driver. the operating system communicates with the hardware devices through these drivers whenever application program sends any request to use the device. it is the device driver which is a special system software which actually interacts with the device and get required job done. each device must have a driver to operate the device.
- during the computer system booting process when the operating system is still not loaded, it is the BIOS drivers which provides the initial set of drivers that give the computer basic operational control over your computer’s hardware.
- however, the BIOS handover the control to the operating system once it is loaded.
- the operating system has its own set of device drivers through which the operating system communicates with the devices attached to the computer system.
- some device drivers are required to be installed separately.
- after the operating system is loaded, more elaborate set drivers which are part of the operating system are loaded, which replace the bios basic routines. the BIOS also supports internal services such as the real-time clock
- on start-up, the Bios tests the system and prepares the computer for operation based on the installed hardware and the configuration settings from the manufacturer and user.
- BIOS/CMOS setup :
- configuration program that allows user to configure hardware settings including system settings such as computer passwords, time and date.
- this configuration utility program can be accessed just before the booting process is initiated by the CPU by pressing specific key such as escape key or predefined function key depending upon the computer system.
- the BIOS need to be configured when the new internal hardware components is added to the computer system.
- RTC CMOS
-
A real-time clock(RTC) is a battery-powered clock that is included in a microchip on a computer motherboard. this microchip is usually sperate from the microprocessor and other chips. the RTC is often simply referred to as “The CMOS”
-
A small memory on this microchip stores system description or setup values which includes current time values stored by the real-time clock.
-
when the computer is turned on, the BIOS that is stored in the computer’s read-only memory (ROM) microchip reads the current time from the memory in the chip with the real-time clock
-
the CMOS is also a computer chip on the motherboard, but more specifically, it is a RAM chip. this is a type of memory chip which stores information about the computer components and configuration settings for these components.
-
However, the normal RAM chips lose the information stored in them when power is disconnected once the system is switched off. in order to retain the information in the CMOS chip, a CMOS battery on the motherboard supplies constant power to the CMOS chip









Comments