41. Object oriented programming
20 May 2020 | CS
Limitations of Procedural programming
-
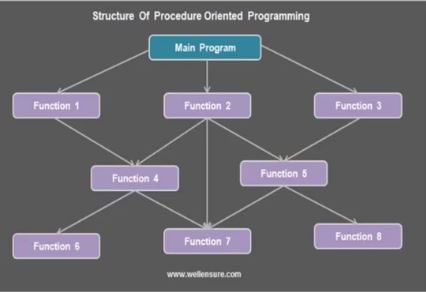
in procedural programming the program code is organized around functions/methods.
-
these function have access to the program data which is mostly global.
-
in procedural programming it is difficult to model the real world problem.
-
in procedural programming the data(program variables) are mostly global and accessible to all the functions. for a large programs it is very difficult to keep the track of the changes in the data being operated upon by many functions. such changes in the data can adversely affect the functionality of other functions.
-
Similarly, when the new data is added all the functions operating on that data also need to be modified accordingly.
-
the most serious limitation of the procedural programming is the tendency for large procedural-based program to turn into “spaghetti-code”
-
in large program number of functions operate on the global data and some programmer working on the same project may write functions to modify the global data which adversely affect the functionality of the other functions.
Object Oriented Programming Design Concepts
-
the OOP is a programming style that is associated with some fundamental design the concepts which govern the manner in which a program code is organized and written in OOP
-
these design concepts are concept of Class and Object. there are some other concepts which revolve around concept of class and object that includes inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism(多型现象), Abstractions
- OOP is an approach to software application development where all application components are treated as objects. An object is a component of a program that knows how to perform certain action and how to interact with other elements of the program. Object are the basic units of Object Oriented Programming.
- An object represents an entity(独立存在物) in the real world such as a person, thing or concept etc. An object is identified by its name. An object need not be tangible but in order to qualify to be an valid object, it must have following characteristics
- Unique identity
- State
- Behaviour
-
in OOP the program code is organized in the form of objects unlike procedural programming where the program code is organized around functions.
- to overcome the limitations of procedural programming, in OOP the program code is organized around data and the ownership of the data is clearly define in terms of functions which allowed to operate on the data. in OOP the data is not allowed to flow freely and only has restricted access. An object binds the data and functions together
-
An object must have unique identity, attributes(current state) and methods(behaviour)
-
Most object have multiple attributes(Properties / Data)
-
the state of one object is NOT dependent upon other objects.
-
Object can have behaviour specific to that object.
-
the OOP program structure decomposes the program in to number of objects. Each object encapsulates the data(attributes OR state) and associated methods(functions) represents object behaviour.
-
During the program execution the objects communicate with each other y sending messages to each other. the object associated methods operate on the data and perform the required operation.
-
In OOP a class is simply a description of an object and the class defines the datatype for an object. A class is a design time entity whereas an object is a runtime entity
- A class is the blueprint, or a plan, or a template that describes the details of an object. A class is the blueprint from which the individual objects are created. Class is composed of three things:
- Class name
- Attributes
- Operations
-
in object oriented programming, a class is basically a user defined data type which consists of data member and member functions. the data members are also called as fields of a class, these fields are the Attributes of this custom defined data type.
-
the member functions are used to define the behaviour of a class and the functionality of a class is defined in these member functions.
-
In OOP the classes are used to define the characteristics and functionality of the different objects of the same data type.
- A class is used as a template to create different objects of class type. for example, a class Vehicle can be used to define the attributes and functions of different types of vehicles. the engineering cloud make as many different types of vehicles from the blueprint of a vehicle class
Limitations of Procedural programming
-
in procedural programming the program code is organized around functions/methods.
-
these function have access to the program data which is mostly global.
-
in procedural programming it is difficult to model the real world problem.
-
in procedural programming the data(program variables) are mostly global and accessible to all the functions. for a large programs it is very difficult to keep the track of the changes in the data being operated upon by many functions. such changes in the data can adversely affect the functionality of other functions.
-
Similarly, when the new data is added all the functions operating on that data also need to be modified accordingly.
-
the most serious limitation of the procedural programming is the tendency for large procedural-based program to turn into “spaghetti-code”
-
in large program number of functions operate on the global data and some programmer working on the same project may write functions to modify the global data which adversely affect the functionality of the other functions.
Object Oriented Programming Design Concepts
-
the OOP is a programming style that is associated with some fundamental design the concepts which govern the manner in which a program code is organized and written in OOP
-
these design concepts are concept of Class and Object. there are some other concepts which revolve around concept of class and object that includes inheritance, Encapsulation, Polymorphism(多型现象), Abstractions
- OOP is an approach to software application development where all application components are treated as objects. An object is a component of a program that knows how to perform certain action and how to interact with other elements of the program. Object are the basic units of Object Oriented Programming.
- An object represents an entity(独立存在物) in the real world such as a person, thing or concept etc. An object is identified by its name. An object need not be tangible but in order to qualify to be an valid object, it must have following characteristics
- Unique identity
- State
- Behaviour
-
in OOP the program code is organized in the form of objects unlike procedural programming where the program code is organized around functions.
- to overcome the limitations of procedural programming, in OOP the program code is organized around data and the ownership of the data is clearly define in terms of functions which allowed to operate on the data. in OOP the data is not allowed to flow freely and only has restricted access. An object binds the data and functions together
-
An object must have unique identity, attributes(current state) and methods(behaviour)
-
Most object have multiple attributes(Properties / Data)
-
the state of one object is NOT dependent upon other objects.
-
Object can have behaviour specific to that object.
-
the OOP program structure decomposes the program in to number of objects. Each object encapsulates the data(attributes OR state) and associated methods(functions) represents object behaviour.
-
During the program execution the objects communicate with each other y sending messages to each other. the object associated methods operate on the data and perform the required operation.
-
In OOP a class is simply a description of an object and the class defines the datatype for an object. A class is a design time entity whereas an object is a runtime entity
- A class is the blueprint, or a plan, or a template that describes the details of an object. A class is the blueprint from which the individual objects are created. Class is composed of three things:
- Class name
- Attributes
- Operations
-
in object oriented programming, a class is basically a user defined data type which consists of data member and member functions. the data members are also called as fields of a class, these fields are the Attributes of this custom defined data type.
-
the member functions are used to define the behaviour of a class and the functionality of a class is defined in these member functions.
-
In OOP the classes are used to define the characteristics and functionality of the different objects of the same data type.
- A class is used as a template to create different objects of class type. for example, a class Vehicle can be used to define the attributes and functions of different types of vehicles. the engineering cloud make as many different types of vehicles from the blueprint of a vehicle class










Comments