1. Two Sum
31 May 2020 | Daily Algorithms
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int k;
int TwoSum(std::vector<int> M, int key)
{
int size_ = M.size();
std::unique_ptr<int[]> hash_table(new int[10]);
for ( m : M)
{
hash_table[m] = 1;
}
for (int i =0; i<=size_;i++)
{
int diff = key - M[i];
if (hash_table[diff] == 1)
{
k=i;
return diff;
}
}
}
int main () {
std::vector<int> A = {2,3,6,8};
int sum =9;
int result_index= TwoSum(A,sum);
cout<<result_index<<" " <<k<<endl;
return 0;
}
설명
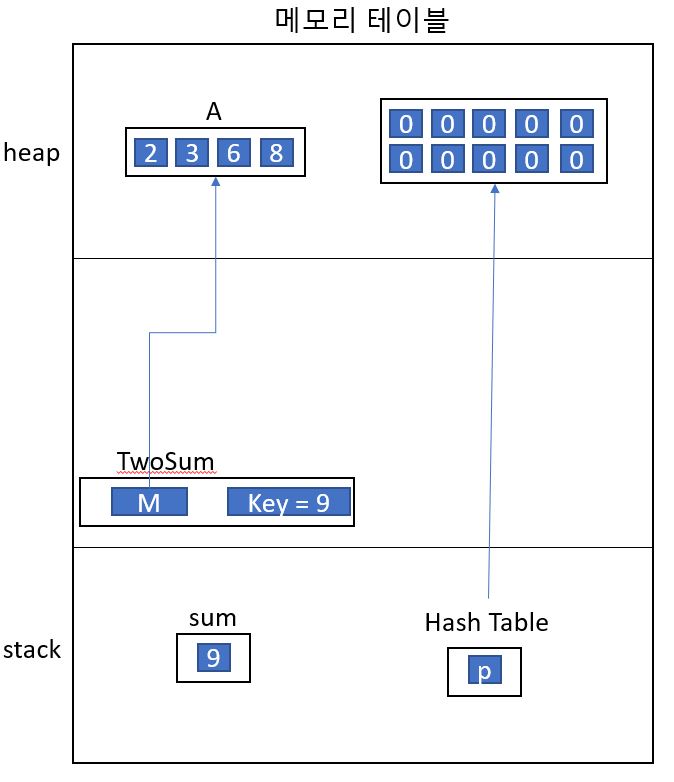
- 벡터를 이용하여 Heap Memory 4개의 어레이에 value가 있다.
- 찾고자하는 합은 9이다.
- 인덱스들을 찾아라
- Hash Table을 이용하여 인덱스 구함
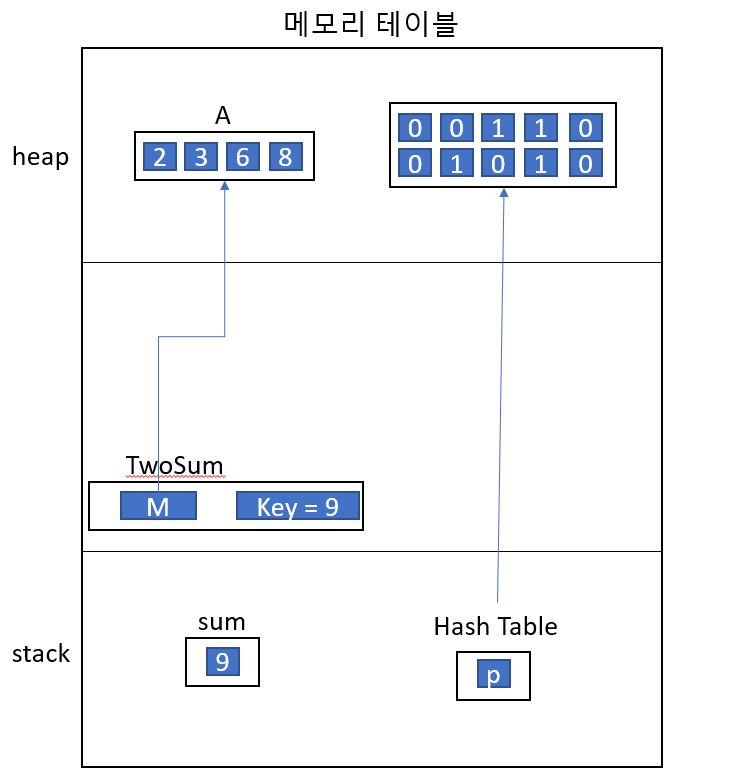
- A의 인덱스 벨류 값들을 Hash_table 행렬에다가 할당을 한다.(1로 표시한다.)
- 즉 A[1] = 2이면, Hash_table[2] = 1로 업데이트 한다.
- 찾고자 하는 인덱스:
- 우리가 찾고자 하는 값은 합이 9(sum)
- 그렇다면 합-어레이[i] = 찾고자 하는 값
- Hash_table[찾고자 하는 값]이 만약 ==1이라면, 즉 A어레이로부터 찾고자 하는 값이 존재한다면
- 인덱스 값들을 return 한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int k;
int TwoSum(std::vector<int> M, int key)
{
int size_ = M.size();
std::unique_ptr<int[]> hash_table(new int[10]);
for ( m : M)
{
hash_table[m] = 1;
}
for (int i =0; i<=size_;i++)
{
int diff = key - M[i];
if (hash_table[diff] == 1)
{
k=i;
return diff;
}
}
}
int main () {
std::vector<int> A = {2,3,6,8};
int sum =9;
int result_index= TwoSum(A,sum);
cout<<result_index<<" " <<k<<endl;
return 0;
}
설명
- 벡터를 이용하여 Heap Memory 4개의 어레이에 value가 있다.
- 찾고자하는 합은 9이다.
- 인덱스들을 찾아라
- Hash Table을 이용하여 인덱스 구함
- A의 인덱스 벨류 값들을 Hash_table 행렬에다가 할당을 한다.(1로 표시한다.)
- 즉 A[1] = 2이면, Hash_table[2] = 1로 업데이트 한다.
- 찾고자 하는 인덱스:
- 우리가 찾고자 하는 값은 합이 9(sum)
- 그렇다면 합-어레이[i] = 찾고자 하는 값
- Hash_table[찾고자 하는 값]이 만약 ==1이라면, 즉 A어레이로부터 찾고자 하는 값이 존재한다면
- 인덱스 값들을 return 한다.

Comments