9.Queue
09 May 2020 | Data structure_1
Introduction
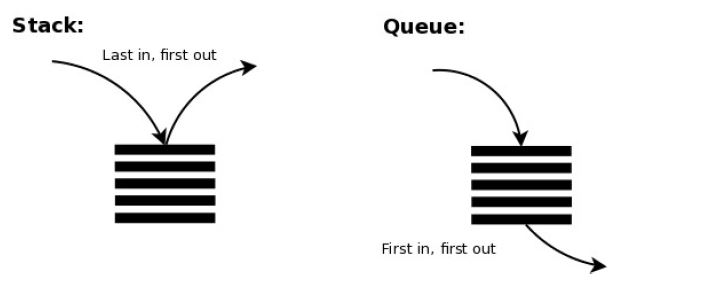
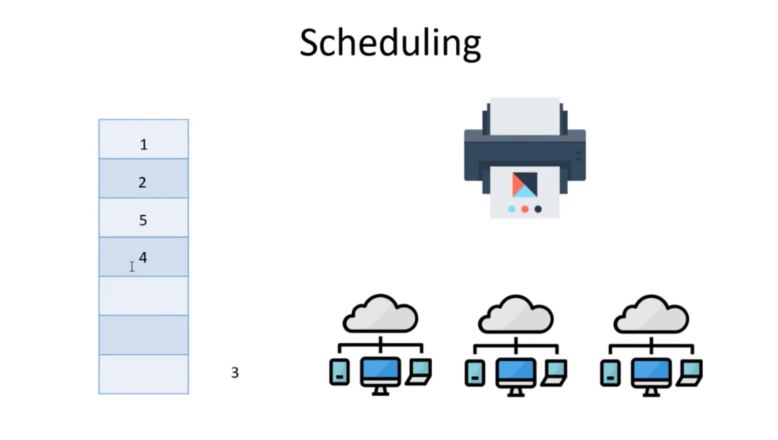
- A queue is similar to a stack, but with one large difference, insertions and deletions take part from separate ends.
Why is it Important?
- Queues, just like stacks, are used for a variety of different tasks throughout computer science. They are great for processing data where order is important, like CPU operations, or tree traversals.
Lesson Notes
- A queue and a stack are very similar, except that a queue inserts and deletes from separate sides. This creates a data structure that is a lot like a line/queue to buy tickets for a concert. Everyone lines up near the box office. The first one that arrives is the first one that is served. The last one to arrive is the last one that gets served.
-
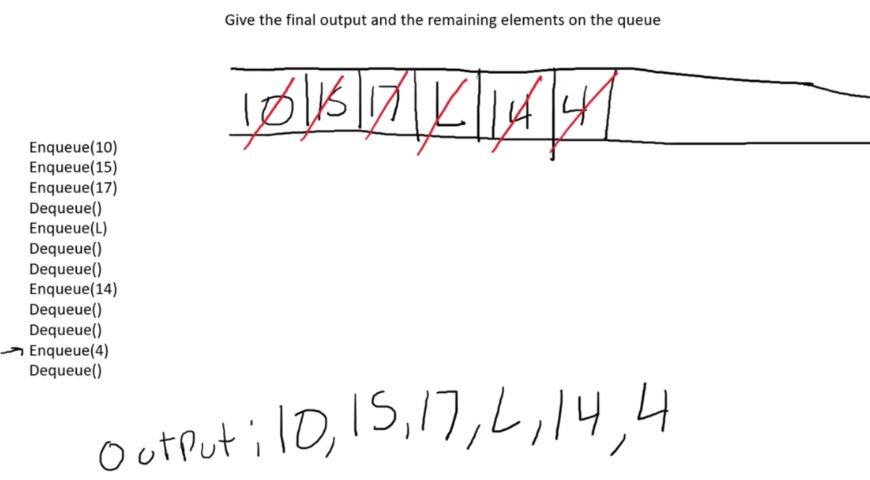
This creates a “First In First Out” relationship with the data. Where in a stack there is a chance the first element could never get touched, in a queue it is a lot more “fair”. The most recent to come in will not be removed until every piece of data that was there before it is removed.
-
The naming convention for removing and adding to a queue are typically dequeue and enqueue, respectively. However, it isn’t uncommon to see pop and push used for a queue as well.
Stack and Queue Run Benefits?
-
Why use a stack or queue, what makes them special? In computer science, modeling is very important. Through modeling and abstraction we can take a machine that only does 1’s and 0’s and turn it in to anything we want.
-
Stacks and queues are just another example of this abstraction. It’s just another layer of rules to add onto a pre-existing structure, so that we can control the data in a slightly different manner.
-
Stacks are widely used in almost every aspect of computer design. Just through reading your email, hundreds of stacks are probably being implemented. Same with queues. Processors love queues as they give it a linear set of instructions to execute.
Stack and Queue Run Times
-
Now, let’s take a look at some run times associated with these data structures.
-
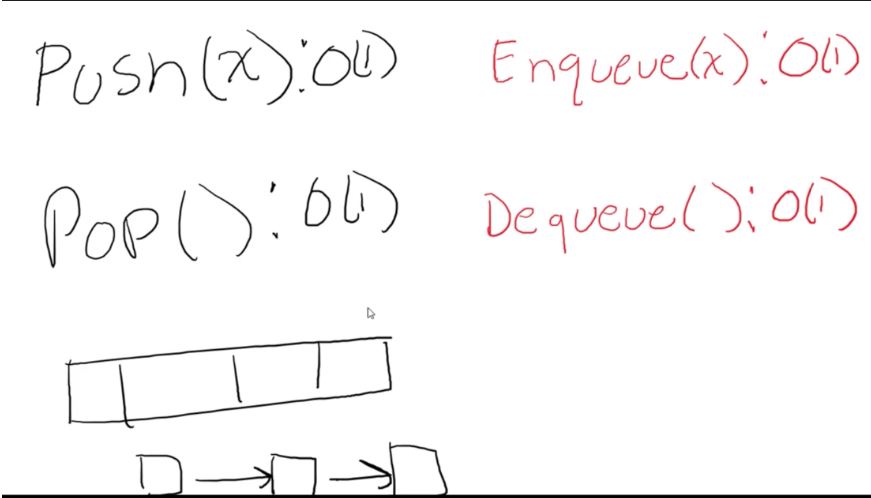
Because these data structures are so specialized, we can actually get O(1) run time on all operations of both stacks and queues. This is because we are only accessing the “ends” of the data structures. So we don’t have to worry about trying to get to the middle.
-
Linked lists are usually best for these structures, as they can expand indefinitely
-
With a stack, we just keep inserting and removing from the front of the data structure. We learned in the previous lessons that both of these operations are O(1).
-
With a queue, we insert to the front and remove from the back. We can do this in O(1) time as well. (We would need to implement a tail pointer for this to work. It’s simply a piece of data that always points to the end of the linked list).
Example
Quiz
Introduction
- A queue is similar to a stack, but with one large difference, insertions and deletions take part from separate ends.
Why is it Important?
- Queues, just like stacks, are used for a variety of different tasks throughout computer science. They are great for processing data where order is important, like CPU operations, or tree traversals.
Lesson Notes
- A queue and a stack are very similar, except that a queue inserts and deletes from separate sides. This creates a data structure that is a lot like a line/queue to buy tickets for a concert. Everyone lines up near the box office. The first one that arrives is the first one that is served. The last one to arrive is the last one that gets served.
-
This creates a “First In First Out” relationship with the data. Where in a stack there is a chance the first element could never get touched, in a queue it is a lot more “fair”. The most recent to come in will not be removed until every piece of data that was there before it is removed.
-
The naming convention for removing and adding to a queue are typically dequeue and enqueue, respectively. However, it isn’t uncommon to see pop and push used for a queue as well.
Stack and Queue Run Benefits?
-
Why use a stack or queue, what makes them special? In computer science, modeling is very important. Through modeling and abstraction we can take a machine that only does 1’s and 0’s and turn it in to anything we want.
-
Stacks and queues are just another example of this abstraction. It’s just another layer of rules to add onto a pre-existing structure, so that we can control the data in a slightly different manner.
-
Stacks are widely used in almost every aspect of computer design. Just through reading your email, hundreds of stacks are probably being implemented. Same with queues. Processors love queues as they give it a linear set of instructions to execute.
Stack and Queue Run Times
-
Now, let’s take a look at some run times associated with these data structures.
-
Because these data structures are so specialized, we can actually get O(1) run time on all operations of both stacks and queues. This is because we are only accessing the “ends” of the data structures. So we don’t have to worry about trying to get to the middle.
-
Linked lists are usually best for these structures, as they can expand indefinitely
-
With a stack, we just keep inserting and removing from the front of the data structure. We learned in the previous lessons that both of these operations are O(1).
-
With a queue, we insert to the front and remove from the back. We can do this in O(1) time as well. (We would need to implement a tail pointer for this to work. It’s simply a piece of data that always points to the end of the linked list).

Comments