10. Bubble Sort
10 May 2020 | Data structure_1
Introduction
- Bubble Sort is arguably the simplest sorting algorithm. It works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements that are in the wrong order.
Why is it Important?
- A study of sorting algorithms always starts here. This is because the intuition behind Bubble Sort is really easy to understand, and it’s good to analyze why this algorithm is not efficient. We can then use that to move in to the more advanced sorting algorithms.
Lesson Notes
- The algorithm works by “bubbling up” the largest value each time. It does this through simple swaps of data in the array.
-
This creates a “First In First Out” relationship with the data. Where in a stack there is a chance the first element could never get touched, in a queue it is a lot more “fair”. The most recent to come in will not be removed until every piece of data that was there before it is removed.
-
The naming convention for removing and adding to a queue are typically dequeue and enqueue, respectively. However, it isn’t uncommon to see pop and push used for a queue as well.
-
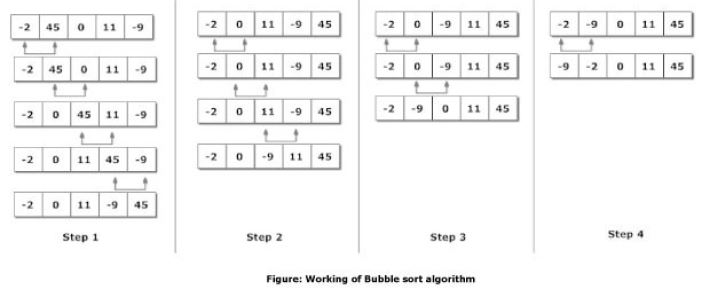
As you can see in the figure above, in each pass through the algorithm it starts at the left side of the array. It grabs the first number and sets it as the maximum. If the next number in the array is smaller than this number, it swaps their position. If the next number is larger, it sets the max to this number, and continues down the array.
-
Items are only swapped with adjacent numbers. So each pass will successfully “bubble” the next largest number up to the top of the array.
-
For example, above in step 1, it starts at the -2 and set’s that to max. It then looks at the 45. Well the 45 is larger than -2, so it makes 45 the new max. It then looks to the right of 45 to the 0. It sees that the 0 is less than 45, so it swaps the two. It does the same with the 11 and the -9. It is now the farthest to the right that it can go, so it stops and starts over again.
-
This program however is not very efficient. On average it will run at O(n^2) time. This is because if the array is completely unsorted, or sorted backwards, there is a good chance it will have to run through the entire array, which has n amount of elements, n amount of times. (Since
only one element is sorted at a time. It has to keep running through the array over and over again)
-
Best Time: Ω(n) : This happens if the array is already sorted. It only has to run through the array one time. However, this is a sorting algorithm, so the chance the data is coming in sorted is very slim.
-
Average Time: Θ(n^2) : This happens because of the fact that it will most likely have to run through the array n times. Since the array is length n, this means that it will be nXn or n^2
-
Worst Time: O(n^2) : This happens because of the fact that it in it’s worst case, it will have to run through the n array n amount of times. Since the array is length n, this means that it will be nXn or n^2. The worst case scenario for bubble sort is if the array comes in in reverse sorted order.
Introduction
- Bubble Sort is arguably the simplest sorting algorithm. It works by repeatedly swapping adjacent elements that are in the wrong order.
Why is it Important?
- A study of sorting algorithms always starts here. This is because the intuition behind Bubble Sort is really easy to understand, and it’s good to analyze why this algorithm is not efficient. We can then use that to move in to the more advanced sorting algorithms.
Lesson Notes
- The algorithm works by “bubbling up” the largest value each time. It does this through simple swaps of data in the array.
-
This creates a “First In First Out” relationship with the data. Where in a stack there is a chance the first element could never get touched, in a queue it is a lot more “fair”. The most recent to come in will not be removed until every piece of data that was there before it is removed.
-
The naming convention for removing and adding to a queue are typically dequeue and enqueue, respectively. However, it isn’t uncommon to see pop and push used for a queue as well.
-
As you can see in the figure above, in each pass through the algorithm it starts at the left side of the array. It grabs the first number and sets it as the maximum. If the next number in the array is smaller than this number, it swaps their position. If the next number is larger, it sets the max to this number, and continues down the array.
-
Items are only swapped with adjacent numbers. So each pass will successfully “bubble” the next largest number up to the top of the array.
-
For example, above in step 1, it starts at the -2 and set’s that to max. It then looks at the 45. Well the 45 is larger than -2, so it makes 45 the new max. It then looks to the right of 45 to the 0. It sees that the 0 is less than 45, so it swaps the two. It does the same with the 11 and the -9. It is now the farthest to the right that it can go, so it stops and starts over again.
-
This program however is not very efficient. On average it will run at O(n^2) time. This is because if the array is completely unsorted, or sorted backwards, there is a good chance it will have to run through the entire array, which has n amount of elements, n amount of times. (Since only one element is sorted at a time. It has to keep running through the array over and over again)
-
Best Time: Ω(n) : This happens if the array is already sorted. It only has to run through the array one time. However, this is a sorting algorithm, so the chance the data is coming in sorted is very slim.
-
Average Time: Θ(n^2) : This happens because of the fact that it will most likely have to run through the array n times. Since the array is length n, this means that it will be nXn or n^2
-
Worst Time: O(n^2) : This happens because of the fact that it in it’s worst case, it will have to run through the n array n amount of times. Since the array is length n, this means that it will be nXn or n^2. The worst case scenario for bubble sort is if the array comes in in reverse sorted order.

Comments