1.Modern C++ Introduction
28 May 2020 | Modern C++
Outline
-
Linux Introduction
-
C++ syntax
what we will learn
- how to work in Linux
- How to write software with modern c++
- core software development techniques
- how to work with image using OpenCV
- how to implement inverse image search
Check out Google Image search for example: https://images.google.come/
why C++? why Linux? Why?
- over 50000 developers surveyed
- nearly half of them use linux
- C++ is the most used systems language(4.5 million users in 2015)
- All companies want C++ in our field.
What is Linux?
- Linux is a free Unix-like OS
- Linux kernel implemented by Linus Torvalds.
- Extremely popular: Android, ChromeOS, servers, supercomputers.
- use any distribution if we have preference
Linux Directory tree
- Tree organization starting with root: /
- There are no volume letters, e.g. C:, D:
- User can only access his/her own folder
Understanding files and folders
- Folders end with / e.g. /path/folder/
- Everything else is files, e.g. /path/file
- Absolute paths start with / while all other paths are relative:
- /home/igor/folder/ — absolute path to a folder
- /home/igor/file.cpp — absolute path to a file
- folder/file — relative path to a file
- Paths are case sensitive:
- filename is different from FileName
- Extension is part of a name:
- filename.cpp is different from filename.png
Linux Terminal
- Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open terminal
- Linux terminal is a very powerful tool
- Most tasks can be done faster from the terminal than from the GUI
Navigating tree from terminal
- Terminal is always in some folder
- pwd: print working directory
- cd
: change directory to
- ls
: list contents of a directory
- Special folders:
- / — root folder
- ~ — home folder
- . — current folder
- .. — parent folder
Structure of Linux commands
Typical structure
${PATH}/command [ options ] [ parameters ]
- ${PATH}/command: absolute or relative path to the program binary
-
- e.g. -h, or –help
-
- e.g. input files, etc.
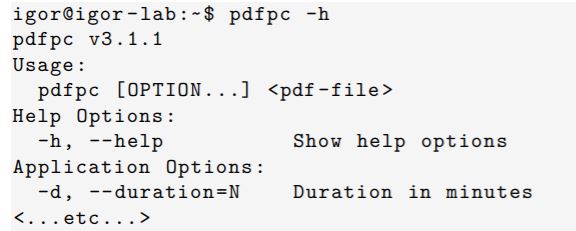
Use help with Linux programs
- man
- exhaustive(철저한) manual on program usage
- command -h
- command –help
- usually shorter help message
Using command completion
Pressing [tab] while typing:
- completes name of a file, folder or program
- “beeps” if current text does not match any file or folder uniquely
Pressing [tab] + [tab] shows all potential matches
Example :
Creating and manipulating files and folders
- mkdir [-p]
— make directory
- Create a folder
(with all parent folders [-p])
- rm [-r]
— remove [recursive]
- Remove file or folder
(With folder contents [-r])
- cp [-r]
— copy
- Copy file or folder from
- mv
— move
- Move file or folder from
Using placeholders
- Can be used with most of terminal commands: ls, rm, mv etc.
Example
Standard input/output channels
- Single input channel: stdin
- Two output channels:
- stdout: Standard output: channel 1
- stderr: Standard error output: channel 2
- Redirecting stdout
- command 1> out.txt
- command » out.txt
- Redirecting stderr
- command 2> out.txt
- Redirect stdout and stderr into a file
- progamm > out.txt 2>&1
- Write stdout and stderr into different files
- progamm 1>stdout.txt 2>stderr.txt
Working with files
- more/less/cat
- Most of the time using cat if enough
- find
-name
- Search for file
in folder
-
, allows wildcards
- grep
- Search for a string
in a file
Chaining commands
- command1; command2; command3
- Calls commands one after another
- command1 && command2 && command3
- Same as above but fails if any of the commands returns a non-zero code
-
command1
command2
command3
- Pipe stdout of command1 to stdin of command2 and stdout of command2 to stdin of command3
- Piping commonly used with grep:
-
ls
grep smth look for smth in output of ls
Canceling commands
- CTRL + C
- Cancel currently running command
- kill -9
- Kill the process with id pid
- killall
- Kill all processes with name pname
- htop (top)
- Shows an overview of running processes
- Allows to kill processes by pressing F9
Command history
- The shell saves the history of commands in the ~/.bash_history file
Installing software
Most of the software is available in the system repository. To install a program in Ubuntu type this into terminal:
- sudo apt update to update information about available packages
- **sudo apt install
** to install the program that you want
- **Use apt search
** to find all packages that provide
- Same for any library, just with lib prefix
where to write C++ code
Good code style
Programs are meant to be read by humans and only incidentally for computers to execute. - Donald Knuth
- Use clang_format to format your code
- use cpplint to check the style
- Following a style guide will save you time and make the code more readable
- We use Google Code Style Sheet
- Naming and style recommendations will be marked by GOOGLE-STYLE tag in slides
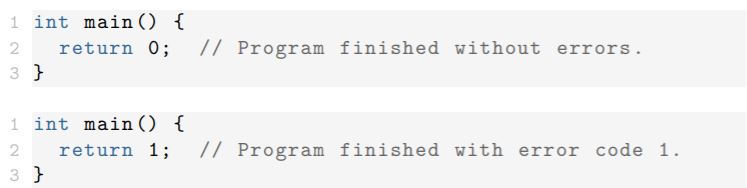
Everything starts with main
- Every C++ program starts with main
- main is a function that returns an error code
- Error code 0 means OK
- Error code can be any number in [1, 255]
#include directive
Two variants:
- #include
— system include files
- #include “file” — local include files
- Copies the content of file into the current file
I/O streams for simple input and output
- Handle stdin, stdout and stderr:
- std::cin — maps to stdin
- std::cout — maps to stdout
- std::cerr — maps to stderr
- #include
to use I/O streams
- #include <bits/strc++> to use I/O streams
- Part of C++ standard library
Compile and run Hello World!
- We understand text
- Computer understands machine code
- Compilation is translation from text to machine code
- Compilers we can use on Linux:
- GCC
- Clang [*] [used in examples]
- Compile and run Hello World example:
Reference
https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/teaching/modern-cpp/
Cpp Core Guidelines:
https://github.com/isocpp/CppCoreGuidelines
Git guide:
http://rogerdudler.github.io/git-guide/
C++ Tutorial:
http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/
Book: Code Complete 2 by Steve McConnell
Outline
-
Linux Introduction
-
C++ syntax
what we will learn
- how to work in Linux
- How to write software with modern c++
- core software development techniques
- how to work with image using OpenCV
- how to implement inverse image search
Check out Google Image search for example: https://images.google.come/
why C++? why Linux? Why?
- over 50000 developers surveyed
- nearly half of them use linux
- C++ is the most used systems language(4.5 million users in 2015)
- All companies want C++ in our field.
What is Linux?
- Linux is a free Unix-like OS
- Linux kernel implemented by Linus Torvalds.
- Extremely popular: Android, ChromeOS, servers, supercomputers.
- use any distribution if we have preference
Linux Directory tree
- Tree organization starting with root: /
- There are no volume letters, e.g. C:, D:
- User can only access his/her own folder
Understanding files and folders
- Folders end with / e.g. /path/folder/
- Everything else is files, e.g. /path/file
- Absolute paths start with / while all other paths are relative:
- /home/igor/folder/ — absolute path to a folder
- /home/igor/file.cpp — absolute path to a file
- folder/file — relative path to a file
- Paths are case sensitive:
- filename is different from FileName
- Extension is part of a name:
- filename.cpp is different from filename.png
Linux Terminal
- Press Ctrl + Alt + T to open terminal
- Linux terminal is a very powerful tool
- Most tasks can be done faster from the terminal than from the GUI
Navigating tree from terminal
- Terminal is always in some folder
- pwd: print working directory
- cd
: change directory to - ls
: list contents of a directory - Special folders:
- / — root folder
- ~ — home folder
- . — current folder
- .. — parent folder
Structure of Linux commands
Typical structure
${PATH}/command [ options ] [ parameters ]
- ${PATH}/command: absolute or relative path to the program binary
-
- e.g. -h, or –help
-
- e.g. input files, etc.
Use help with Linux programs
- man
— manual - exhaustive(철저한) manual on program usage
- command -h
- command –help
- usually shorter help message
Using command completion
Pressing [tab] while typing:
- completes name of a file, folder or program
- “beeps” if current text does not match any file or folder uniquely Pressing [tab] + [tab] shows all potential matches
Example :
Creating and manipulating files and folders
- mkdir [-p]
— make directory - Create a folder
(with all parent folders [-p])
- Create a folder
- rm [-r]
— remove [recursive] - Remove file or folder
(With folder contents [-r])
- Remove file or folder
- cp [-r]
— copy - Copy file or folder from
to
- Copy file or folder from
- mv
— move - Move file or folder from
to
- Move file or folder from
Using placeholders
- Can be used with most of terminal commands: ls, rm, mv etc.
Example
Standard input/output channels
- Single input channel: stdin
- Two output channels:
- stdout: Standard output: channel 1
- stderr: Standard error output: channel 2
- Redirecting stdout
- command 1> out.txt
- command » out.txt
- Redirecting stderr
- command 2> out.txt
- Redirect stdout and stderr into a file
- progamm > out.txt 2>&1
- Write stdout and stderr into different files
- progamm 1>stdout.txt 2>stderr.txt
Working with files
- more/less/cat
- Most of the time using cat if enough
- find
-name - Search for file
in folder -
, allows wildcards
- Search for file
- grep
- Search for a string
in a file
- Search for a string
Chaining commands
- command1; command2; command3
- Calls commands one after another
- command1 && command2 && command3
- Same as above but fails if any of the commands returns a non-zero code
-
command1 command2 command3 - Pipe stdout of command1 to stdin of command2 and stdout of command2 to stdin of command3
- Piping commonly used with grep:
-
ls grep smth look for smth in output of ls
-
Canceling commands
- CTRL + C
- Cancel currently running command
- kill -9
- Kill the process with id pid
- killall
- Kill all processes with name pname
- htop (top)
- Shows an overview of running processes
- Allows to kill processes by pressing F9
Command history
- The shell saves the history of commands in the ~/.bash_history file
Installing software
Most of the software is available in the system repository. To install a program in Ubuntu type this into terminal:
- sudo apt update to update information about available packages
- **sudo apt install
** to install the program that you want - **Use apt search
** to find all packages that provide - Same for any library, just with lib prefix
where to write C++ code
Good code style
Programs are meant to be read by humans and only incidentally for computers to execute. - Donald Knuth
- Use clang_format to format your code
- use cpplint to check the style
- Following a style guide will save you time and make the code more readable
- We use Google Code Style Sheet
- Naming and style recommendations will be marked by GOOGLE-STYLE tag in slides
Everything starts with main
- Every C++ program starts with main
- main is a function that returns an error code
- Error code 0 means OK
- Error code can be any number in [1, 255]
#include directive
Two variants:
- #include
— system include files - #include “file” — local include files
- Copies the content of file into the current file
I/O streams for simple input and output
- Handle stdin, stdout and stderr:
- std::cin — maps to stdin
- std::cout — maps to stdout
- std::cerr — maps to stderr
- #include
to use I/O streams - #include <bits/strc++> to use I/O streams
- Part of C++ standard library
Compile and run Hello World!
- We understand text
- Computer understands machine code
- Compilation is translation from text to machine code
- Compilers we can use on Linux:
- GCC
- Clang [*] [used in examples]
- Compile and run Hello World example:
Reference
https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/teaching/modern-cpp/
Cpp Core Guidelines: https://github.com/isocpp/CppCoreGuidelines
Git guide: http://rogerdudler.github.io/git-guide/
C++ Tutorial: http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/
Book: Code Complete 2 by Steve McConnell











Comments