3. Appendix- Elementary results and notations
03 Oct 2019 | Optimization method
Appendix: Elementary results and notations
1.Derivatives
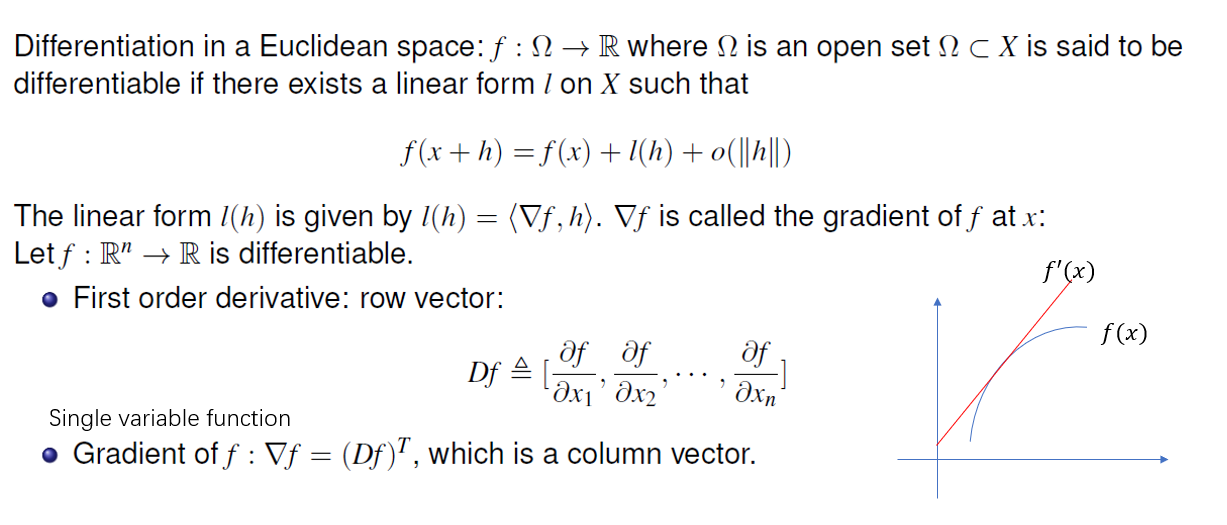
- A gradient represents the slope of the tangent of the graph of the function. It gives the linear approximation of f at a point. It points toward the greatest rate of increase.
2. Hessian
- Let f be twice differentiable.
- A Hessian gives a quadratic approximation of f at a point.
- Gradient and Hessian are local properties that help us recognize local solutions and determine a direction to move at toward the next point.
3. Taylor’s series Expansion
- α is learning rate
Reference
Appendix: Elementary results and notations
1.Derivatives
- A gradient represents the slope of the tangent of the graph of the function. It gives the linear approximation of f at a point. It points toward the greatest rate of increase.
2. Hessian
- Let f be twice differentiable.
- A Hessian gives a quadratic approximation of f at a point.
- Gradient and Hessian are local properties that help us recognize local solutions and determine a direction to move at toward the next point.
3. Taylor’s series Expansion
- α is learning rate



Comments