13. Predicting Revenue Using Simple Linear Regression
13 Sep 2019 | Python
PROBLEM STATEMENT
- You own an ice cream business and you would like to create a model that could predict the daily revenue in dollars based on the outside air temperature (degC). You decide that a Linear Regression model might be a good candidate to solve this problem.
- Data set:
- Independent variable X: Outside Air Temperature
- Dependant variable Y: Overall daily revenue generated in dollars
Step 1 Libraries Import
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
#matplotlib inline, if we execute plot code in notebboot, we can see picture immediatly
Step 2 IMPORT DATASET
IceCream = pd.read_csv("IceCreamData.csv")
IceCream.head(100)
Temperature Revenue
0 24.566884 534.799028
1 26.005191 625.190122
2 27.790554 660.632289
3 20.595335 487.706960
4 11.503498 316.240194
5 14.352514 367.940744
6 13.707780 308.894518
7 30.833985 696.716640
8 0.976870 55.390338
9 31.669465 737.800824
10 11.455253 325.968408
11 3.664670 71.160153
12 18.811824 467.446707
13 13.624509 289.540934
14 39.539909 905.477604
15 18.483141 469.909033
16 25.935375 648.209998
IceCream.tail()
Temperature Revenue
495 22.274899 524.746364
496 32.893092 755.818399
497 12.588157 306.090719
498 22.362402 566.217304
499 28.957736 655.660388
IceCream.describe()
Temperature Revenue
count 500.000000 500.000000
mean 22.232225 521.570777
std 8.096388 175.404751
min 0.000000 10.000000
25% 17.122258 405.558681
50% 22.392791 529.368565
75% 27.740674 642.257922
max 45.000000 1000.000000
IceCream.info()
IceCream.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 500 entries, 0 to 499
Data columns (total 2 columns):
Temperature 500 non-null float64
Revenue 500 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2)
memory usage: 7.9 KB
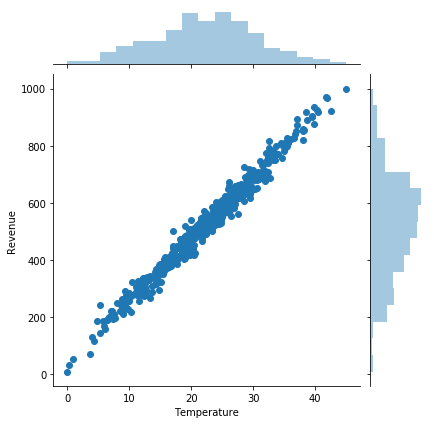
Step 3 Visualize Dataset
sns.jointplot(x='Temperature', y='Revenue', data = IceCream)
# name have to be exactly same as in data dataframe
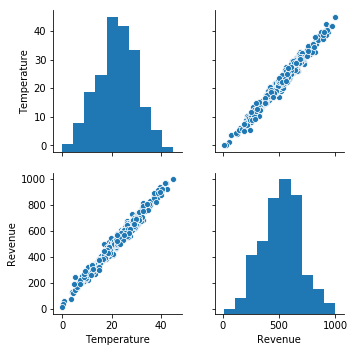
sns.pairplot(IceCream)
#dafaflow nor need here to put X and Y
sns.lmplot(x='Temperature', y='Revenue', data=IceCream)
# plotting linear line wiht line
Step 4 Create Testing And Training Dataset
y = IceCream['Revenue']
X = IceCream['Temperature']
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25)
#define our ratio
#75percent is the train set
Step 5 TRAIN THE MODEL
X_train.shape #(375,)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regressor = LinearRegression(fit_intercept =True)
# we imported the class, 'intercept' meansthat we instantiate with an object
# 'fit_intercept'means we are asking the model to simply update for us not just the slope m but obtain our intercept
# if false, only line only return m value , default will be zero
# intercept 일차함수의 그래프가 축과 만나는 교점의 좌표
regressor.fit(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1),y_train)
#fit the valuable into regression class
print('Linear Model Coefficient (m): ', regressor.coef_) #Linear Model Coefficient (m): [21.4418582]
print('Linear Model Coefficient (b): ', regressor.intercept_) # Linear Model Coefficient (b): 46.867275700132154
# our y intercept is intercepting the at 47
Step 6 Test The model
y_predict = regressor.predict(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1))
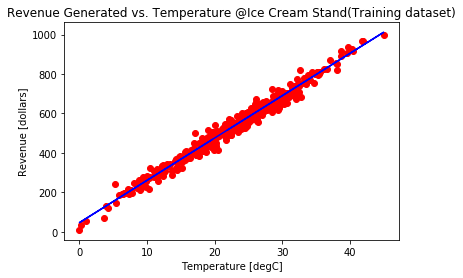
plt.scatter(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1), y_train, color = 'red')
plt.plot(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1), regressor.predict(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'blue')
plt.ylabel('Revenue [dollars]')
plt.xlabel('Temperature [degC]')
plt.title('Revenue Generated vs. Temperature @Ice Cream Stand(Training dataset)')
# VISUALIZE TEST SET RESULTS
plt.scatter(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1), y_test, color = 'red')
plt.plot(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1), regressor.predict(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'blue')
plt.ylabel('Revenue [dollars]')
plt.xlabel('Hours')
plt.title('Revenue Generated vs. Hours @Ice Cream Stand(Test dataset)')
new_x = 30
new_x = np.array(new_x).reshape(1,-1)
y_predict = regressor.predict(new_x)
# 왜냐하면 이미 템프레쳐 트레이닝 데이터가 75퍼로 공부를 시켰기 떄문에
# 30일때 값이 얼마인지 알 수 있다.
y_predict # array([690.1230218])
Sample_T = 35 # this is guessing if temperature 35 in predicting.
Sample_T = np.array(Sample_T).reshape(1,-1)
y_predict = regressor.predict(Sample_T)
y_predict
PROBLEM STATEMENT
- You own an ice cream business and you would like to create a model that could predict the daily revenue in dollars based on the outside air temperature (degC). You decide that a Linear Regression model might be a good candidate to solve this problem.
- Data set:
- Independent variable X: Outside Air Temperature
- Dependant variable Y: Overall daily revenue generated in dollars
Step 1 Libraries Import
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
#matplotlib inline, if we execute plot code in notebboot, we can see picture immediatly
Step 2 IMPORT DATASET
IceCream = pd.read_csv("IceCreamData.csv")
IceCream.head(100)
Temperature Revenue
0 24.566884 534.799028
1 26.005191 625.190122
2 27.790554 660.632289
3 20.595335 487.706960
4 11.503498 316.240194
5 14.352514 367.940744
6 13.707780 308.894518
7 30.833985 696.716640
8 0.976870 55.390338
9 31.669465 737.800824
10 11.455253 325.968408
11 3.664670 71.160153
12 18.811824 467.446707
13 13.624509 289.540934
14 39.539909 905.477604
15 18.483141 469.909033
16 25.935375 648.209998
IceCream.tail()
Temperature Revenue
495 22.274899 524.746364
496 32.893092 755.818399
497 12.588157 306.090719
498 22.362402 566.217304
499 28.957736 655.660388
IceCream.describe()
Temperature Revenue
count 500.000000 500.000000
mean 22.232225 521.570777
std 8.096388 175.404751
min 0.000000 10.000000
25% 17.122258 405.558681
50% 22.392791 529.368565
75% 27.740674 642.257922
max 45.000000 1000.000000
IceCream.info()
IceCream.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 500 entries, 0 to 499
Data columns (total 2 columns):
Temperature 500 non-null float64
Revenue 500 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2)
memory usage: 7.9 KB
Step 3 Visualize Dataset
sns.jointplot(x='Temperature', y='Revenue', data = IceCream)
# name have to be exactly same as in data dataframe
sns.pairplot(IceCream)
#dafaflow nor need here to put X and Y
sns.lmplot(x='Temperature', y='Revenue', data=IceCream)
# plotting linear line wiht line
Step 4 Create Testing And Training Dataset
y = IceCream['Revenue']
X = IceCream['Temperature']
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25)
#define our ratio
#75percent is the train set
Step 5 TRAIN THE MODEL
X_train.shape #(375,)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
regressor = LinearRegression(fit_intercept =True)
# we imported the class, 'intercept' meansthat we instantiate with an object
# 'fit_intercept'means we are asking the model to simply update for us not just the slope m but obtain our intercept
# if false, only line only return m value , default will be zero
# intercept 일차함수의 그래프가 축과 만나는 교점의 좌표
regressor.fit(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1),y_train)
#fit the valuable into regression class
print('Linear Model Coefficient (m): ', regressor.coef_) #Linear Model Coefficient (m): [21.4418582]
print('Linear Model Coefficient (b): ', regressor.intercept_) # Linear Model Coefficient (b): 46.867275700132154
# our y intercept is intercepting the at 47
Step 6 Test The model
y_predict = regressor.predict(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1))
plt.scatter(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1), y_train, color = 'red')
plt.plot(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1), regressor.predict(X_train.values.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'blue')
plt.ylabel('Revenue [dollars]')
plt.xlabel('Temperature [degC]')
plt.title('Revenue Generated vs. Temperature @Ice Cream Stand(Training dataset)')
# VISUALIZE TEST SET RESULTS
plt.scatter(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1), y_test, color = 'red')
plt.plot(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1), regressor.predict(X_test.values.reshape(-1,1)), color = 'blue')
plt.ylabel('Revenue [dollars]')
plt.xlabel('Hours')
plt.title('Revenue Generated vs. Hours @Ice Cream Stand(Test dataset)')
new_x = 30
new_x = np.array(new_x).reshape(1,-1)
y_predict = regressor.predict(new_x)
# 왜냐하면 이미 템프레쳐 트레이닝 데이터가 75퍼로 공부를 시켰기 떄문에
# 30일때 값이 얼마인지 알 수 있다.
y_predict # array([690.1230218])
Sample_T = 35 # this is guessing if temperature 35 in predicting.
Sample_T = np.array(Sample_T).reshape(1,-1)
y_predict = regressor.predict(Sample_T)
y_predict


Comments