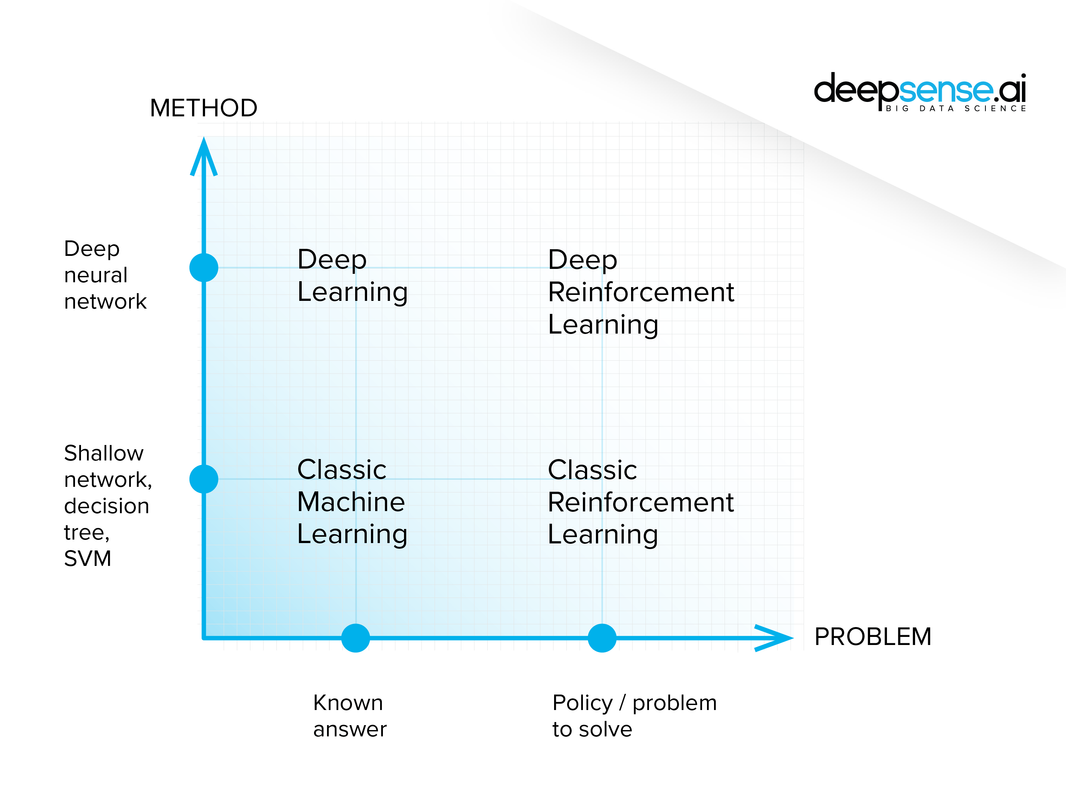
2. Defining Reinforcement Learning
19 Sep 2019 | Reinforcement Learning
What is Reinforcement Learning?
- Humans/ AIs alike never sense the entire world/universe at once
- We have sensors which feed signals to our brain from the environment
- We don’t even know everything that’s going on in a room
- Thus the Sensors limit the amount of information we get
- The measurements we get from these sensors(e.g. sight, sound touch) make up a “state”
- we’ll only discuss finite state spaces
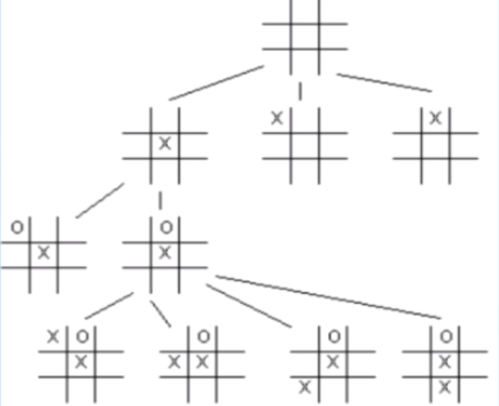
- state spaces with an infinite number of states are possible too
- what’s the # of states?
- if we simplify the problem so that we can keep adding x’s and o’s even after a player gets 3 in a row
- Each Location on the board has 3 possibilities: empty, X, O
- 9 Locations on the Board
- therefore, # states = 3 x 3 … x3 = $ 3^9 $
Recap so far
3 Important Terms
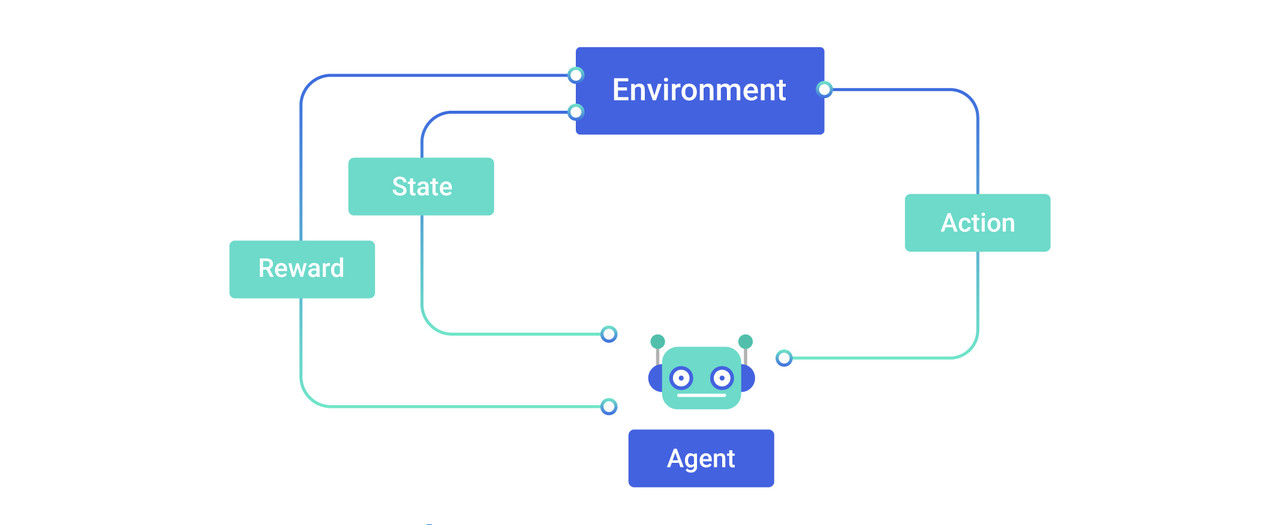
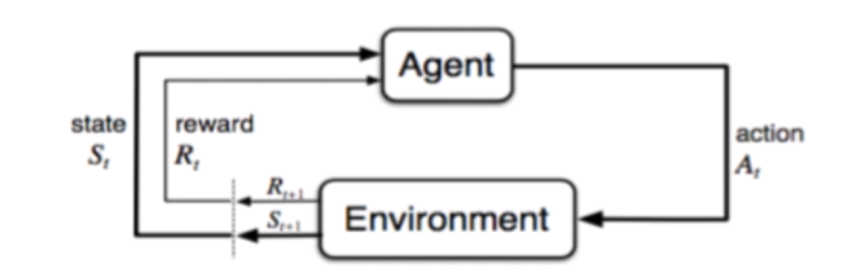
- Agent: thing that sense the environment, thing we’re trying to code intelligence/learning into
- Environment: Real World or simulated world that the agent lives in
- State: Different Configurations of the environment that the agent can sense
- Reward
- this is what differentiates RL from other types of ML
- An agent not only tries to maximize its immediate reward, but future rewards as well
- RL algorithms will find novel ways of accomplishing this
- Alphago: learning unique/unpredictable strategies that led to beating a world champion
- Not intuitive to humans, But Rl can figure it out
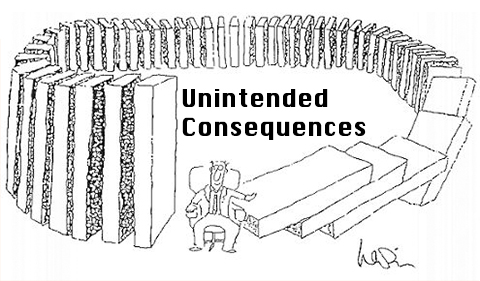
Unintended consequence(의도치 않은 결과)
- possible danger of RL: Unintended consequence
- Commonly repeated ideaL AI could wipe out humanity if it decides that’s the best thing for us(Ex. Minimize human Deaths)
- AI decided that since # humans grows exponentially, that more people will die in the future, then best to destroy everyone now to minimize dying in the future
- Lower level example : robot trying to solve a maze
- Reasonable goal: solve the maze
- Reward = 1 if solved, reward = 0 if not solved
- Possible solution: move randomly until maze is solved
- is that a good strategy? No!
- we never told the AI that it needs to solve the maze efficiently(we always get the reward in the end)
- what about this: reward of -1 for every step taken
- in order to maximize total reward, must minimize # steps
- Note: reward is always a real number
Terms
So far: agent, environment, state, reward
Next : actions
Actions are what an agent does in its environment. (Ex. agent = a 2-D video game character. Action = {up, down, left, right, jump}). we look at finite sets of actions only.
Sar Triples
We often think about (state, action, reward) as a Triple
Notation : (S,A,R)
Timing
- Timing is Important in RL
- Every game is a Sequence of states, actions, rewards.
- Convention(관습): Start in state S(t), take action A(t), receive a reward of R(t+1)
- Reward always result from (s,a) we took at previous time
- S(t), A(t) also brings us to a new state, S(t+1)
- this also makes a triple: [S(t), A(t), S(t+1)]
- Also Denoted as : (s,a,s’)
Summary
- Program the agent to be intelligent
- Agent interacts with its environment by being in a state, taking action based on that state, which brings it to a new state
- Environment gives the agent a reward, can be +ve or -ve(but must be real number)
- Reward is received in next state
Reference:
Artificial Intelligence Reinforcement Learning
What is Reinforcement Learning?
- Humans/ AIs alike never sense the entire world/universe at once
- We have sensors which feed signals to our brain from the environment
- We don’t even know everything that’s going on in a room
- Thus the Sensors limit the amount of information we get
- The measurements we get from these sensors(e.g. sight, sound touch) make up a “state”
- we’ll only discuss finite state spaces
- state spaces with an infinite number of states are possible too
- what’s the # of states?
- if we simplify the problem so that we can keep adding x’s and o’s even after a player gets 3 in a row
- Each Location on the board has 3 possibilities: empty, X, O
- 9 Locations on the Board
- therefore, # states = 3 x 3 … x3 = $ 3^9 $
Recap so far
3 Important Terms
- Agent: thing that sense the environment, thing we’re trying to code intelligence/learning into
- Environment: Real World or simulated world that the agent lives in
- State: Different Configurations of the environment that the agent can sense
- Reward
- this is what differentiates RL from other types of ML
- An agent not only tries to maximize its immediate reward, but future rewards as well
- RL algorithms will find novel ways of accomplishing this
- Alphago: learning unique/unpredictable strategies that led to beating a world champion
- Not intuitive to humans, But Rl can figure it out
Unintended consequence(의도치 않은 결과)
- possible danger of RL: Unintended consequence
- Commonly repeated ideaL AI could wipe out humanity if it decides that’s the best thing for us(Ex. Minimize human Deaths)
- AI decided that since # humans grows exponentially, that more people will die in the future, then best to destroy everyone now to minimize dying in the future
- Lower level example : robot trying to solve a maze
- Reasonable goal: solve the maze
- Reward = 1 if solved, reward = 0 if not solved
- Possible solution: move randomly until maze is solved
- is that a good strategy? No!
- we never told the AI that it needs to solve the maze efficiently(we always get the reward in the end)
- what about this: reward of -1 for every step taken
- in order to maximize total reward, must minimize # steps
- Note: reward is always a real number
Terms
So far: agent, environment, state, reward
Next : actions
Actions are what an agent does in its environment. (Ex. agent = a 2-D video game character. Action = {up, down, left, right, jump}). we look at finite sets of actions only.
Sar Triples
We often think about (state, action, reward) as a Triple Notation : (S,A,R)
Timing
- Timing is Important in RL
- Every game is a Sequence of states, actions, rewards.
- Convention(관습): Start in state S(t), take action A(t), receive a reward of R(t+1)
- Reward always result from (s,a) we took at previous time
- S(t), A(t) also brings us to a new state, S(t+1)
- this also makes a triple: [S(t), A(t), S(t+1)]
- Also Denoted as : (s,a,s’)
Summary
- Program the agent to be intelligent
- Agent interacts with its environment by being in a state, taking action based on that state, which brings it to a new state
- Environment gives the agent a reward, can be +ve or -ve(but must be real number)
- Reward is received in next state
Reference:
Artificial Intelligence Reinforcement Learning

Comments