1. ROBOTIC FUNDAMENTAL
01 Oct 2019 | ROBOTICS
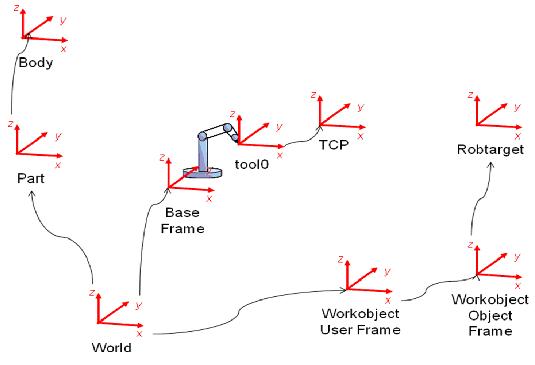
Corrdinate Systems
- he coordinate systems relate to each other hierarchically, where the origin of each coordinate system is defined as a position in one of its ancestries(祖宗). Below are descriptions of commonly used coordinate systems, starting at the top of the hierarchy.
- World coordinate system
- The world coordinate system represents the entire station or robot cell. This is the top of the hierarchy to which all other coordinate systems are related.
- Task frame coordinate system
- The task frame coordinate system is useful to define within a station or robot cell, in particular with multiple robots or mechanisms. One task frame can coordinate the placement of several mechanisms, whereas several task frames are suitable when working with MultiMove Independent.
- Base frame coordinate system
- Each robot in the station has a base coordinate system, which is always located at the base of the robot.
- Tool-centre point (TCP) coordinate system
- The tool center point coordinate system, also called TCP, is the center point of the tool. Several different TCPs may be defined for one robot. All robots have one predefined TCP at the robot’s tool mounting point, called tool0. When a program runs, the robot moves the TCP to the programmed position.
- WorkObject coordinate system
- The workobject normally represents the physical work piece. It is composed of two coordinate systems: the User frame and the Object frame, where the latter is a child to the former.
RobotStudio Developer Center
Robot 특성
- joint axes and TCP related to each other
- the process of finidng position and orientation of the TCP given the actual joint values is called Forward Kinemetic
- Finding out the joint values that correspond to a given TCP position and orientation is solved by Inverse Kinematic
- Robot movements
- point to point (PTP)
- Line
- Circle
- Speed Definition
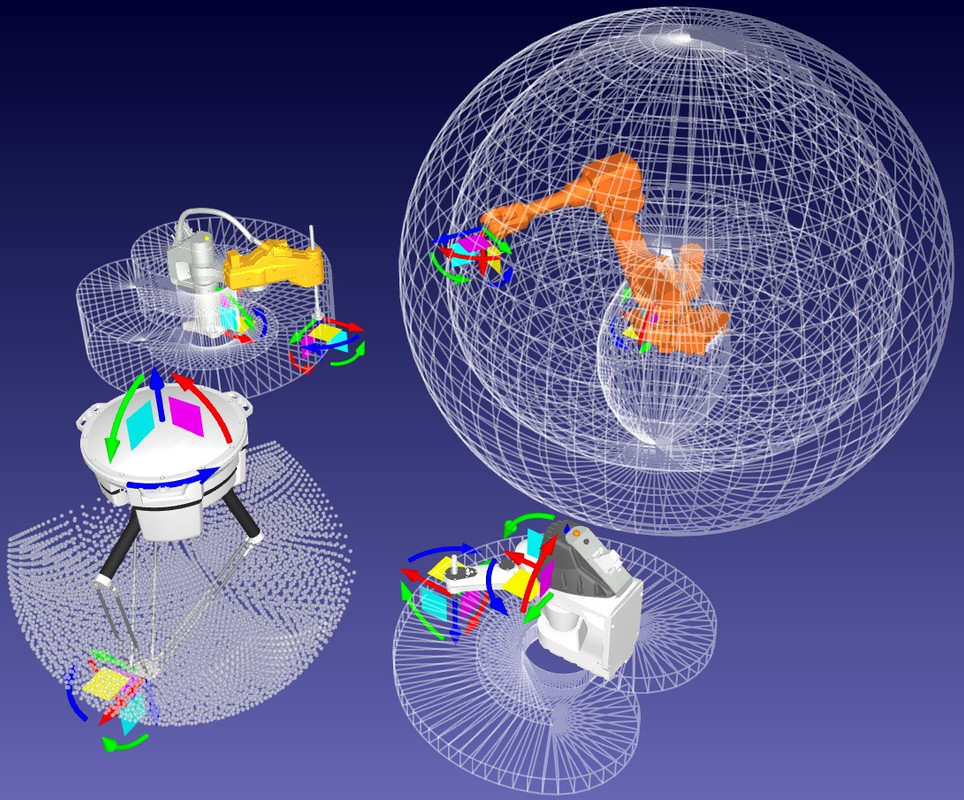
- Work Space
- Safe zone
- Forbidden zones (if the TCP or joint is out of safe zone)
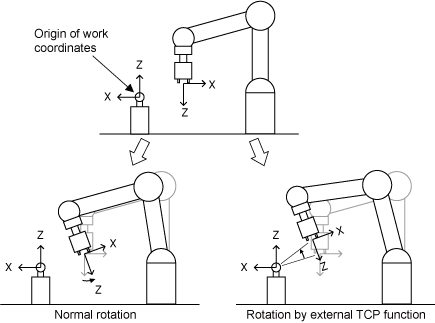
Frame
- A frame is essentially a coordinate system with a specific position and orientation
- Frame are the geometrical foundation of the robot arm and understand how to handle them is a critical systems

- Global coordinate system(GCS)
- Machine coordinate system(MCS)
- Tool coordinate system(TCS)
- Workspace coordinate system(WCS)
- all the programmed points and movements refer to this system (Product coordinate system)
Corrdinate Systems
- he coordinate systems relate to each other hierarchically, where the origin of each coordinate system is defined as a position in one of its ancestries(祖宗). Below are descriptions of commonly used coordinate systems, starting at the top of the hierarchy.
- World coordinate system
- The world coordinate system represents the entire station or robot cell. This is the top of the hierarchy to which all other coordinate systems are related.
- Task frame coordinate system
- The task frame coordinate system is useful to define within a station or robot cell, in particular with multiple robots or mechanisms. One task frame can coordinate the placement of several mechanisms, whereas several task frames are suitable when working with MultiMove Independent.
- Base frame coordinate system
- Each robot in the station has a base coordinate system, which is always located at the base of the robot.
- Tool-centre point (TCP) coordinate system
- The tool center point coordinate system, also called TCP, is the center point of the tool. Several different TCPs may be defined for one robot. All robots have one predefined TCP at the robot’s tool mounting point, called tool0. When a program runs, the robot moves the TCP to the programmed position.
- WorkObject coordinate system
- The workobject normally represents the physical work piece. It is composed of two coordinate systems: the User frame and the Object frame, where the latter is a child to the former. RobotStudio Developer Center
Robot 특성
- joint axes and TCP related to each other
- the process of finidng position and orientation of the TCP given the actual joint values is called Forward Kinemetic
- Finding out the joint values that correspond to a given TCP position and orientation is solved by Inverse Kinematic
- Robot movements
- point to point (PTP)
- Line
- Circle
- Speed Definition
- Work Space
- Safe zone
- Forbidden zones (if the TCP or joint is out of safe zone)
Frame
- A frame is essentially a coordinate system with a specific position and orientation
- Frame are the geometrical foundation of the robot arm and understand how to handle them is a critical systems

- Global coordinate system(GCS)
- Machine coordinate system(MCS)
- Tool coordinate system(TCS)
- Workspace coordinate system(WCS)
- all the programmed points and movements refer to this system (Product coordinate system)

Comments