6. path planning
06 Oct 2019 | ROBOTICS
path planning
- Geometrical description of the robot’s movement in space
- smooth transition between two or more target points
- A unique geometrical path can be described by different time dependent trajectories
- Nomenclature(命名法)
- PTP
- Line
- Circle
- Splines
1. Point to Point(PTP)
- Linear interpolation of joint axes
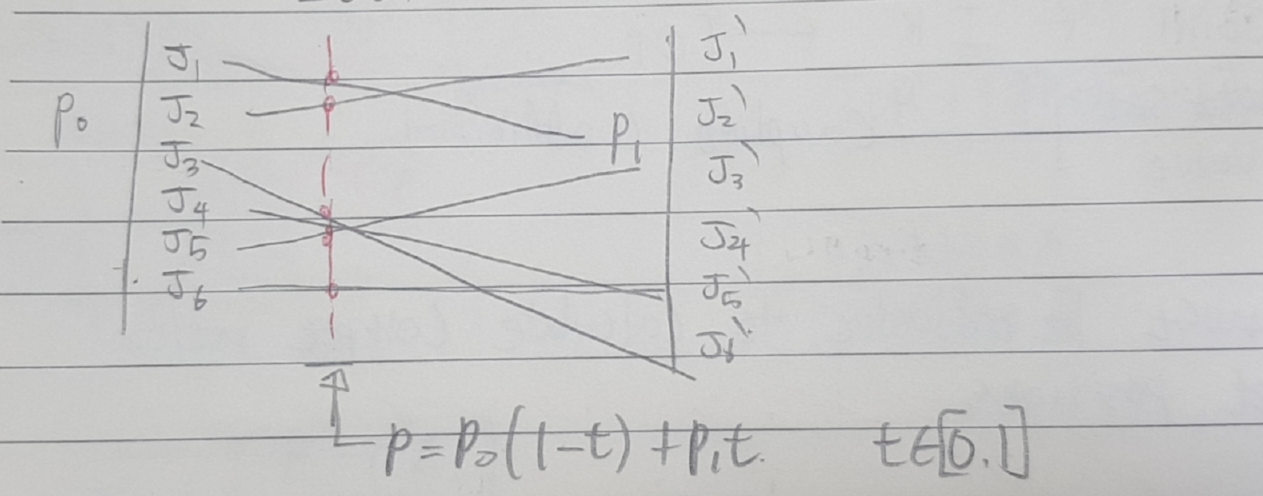
- t is just parameter describing the curve from zero to one only geometrically
- no direct control over TCP position and orientation
- they have no control over the actual path of the end effector of the robot
- cyclic call of the kinematic
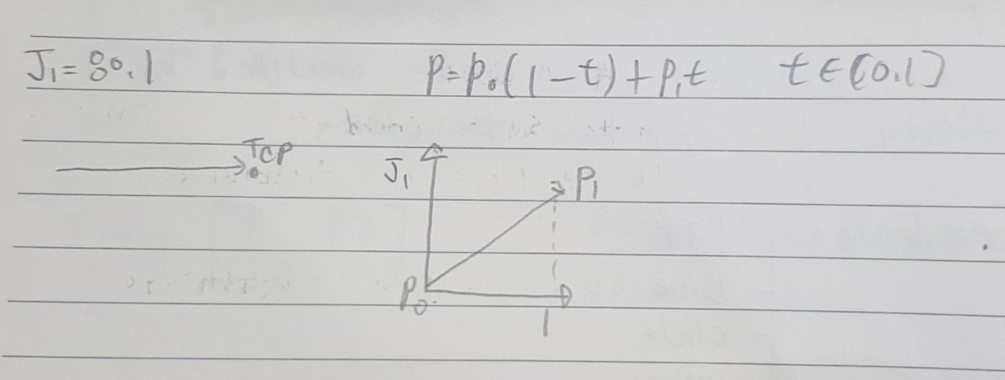
- time-optimal movement(move as fast as joint axes can)
- only movement that can modify joint configuration
2. path-interpolated movements
- orientation cannot be interpolated linearly when using Euler angle
3. Quaternions
- convenient way to express an orientation

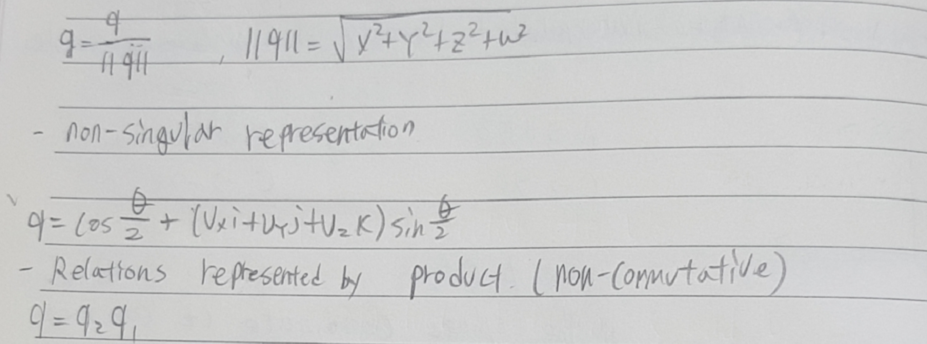
- commutative means that (교환법칙이 성립할 때를 의미함)
- Vs Euler angles
- unique representation of rotation
- can be easily interpolated
- Vs Rotation Matrix
- more compact representation
- easy to interpolate
- do not suffer from numerical approximation
- slerp(Spherical Linear interpolation:구면보간법)
- Optimal(shortest) path between $q_1$ and $q_2$
4. Line and Circle
- Interpolate position linearly
- Circle detail
- point must be non collinear(동일선상)
- N = $v_1$ x $v_2$
- direction N stays the same, only magnitude changed
- normalize N after the product
5. spline(매끄러운 곡선)
- The operator needs a “smooth” path between points
5.1 Practice
- place control point along targets
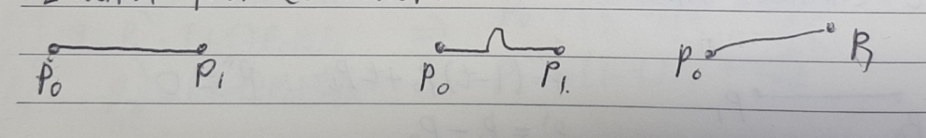
6 transition(변화)
- round edge
- sharp edges are a problem
- smooth geometrical path
- increase path speed
- reduces mechanical wear
7 path length and corrections
- analytical calculation for lines and circles
- numerically calculation for PTP and splines
- external path corrections
- happen at runtime, not planned, not predictable
- typical case : conveyor tracking(increased productivity)
- position limits must be monitored at runtime
- path length changes, so dynamic limits must also be monitored at runtime
path planning
- Geometrical description of the robot’s movement in space
- smooth transition between two or more target points
- A unique geometrical path can be described by different time dependent trajectories
- Nomenclature(命名法)
- PTP
- Line
- Circle
- Splines
1. Point to Point(PTP)
- Linear interpolation of joint axes

- t is just parameter describing the curve from zero to one only geometrically
- no direct control over TCP position and orientation
- they have no control over the actual path of the end effector of the robot
- cyclic call of the kinematic
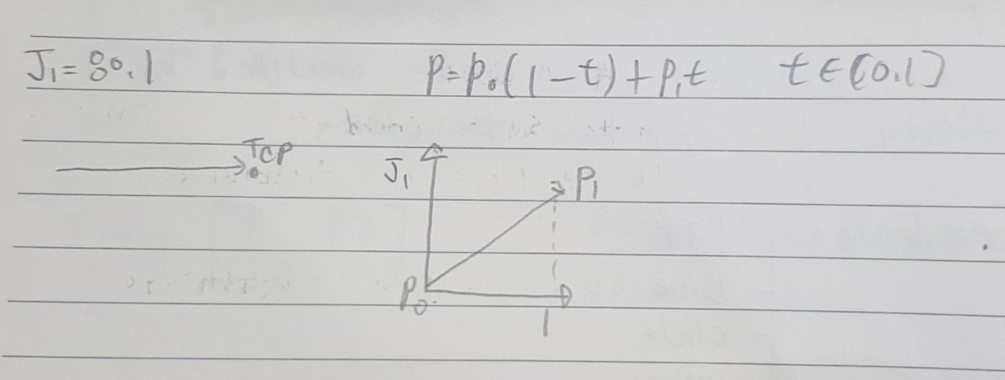
- time-optimal movement(move as fast as joint axes can)
- only movement that can modify joint configuration
2. path-interpolated movements
- orientation cannot be interpolated linearly when using Euler angle
3. Quaternions
- convenient way to express an orientation

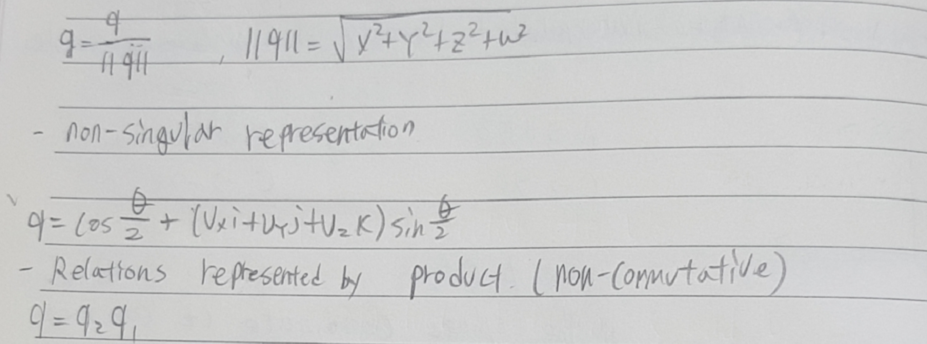
- commutative means that (교환법칙이 성립할 때를 의미함)
- Vs Euler angles
- unique representation of rotation
- can be easily interpolated
- Vs Rotation Matrix
- more compact representation
- easy to interpolate
- do not suffer from numerical approximation
- slerp(Spherical Linear interpolation:구면보간법)
- Optimal(shortest) path between $q_1$ and $q_2$
4. Line and Circle
- Interpolate position linearly
- Circle detail
- point must be non collinear(동일선상)
- N = $v_1$ x $v_2$
- direction N stays the same, only magnitude changed
- normalize N after the product
5. spline(매끄러운 곡선)
- The operator needs a “smooth” path between points
5.1 Practice
- place control point along targets
6 transition(변화)
- round edge
- sharp edges are a problem
- smooth geometrical path
- increase path speed
- reduces mechanical wear
7 path length and corrections
- analytical calculation for lines and circles
- numerically calculation for PTP and splines
- external path corrections
- happen at runtime, not planned, not predictable
- typical case : conveyor tracking(increased productivity)
- position limits must be monitored at runtime
- path length changes, so dynamic limits must also be monitored at runtime





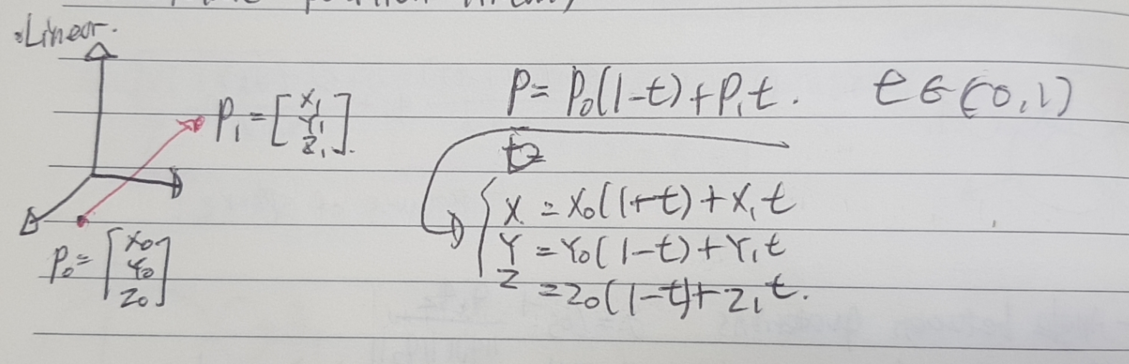

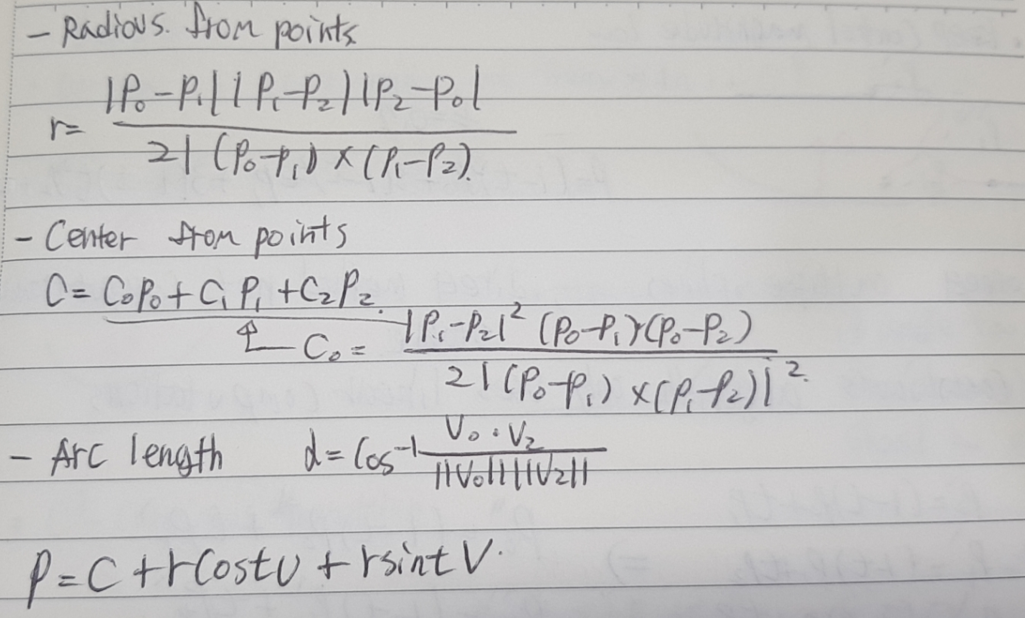



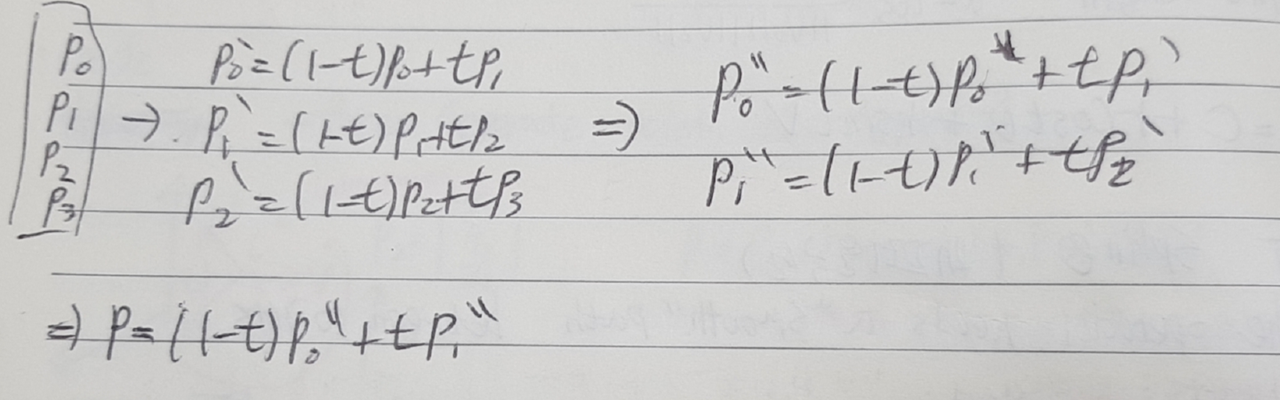


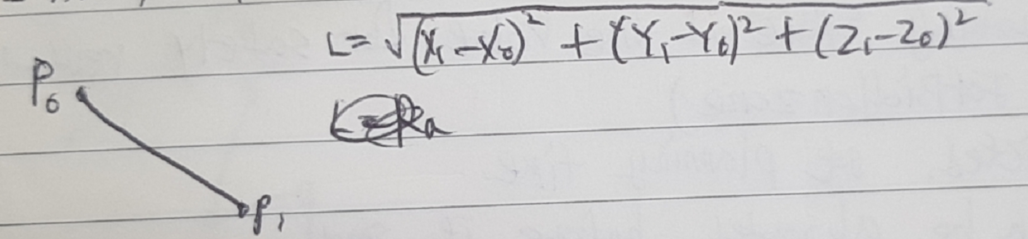

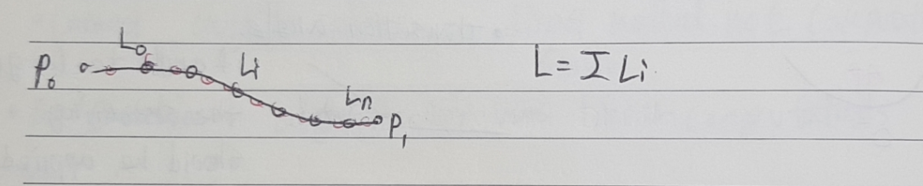
Comments