1. Introduction to Autnomous Navigation
13 May 2020 | ROBOTICS
Autonomous Navigation
- A system in which a number of sub-systems, rather than a single technology, are composed of very complex(一个系统,其中许多子系统(而不是单一技术)由非常复杂的系统组成)
- Algorithm(算法)
- Sensing(感测), perception(知觉), decision(决定)
- Client System (客户系统)
- Composed of OS and hardware platform(由操作系统和硬件平台组成)
- Client Platform (客户平台)
- Provide HD maps and deep learning model training, simulation, data storage, etc.(提供高清地图和深度学习模型训练,模拟,数据存储等)
Sensing
- Commonly used sensors(常用传感器)
- GPS, IMU, LIDAR, Camera, Radar, Sonar
- GPS
- it is used for location estimation(位置估计所需)
- GPS generates data at 10 Hz(GPS会以10 Hz的慢周期生成数据。)
- Not usable in shaded areas such as underground, tunnel, or indoor spaces(不适用于阴影区域,例如地下,隧道或室内空间)
- IMU
- it is used for location estimation(位置估计所需)
- IMU generates data at over 200 Hz(IMU以超过200 Hz的快速周期生成数据)
- Accumulated errors occur over time(随着时间的推移会出现累积的错误)
- Camera
- Used for object recognition and tracking such as lane detection, traffic light detection, and pedestrian detection(用于物体识别和跟踪,例如车道检测,交通信号灯检测和行人检测)
- obatain FOV(Field of View) by multiple HD-class cameras(通过安装多个高清级摄像机来保护FOV)
- 앞 뒤 옆 전방향으로 Frame 얻음
- Lidar
- Measure distance using laser (light) (使用激光(光)测量距离)
- high resolution(高分辨率)
- using in Mapping, location estimation, obstacle avoidance, etc.(使用在于映射,位置估计,避障等)
- Create HD maps to estimate the location of a moving car(创建高清地图以估算行驶中的汽车的位置)
- Detect obstacles around(检测周围的障碍)
- Radar
- Measure the distance using electromagnetic waves(使用电磁波测量距离)
- Used as a last resort to avoid obstacles(作为避开障碍的最后手段)
- Includes speed information as well as vehicle distance(包括速度信息以及车辆距离)
- Can be used in snow, rain and night environments(可在下雪,下雨和夜晚的环境中使用)
- Used to perform urgent operation by transferring the original data to the control device without data processing(用于通过将原始数据传输到控制设备而不进行处理来执行紧急操作)
pose estimation
- Position estimation using GPS and IMU()使用GPS和IMU进行位置估计)
- IMUs have a fast update frequency while low accuracy(IMU的更新周期快而准确性低)
- GPS has a slow update frequency, but relatively high accuracy(GPS更新周期较慢,但准确性较高)
- Combining two values using a Kalman filter(使用卡尔曼滤波器组合两个值)
- Disadvantages of location estimation using GPS(使用GPS进行位置估算的缺点)
- Accuracy error in meters(精度误差(米))
- Noise increases when the signal is reflected off a building(当信号被建筑物反射时,噪声会增加)
- Accurate GPS values cannot be obtained where the sky is obscured(遮盖天空的地方无法获得准确的GPS值)
State Prediction
- what happend when previous state we know, and IMU input comes in.(当我们知道先前的状态并且输入IMU时会发生什么)
Measurement Update
- what if we known state prediction value of, and GPS(Measurement) input comes in(如果我们知道状态预测值和GPS(测量)输入怎么办)
Localization
- Position estimation using camera(使用相机进行位置估计)
- Extract depth information for a scene from a stereo camera(从立体相机中提取场景的深度信息)
- Construct a map by detecting feature points from images(通过检测图像中的特征点来构建地图)
- Disadvantages of Position estimation using a camera
- Sensitive to lighting conditions(对照明条件敏感)
- Dark tunnels, sunset roads, dark nights, bad weather, etc.(黑暗的隧道,落日的道路,漆黑的夜晚,恶劣的天气等。)
- position estimation using Lidar(使用激光雷达进行位置估计)
- using Particle Filter
- Disadvantages of position estimation using a Lidar
- When there is a lot of snow, rain or dust(当下大雪,下雨或灰尘时)
- If there are many suspended particles in the air, noise will occur in the measured value.(如果空气中有许多悬浮颗粒,则测量值中会产生噪音。)
- Needs a sensor fusion process that only collects the advantages of multiple sensors(需要仅融合多个传感器优势的传感器融合过程)
Object detection and tracking
- pupular using Deep learning based object detection and tracking using Lidar point cloud(使用Lidar点云的基于深度学习的对象检测和跟踪)
- Point Cloud Features(点云功能)
- Deep learning based object detection method using point cloud(基于深度学习的基于点云的目标检测方法)
Motion prediction
- Predict the various actions of other drivers and reflect them in their driving(预测其他驾驶员的各种动作并在驾驶中反映出来)
- Create probability models for reachable points of other vehicles(创建其他车辆可到达点的概率模型)
- Find the probability distribution for reachable points(Find the probability distribution for reachable points)
path planning
- Input(输入)
- Environmental map(环境图)
- Robot position(机器人位置)
- starting point(开始点)
- goal point(目的点)
- output
- Route from start point to arrival point(从起点到到达点的路线)
- terminology
- Complete
- This algorithm is complete if it is possible to find a route to the starting and ending points.
- However, there should be a possible route between the starting point and the arrival point.
- Optimal
- This algorithm is optimal if it is possible to find the optimal path between the start and end points.
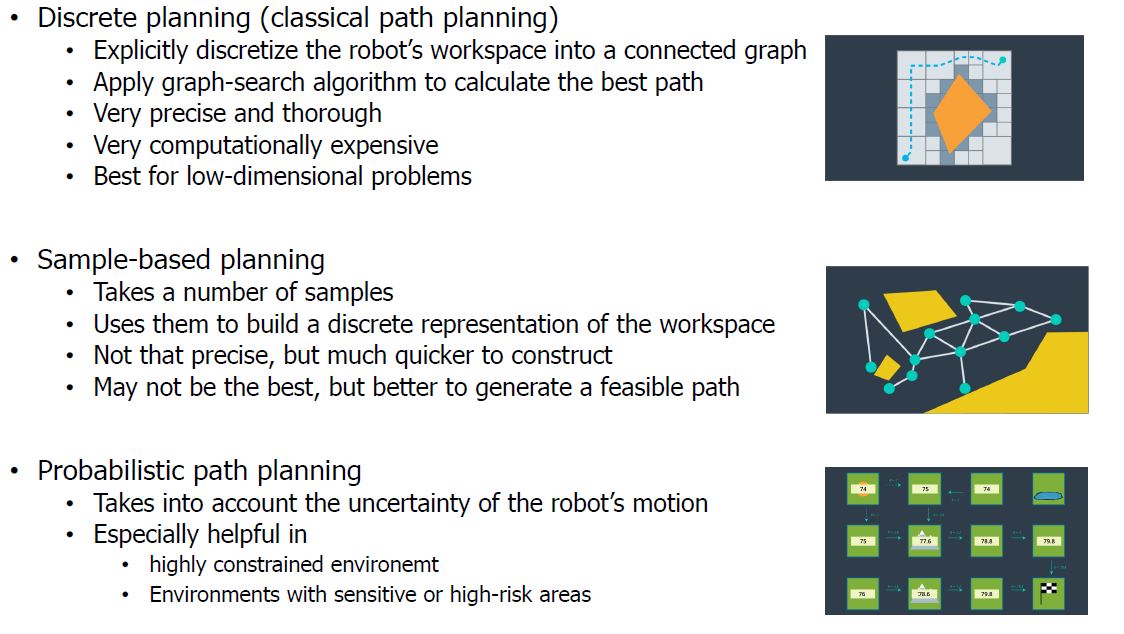
- Methods
- Reference
SLAM KR
Autonomous Navigation
- A system in which a number of sub-systems, rather than a single technology, are composed of very complex(一个系统,其中许多子系统(而不是单一技术)由非常复杂的系统组成)
- Algorithm(算法)
- Sensing(感测), perception(知觉), decision(决定)
- Client System (客户系统)
- Composed of OS and hardware platform(由操作系统和硬件平台组成)
- Client Platform (客户平台)
- Provide HD maps and deep learning model training, simulation, data storage, etc.(提供高清地图和深度学习模型训练,模拟,数据存储等)
Sensing
- Commonly used sensors(常用传感器)
- GPS, IMU, LIDAR, Camera, Radar, Sonar
- GPS
- it is used for location estimation(位置估计所需)
- GPS generates data at 10 Hz(GPS会以10 Hz的慢周期生成数据。)
- Not usable in shaded areas such as underground, tunnel, or indoor spaces(不适用于阴影区域,例如地下,隧道或室内空间)
- IMU
- it is used for location estimation(位置估计所需)
- IMU generates data at over 200 Hz(IMU以超过200 Hz的快速周期生成数据)
- Accumulated errors occur over time(随着时间的推移会出现累积的错误)
- Camera
- Used for object recognition and tracking such as lane detection, traffic light detection, and pedestrian detection(用于物体识别和跟踪,例如车道检测,交通信号灯检测和行人检测)
- obatain FOV(Field of View) by multiple HD-class cameras(通过安装多个高清级摄像机来保护FOV)
- 앞 뒤 옆 전방향으로 Frame 얻음
- Lidar
- Measure distance using laser (light) (使用激光(光)测量距离)
- high resolution(高分辨率)
- using in Mapping, location estimation, obstacle avoidance, etc.(使用在于映射,位置估计,避障等)
- Create HD maps to estimate the location of a moving car(创建高清地图以估算行驶中的汽车的位置)
- Detect obstacles around(检测周围的障碍)
- Radar
- Measure the distance using electromagnetic waves(使用电磁波测量距离)
- Used as a last resort to avoid obstacles(作为避开障碍的最后手段)
- Includes speed information as well as vehicle distance(包括速度信息以及车辆距离)
- Can be used in snow, rain and night environments(可在下雪,下雨和夜晚的环境中使用)
- Used to perform urgent operation by transferring the original data to the control device without data processing(用于通过将原始数据传输到控制设备而不进行处理来执行紧急操作)
pose estimation
- Position estimation using GPS and IMU()使用GPS和IMU进行位置估计)
- IMUs have a fast update frequency while low accuracy(IMU的更新周期快而准确性低)
- GPS has a slow update frequency, but relatively high accuracy(GPS更新周期较慢,但准确性较高)
- Combining two values using a Kalman filter(使用卡尔曼滤波器组合两个值)
- Disadvantages of location estimation using GPS(使用GPS进行位置估算的缺点)
- Accuracy error in meters(精度误差(米))
- Noise increases when the signal is reflected off a building(当信号被建筑物反射时,噪声会增加)
- Accurate GPS values cannot be obtained where the sky is obscured(遮盖天空的地方无法获得准确的GPS值)
State Prediction
- what happend when previous state we know, and IMU input comes in.(当我们知道先前的状态并且输入IMU时会发生什么)
Measurement Update
- what if we known state prediction value of, and GPS(Measurement) input comes in(如果我们知道状态预测值和GPS(测量)输入怎么办)
Localization
- Position estimation using camera(使用相机进行位置估计)
- Extract depth information for a scene from a stereo camera(从立体相机中提取场景的深度信息)
- Construct a map by detecting feature points from images(通过检测图像中的特征点来构建地图)
- Disadvantages of Position estimation using a camera
- Sensitive to lighting conditions(对照明条件敏感)
- Dark tunnels, sunset roads, dark nights, bad weather, etc.(黑暗的隧道,落日的道路,漆黑的夜晚,恶劣的天气等。)
- position estimation using Lidar(使用激光雷达进行位置估计)
- using Particle Filter
- Disadvantages of position estimation using a Lidar
- When there is a lot of snow, rain or dust(当下大雪,下雨或灰尘时)
- If there are many suspended particles in the air, noise will occur in the measured value.(如果空气中有许多悬浮颗粒,则测量值中会产生噪音。)
- Needs a sensor fusion process that only collects the advantages of multiple sensors(需要仅融合多个传感器优势的传感器融合过程)
Object detection and tracking
- pupular using Deep learning based object detection and tracking using Lidar point cloud(使用Lidar点云的基于深度学习的对象检测和跟踪)
- Point Cloud Features(点云功能)
- Deep learning based object detection method using point cloud(基于深度学习的基于点云的目标检测方法)
Motion prediction
- Predict the various actions of other drivers and reflect them in their driving(预测其他驾驶员的各种动作并在驾驶中反映出来)
- Create probability models for reachable points of other vehicles(创建其他车辆可到达点的概率模型)
- Find the probability distribution for reachable points(Find the probability distribution for reachable points)
path planning
- Input(输入)
- Environmental map(环境图)
- Robot position(机器人位置)
- starting point(开始点)
- goal point(目的点)
- output
- Route from start point to arrival point(从起点到到达点的路线)
- terminology
- Complete
- This algorithm is complete if it is possible to find a route to the starting and ending points.
- However, there should be a possible route between the starting point and the arrival point.
- Optimal
- This algorithm is optimal if it is possible to find the optimal path between the start and end points.
- Complete
- Methods
- Reference SLAM KR












Comments