3.Global/Local Variable
12 May 2020 | STL Programming Practice_1
- Global Variable
- defined on top
- initialized with 0
- visible everywhere
- Local Variable
- defined in functions
- initialized randomly
- visible just in the function
Global/local variable Example 1
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Aglobal[3]; // global array of variable
int a ;
void printing()
{
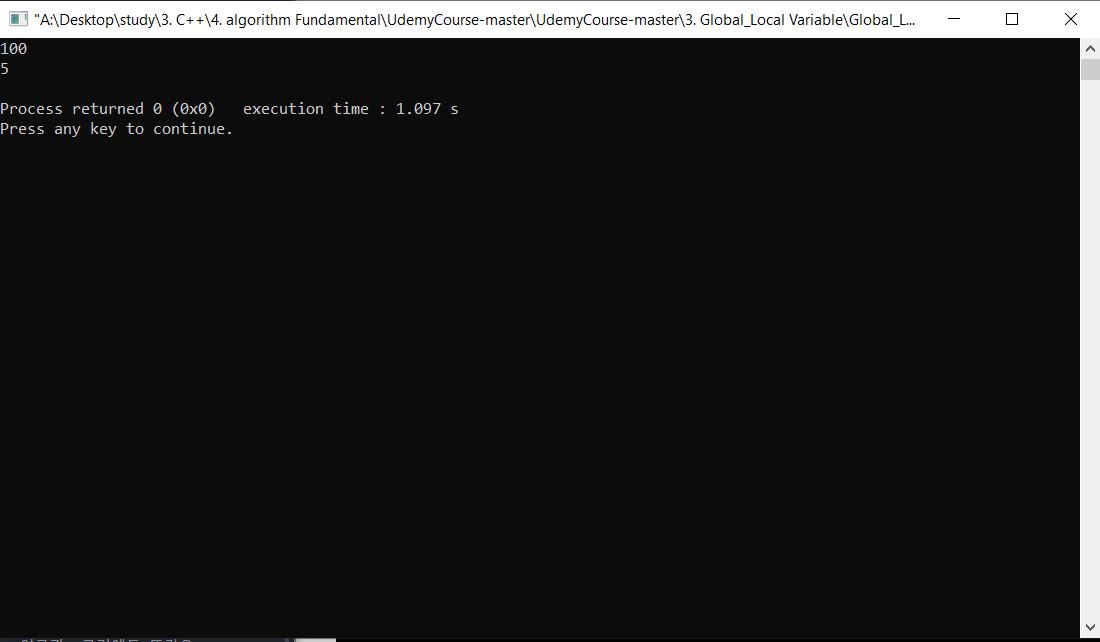
cout<<a;
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[3];
a = 5;
printing();
return 0;
}
- Aglobal is the global array of variable.
- it is allocated in the stack in memory structure as int(4 bits) memory allocation.
- Alocal is the local array of vairble.
- it created in the stack in memory structure as int(4byte) memory allocation.
- printing allocated in the stack in memory structure
-
int a allocated in the stack in memory structure
- 글로벌 variable은 고유의 값으로 local function에서 지정할 수 있고 main function에서 값을 지정할 수 있다.
Global/local variable Example 2
- 그렇다면 만약 global에도 똑같은 variable 이름과, 로컬에도 똑같은 Variable 이름이 있다면 어떻게 되는가
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Aglobal[3]; // global array of variable
int a ;
void printing()
{
cout<<a<<"\n";
int a = 5;
cout <<a<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[3];
a = 100;
printing();
return 0;
}
-
C++는 객체언어로 Sequence대로 출력이 되기 떄문에 ,Global Variable a값이 먼저 출력이 되고 local function에서 지정한 a 값이 출력이 된다.
-
여기서 주의해야할 점은 Local Function에서 지정된 변수 a이의 이름은 Global 변수하고 이름이 같은데, Local Function이 종료가 되면 Allocated 되었던 Local variable 값은 초기화가 되고 Local Funtion이 끝나고 a 변수 값은 Global Variable 값으로 돌아온다
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Aglobal[3]; // global array of variable
int a ;
void printing()
{
cout<<a<<"\n";
int a = 5;
cout <<a<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[3];
a = 100;
printing();
cout<<a<<"\n";
return 0;
}
- after we exit a function, local variable disappear (cannot seen/used in other functions)
Global/local variable Example 3
- Functions parameter are local variables!
- 즉 Function 파라미터들은 로컬 변수로 메모리 구조 Stack에 Allcolate 된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int A[3][5], i ;
void printingRow(int row)
{
for (i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
cout<<A[row][i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
for(i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
printingRow(i);
}
return 0;
}
-
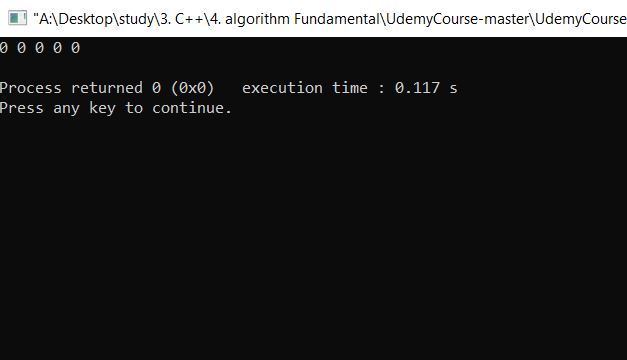
여기서 첫 행밖에 출력이 안되는 이유는 현재 global variable i 만으로 for loop을 사용하기 때문이다
-
더 자세하게 말하자면, 현재 main function에서 i=1이 local function 파라미터로 들어간다. int row로 allocated가 되어서 i=1값이 들어가게 되는데, local function for loop에 global variable i를 쓰면서, 첫번째 행이 끝나고 i의 값은 5가 되어 있다. 그리고 exit local function 했을떄 i의 값은 이미 5가 되어있으므로 main function에 있는 for loop의 조건을 충족하지 못하여 나가게 되는 것이다.
-
그렇기 때문에 Global Variable로 for loop 쓸떄 주의해야 한다.
-
아래와 같이 해결 할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int A[3][5];
void printingRow(int row)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
cout<<A[row][i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
printingRow(i);
}
return 0;
}
Exercise (Array Return)
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void addMatrix (int matrix[][5], int X)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
matrix[i][j]=+X;
}
}
}
void printingmatrix(int matrix[][5])
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[5][5];
// initialize, because local variable value is random when they are allocated. on the other hand, global variable is 0 when they allocated.
for (int i = 0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
Alocal[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addMatrix (Alocal, 1);
addMatrix (Alocal, 10);
printingmatrix(Alocal);
}
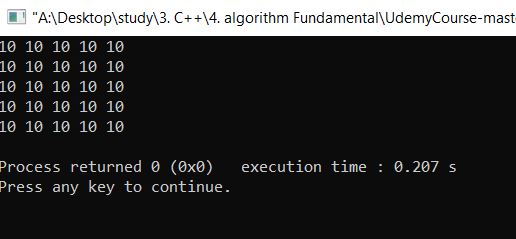
- 값이 11이 아니라 10이 나오는 이유는 matrix[i][j]=+X; 가 아니라 matrix[i][j]+=X;로 하여야 acculate가 된다.
-
메인 function에 있는 Alocal 값이 local function 파라미터 matrix로 변하면서 즉 matrix = Alocal이 되면서 Accoluate가 된다.
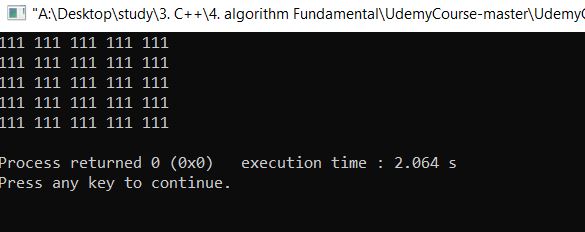
- 해결책
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void addMatrix (int matrix[][5], int X)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
matrix[i][j]=+X;
}
}
}
void printingmatrix(int matrix[][5])
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[5][5];
// initialize, because local variable value is random when they are allocated. on the other hand, global variable is 0 when they allocated.
for (int i = 0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
Alocal[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addMatrix (Alocal, 1);
addMatrix (Alocal, 10);
printingmatrix(Alocal);
}
- Global Variable
- defined on top
- initialized with 0
- visible everywhere
- Local Variable
- defined in functions
- initialized randomly
- visible just in the function
Global/local variable Example 1
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Aglobal[3]; // global array of variable
int a ;
void printing()
{
cout<<a;
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[3];
a = 5;
printing();
return 0;
}
- Aglobal is the global array of variable.
- it is allocated in the stack in memory structure as int(4 bits) memory allocation.
- Alocal is the local array of vairble.
- it created in the stack in memory structure as int(4byte) memory allocation.
- printing allocated in the stack in memory structure
-
int a allocated in the stack in memory structure
- 글로벌 variable은 고유의 값으로 local function에서 지정할 수 있고 main function에서 값을 지정할 수 있다.
Global/local variable Example 2
- 그렇다면 만약 global에도 똑같은 variable 이름과, 로컬에도 똑같은 Variable 이름이 있다면 어떻게 되는가
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Aglobal[3]; // global array of variable
int a ;
void printing()
{
cout<<a<<"\n";
int a = 5;
cout <<a<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[3];
a = 100;
printing();
return 0;
}
-
C++는 객체언어로 Sequence대로 출력이 되기 떄문에 ,Global Variable a값이 먼저 출력이 되고 local function에서 지정한 a 값이 출력이 된다.
-
여기서 주의해야할 점은 Local Function에서 지정된 변수 a이의 이름은 Global 변수하고 이름이 같은데, Local Function이 종료가 되면 Allocated 되었던 Local variable 값은 초기화가 되고 Local Funtion이 끝나고 a 변수 값은 Global Variable 값으로 돌아온다
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Aglobal[3]; // global array of variable
int a ;
void printing()
{
cout<<a<<"\n";
int a = 5;
cout <<a<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[3];
a = 100;
printing();
cout<<a<<"\n";
return 0;
}
- after we exit a function, local variable disappear (cannot seen/used in other functions)
Global/local variable Example 3
- Functions parameter are local variables!
- 즉 Function 파라미터들은 로컬 변수로 메모리 구조 Stack에 Allcolate 된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int A[3][5], i ;
void printingRow(int row)
{
for (i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
cout<<A[row][i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
for(i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
printingRow(i);
}
return 0;
}
-
여기서 첫 행밖에 출력이 안되는 이유는 현재 global variable i 만으로 for loop을 사용하기 때문이다
-
더 자세하게 말하자면, 현재 main function에서 i=1이 local function 파라미터로 들어간다. int row로 allocated가 되어서 i=1값이 들어가게 되는데, local function for loop에 global variable i를 쓰면서, 첫번째 행이 끝나고 i의 값은 5가 되어 있다. 그리고 exit local function 했을떄 i의 값은 이미 5가 되어있으므로 main function에 있는 for loop의 조건을 충족하지 못하여 나가게 되는 것이다.
-
그렇기 때문에 Global Variable로 for loop 쓸떄 주의해야 한다.
-
아래와 같이 해결 할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int A[3][5];
void printingRow(int row)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
cout<<A[row][i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
int main()
{
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
{
printingRow(i);
}
return 0;
}
Exercise (Array Return)
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void addMatrix (int matrix[][5], int X)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
matrix[i][j]=+X;
}
}
}
void printingmatrix(int matrix[][5])
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[5][5];
// initialize, because local variable value is random when they are allocated. on the other hand, global variable is 0 when they allocated.
for (int i = 0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
Alocal[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addMatrix (Alocal, 1);
addMatrix (Alocal, 10);
printingmatrix(Alocal);
}
- 값이 11이 아니라 10이 나오는 이유는 matrix[i][j]=+X; 가 아니라 matrix[i][j]+=X;로 하여야 acculate가 된다.
-
메인 function에 있는 Alocal 값이 local function 파라미터 matrix로 변하면서 즉 matrix = Alocal이 되면서 Accoluate가 된다.
- 해결책
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void addMatrix (int matrix[][5], int X)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
matrix[i][j]=+X;
}
}
}
void printingmatrix(int matrix[][5])
{
for (int i=0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
cout<<matrix[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
}
int main()
{
int Alocal[5][5];
// initialize, because local variable value is random when they are allocated. on the other hand, global variable is 0 when they allocated.
for (int i = 0; i<5; ++i)
{
for (int j=0; j<5; ++j)
{
Alocal[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addMatrix (Alocal, 1);
addMatrix (Alocal, 10);
printingmatrix(Alocal);
}




Comments