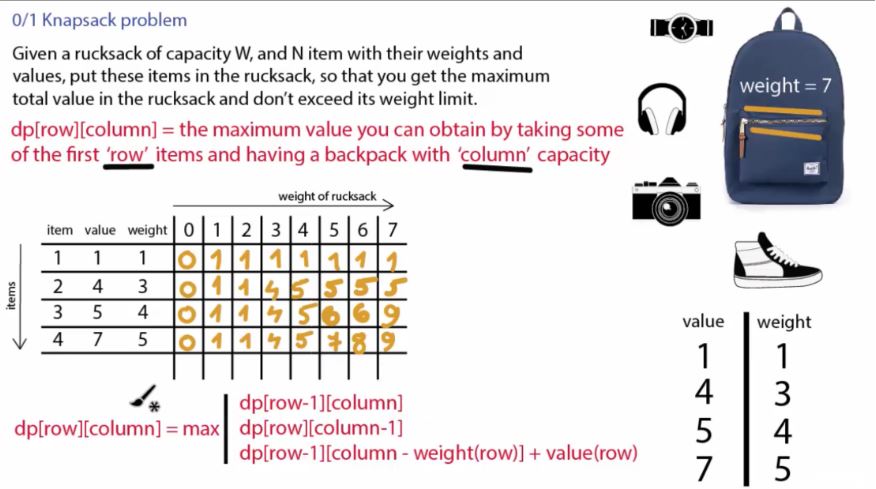
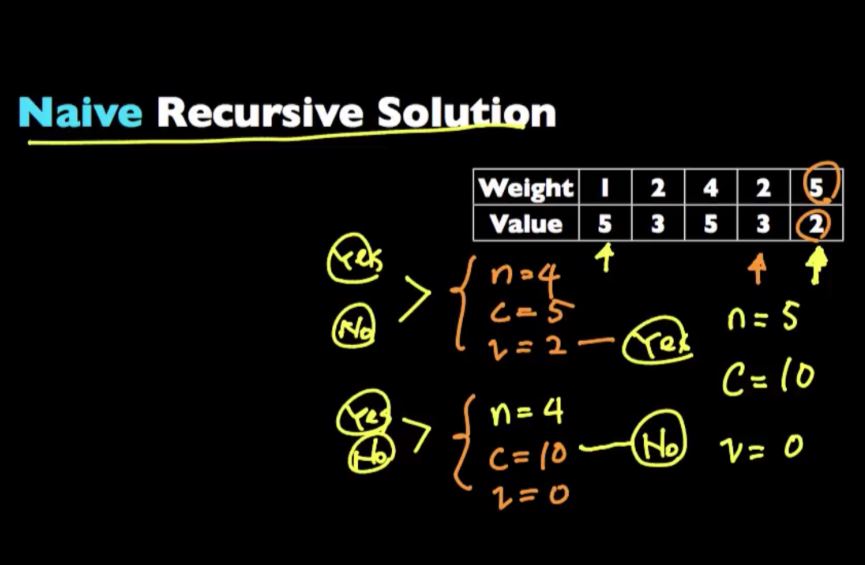
18.Knapsack problem
27 May 2020 | STL Programming Practice_1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int knapSack(int W, int wt[], int val[], int n)
{
// bas case
if(n == 0 || W == 0)
return 0;
// if weight of the n-th item is more than Knapsack capacity W,
// Then this item cannot be included in the optimal solution
if(wt[n-1]>W)
return knapSack(W,wt,val,n-1);
// Return the maximum of two cases:
// (1) n-th item included
// (2) not included
else
return max(val[n-1]+knapSack(W-wt[n-1],wt,val,n-1),knapSack(W,wt,val,n-1));
}
int main()
{
int val[] = {60,100,120};
int wt[] = {10, 20, 30};
int W = 50;
int n = sizeof(val)/sizeof(val[0]); //len of array
cout<<knapSack(W,wt,val,n);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int knapSack(int W, int wt[], int val[], int n)
{
// bas case
if(n == 0 || W == 0)
return 0;
// if weight of the n-th item is more than Knapsack capacity W,
// Then this item cannot be included in the optimal solution
if(wt[n-1]>W)
return knapSack(W,wt,val,n-1);
// Return the maximum of two cases:
// (1) n-th item included
// (2) not included
else
return max(val[n-1]+knapSack(W-wt[n-1],wt,val,n-1),knapSack(W,wt,val,n-1));
}
int main()
{
int val[] = {60,100,120};
int wt[] = {10, 20, 30};
int W = 50;
int n = sizeof(val)/sizeof(val[0]); //len of array
cout<<knapSack(W,wt,val,n);
return 0;
}







Comments