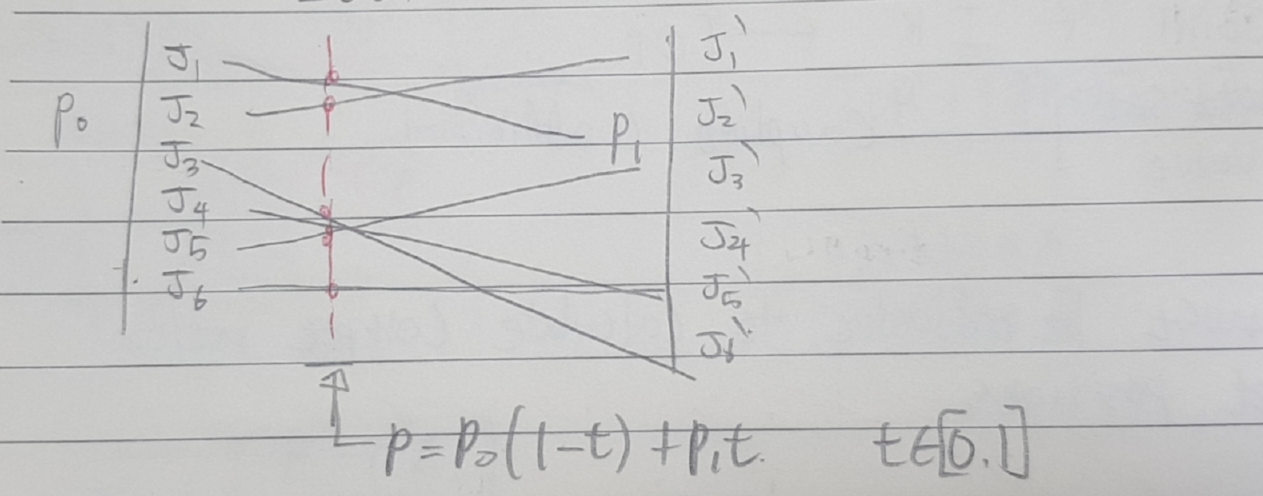
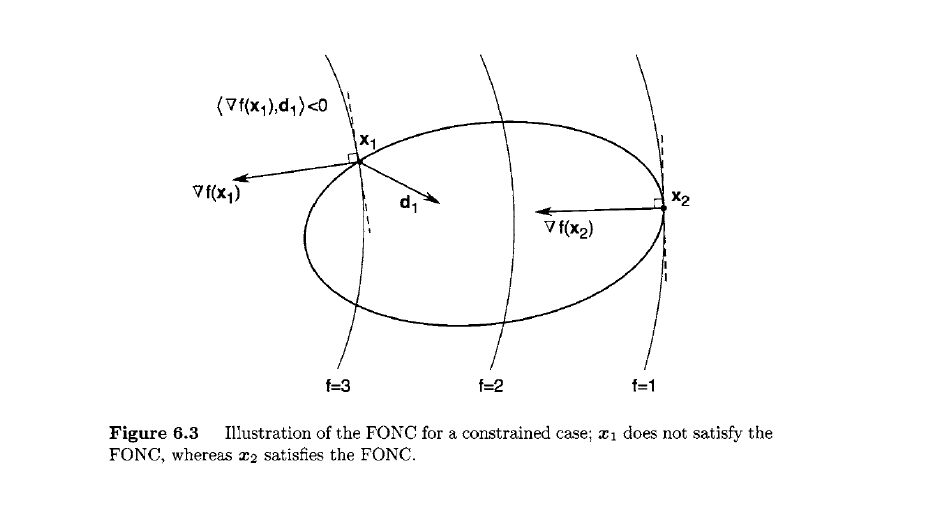
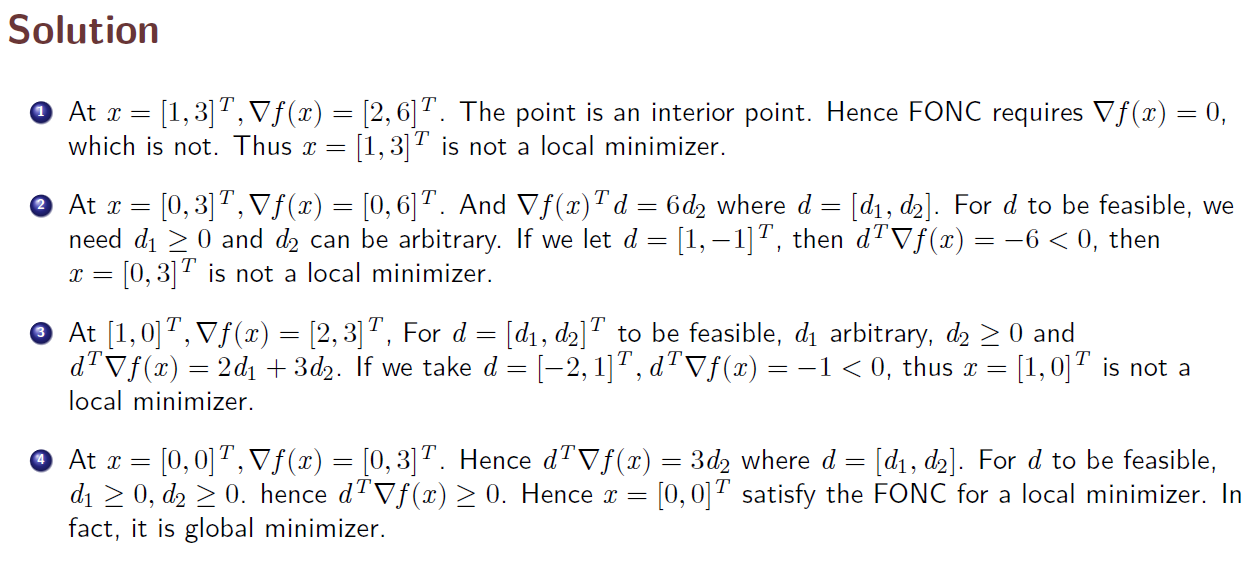
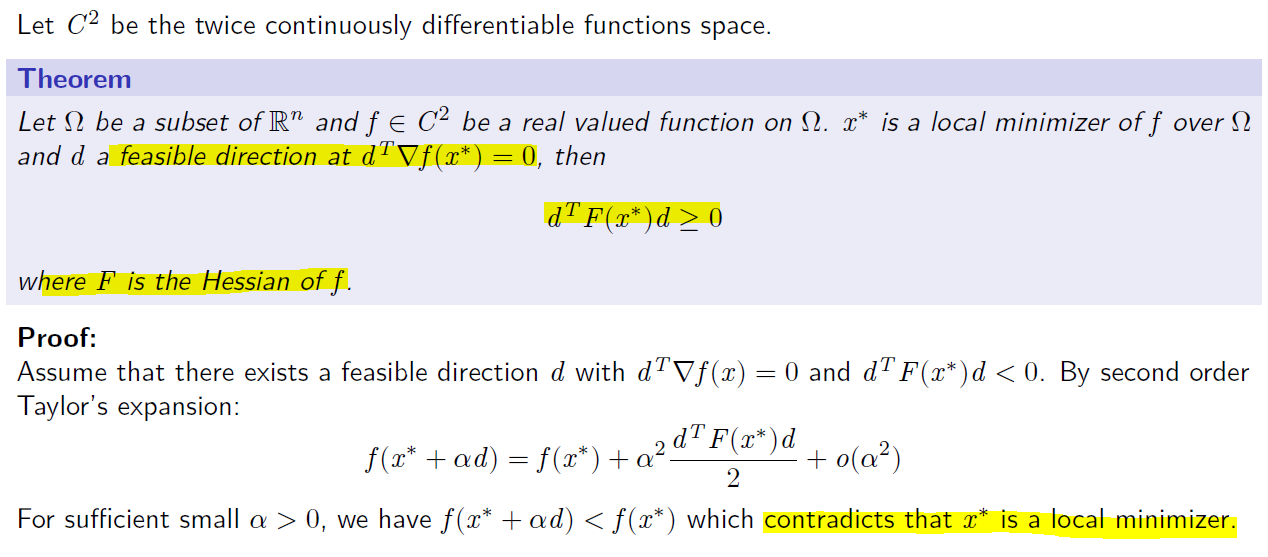
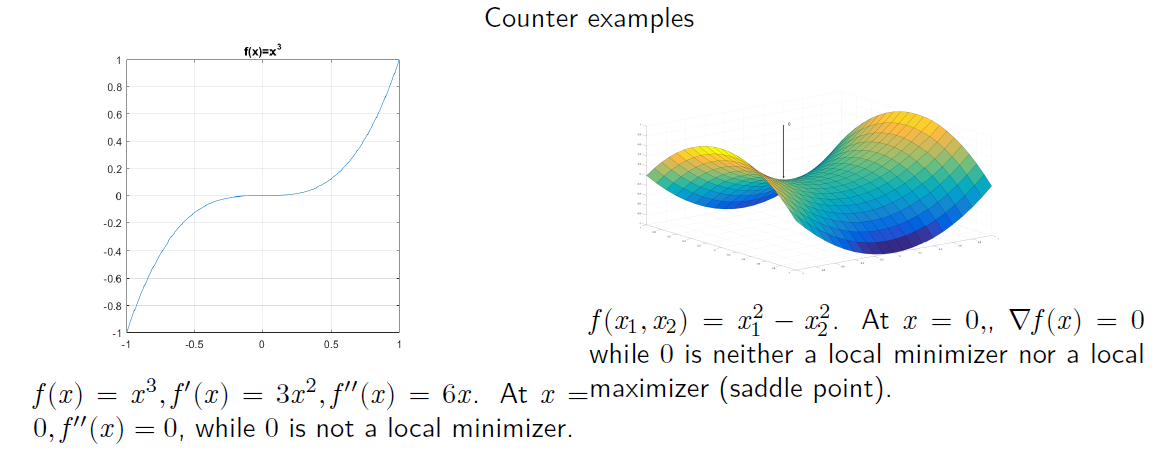
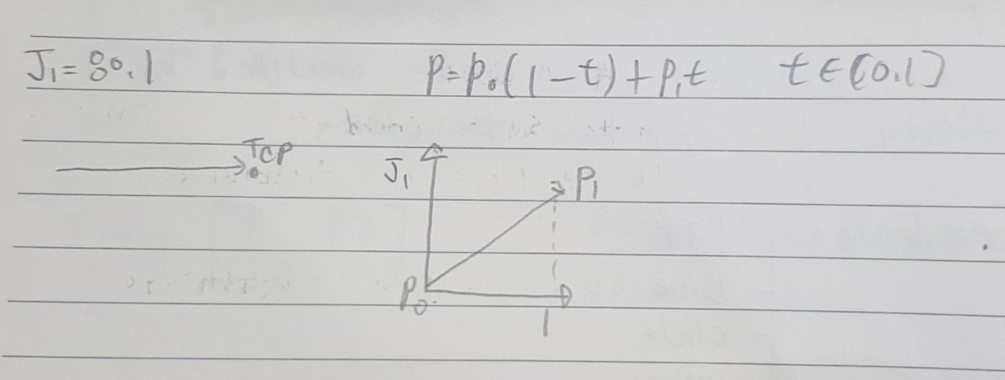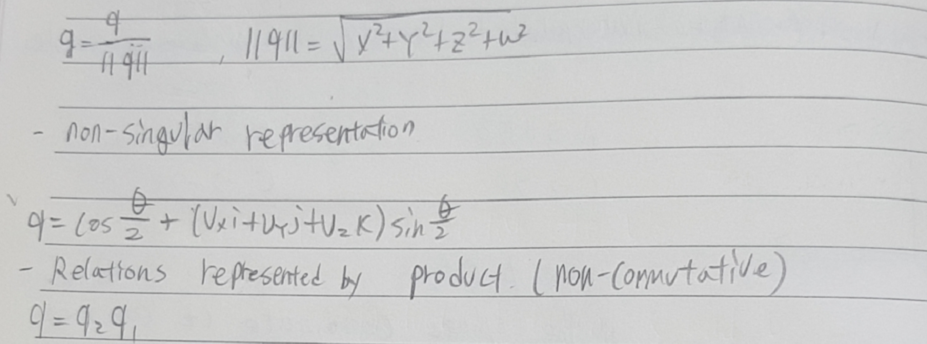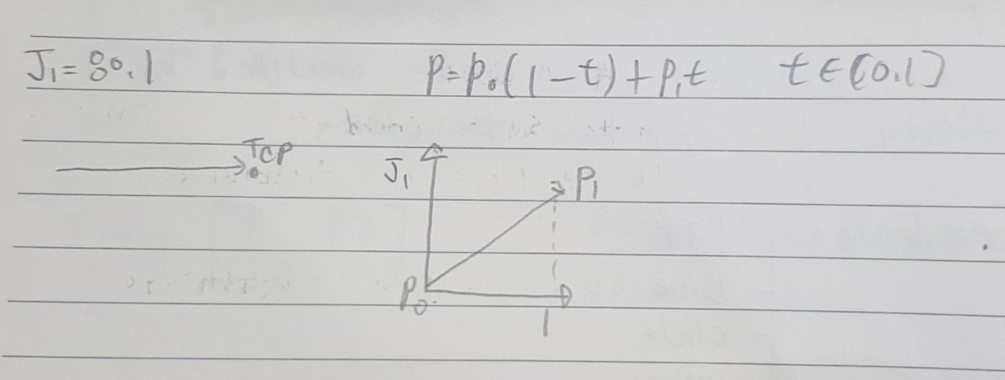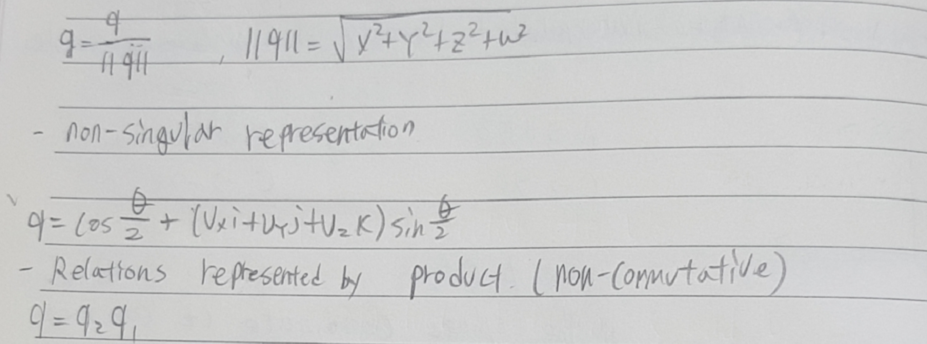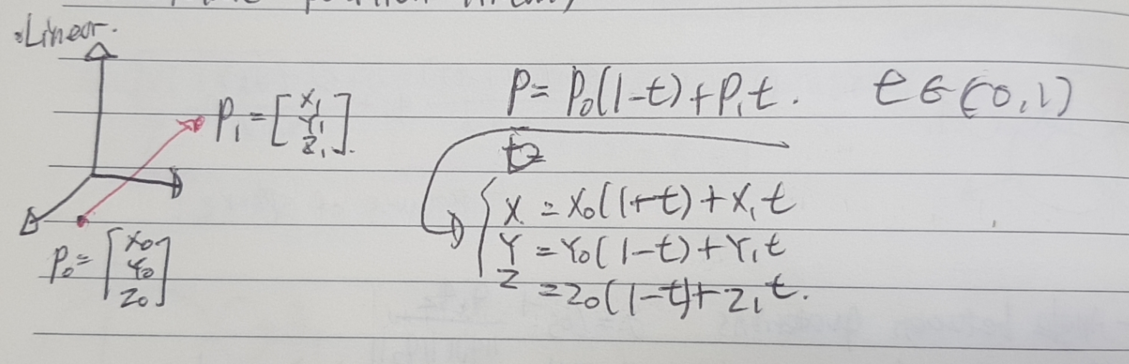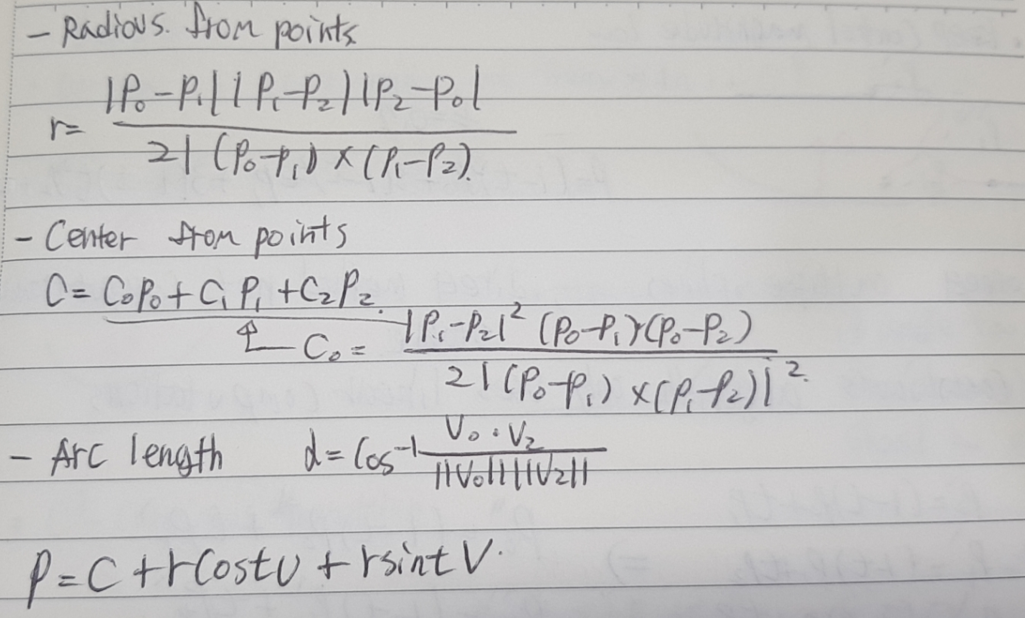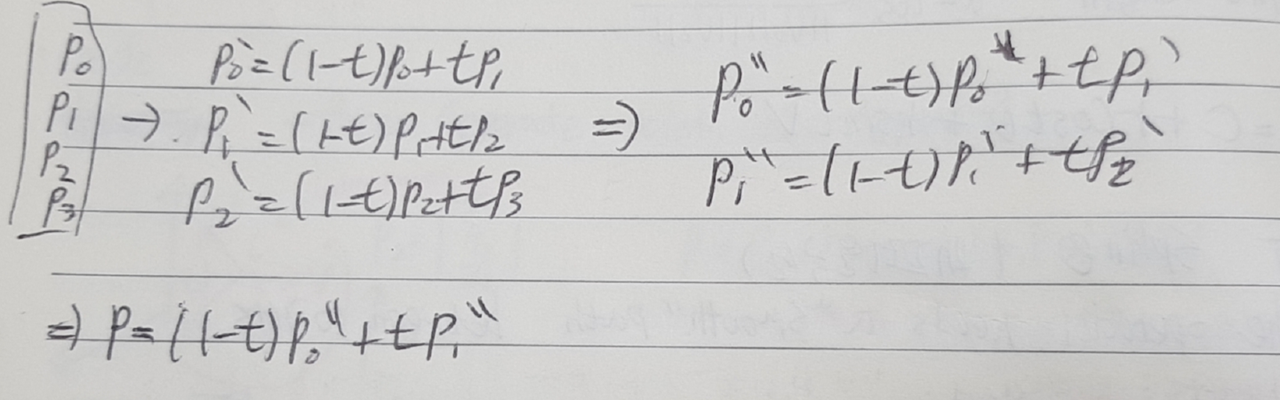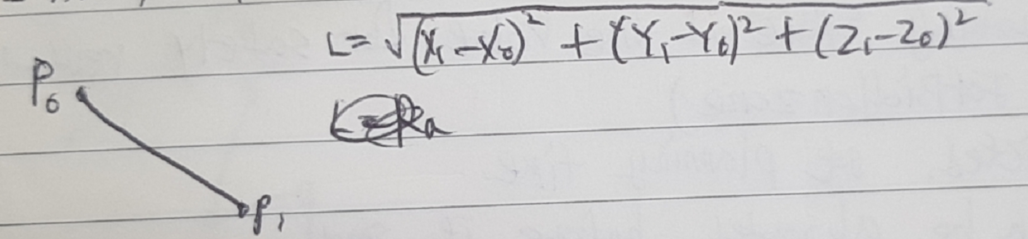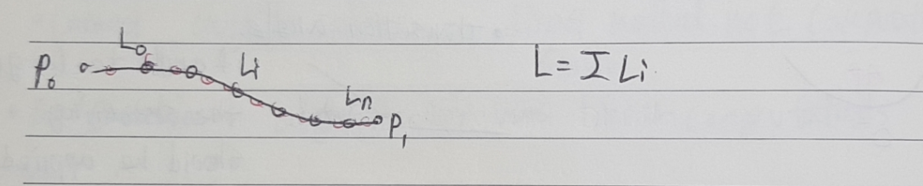def __init__(self):
self.scene = moveit_commander.PlanningSceneInterface()
self.marker_pub = rospy.Publisher("/visualization_marker_array", MarkerArray, queue_size=1)
def remove_planning_obs(self):
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs1")
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs2")
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs3")
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs4")
def no_obs(self):
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs1")
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs2")
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs3")
self.scene.remove_world_object("obs4")
self.scene.remove_world_object("box1")
self.scene.remove_world_object("box2")
self.scene.remove_world_object("box3")
self.scene.remove_world_object("box4")
obs = MarkerArray()
obj1 = Marker()
obj1.ns = 'obstacle'
obj1.id = 1
obj1.action = 2;
obs.markers.append(obj1)
obj2 = Marker()
obj2.ns = 'obstacle'
obj2.id = 2
obj2.action = 2;
obs.markers.append(obj2)
obj3 = Marker()
obj3.ns = 'obstacle'
obj3.id = 3
obj3.action = 2;
obs.markers.append(obj3)
obj4 = Marker()
obj4.ns = 'obstacle'
obj4.id = 4
obj4.action = 2;
obs.markers.append(obj4)
self.marker_pub.publish(obs)
def simple_obs(self):
self.no_obs()
pose_stamped = geometry_msgs.msg.PoseStamped()
pose_stamped.header.frame_id = "world_link"
pose_stamped.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.25, 0.2)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs1", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.1,1))
self.scene.add_box("box1", pose_stamped,(0.05, 0.05, 0.95))
obs = MarkerArray()
obj = Marker()
obj.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj.ns = 'obstacle'
obj.id = 1
obj.type = Marker.CUBE
obj.action = Marker.ADD
obj.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.25, 0.2)) )
obj.scale.x = 0.1
obj.scale.y = 0.1
obj.scale.z = 1.0
obj.color.r = 0.0
obj.color.g = 1.0
obj.color.b = 0.0
obj.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj)
self.marker_pub.publish(obs)
def complex_obs(self):
self.no_obs()
pose_stamped = geometry_msgs.msg.PoseStamped()
pose_stamped.header.frame_id = "world_link"
pose_stamped.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.25, 0.4)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs1", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.1,0.8))
self.scene.add_box("box1", pose_stamped,(0.05,0.05,0.75))
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.0, 0.8)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs2", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.5,0.1))
self.scene.add_box("box2", pose_stamped,(0.05,0.45,0.05))
obs = MarkerArray()
obj1 = Marker()
obj1.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj1.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj1.ns = 'obstacle'
obj1.id = 1
obj1.type = Marker.CUBE
obj1.action = Marker.ADD
obj1.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.25, 0.4)) )
obj1.scale.x = 0.1
obj1.scale.y = 0.1
obj1.scale.z = 0.8
obj1.color.r = 0.0
obj1.color.g = 1.0
obj1.color.b = 0.0
obj1.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj1)
obj2 = Marker()
obj2.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj2.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj2.ns = 'obstacle'
obj2.id = 2
obj2.type = Marker.CUBE
obj2.action = Marker.ADD
obj2.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.0, 0.8)) )
obj2.scale.x = 0.1
obj2.scale.y = 0.5
obj2.scale.z = 0.1
obj2.color.r = 0.0
obj2.color.g = 1.0
obj2.color.b = 0.0
obj2.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj2)
self.marker_pub.publish(obs)
def super_obs(self):
self.no_obs()
pose_stamped = geometry_msgs.msg.PoseStamped()
pose_stamped.header.frame_id = "world_link"
pose_stamped.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.25, 0.4)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs1", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.1,0.8))
self.scene.add_box("box1", pose_stamped,(0.05,0.05,0.75))
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.0, 0.8)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs2", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.5,0.1))
self.scene.add_box("box2", pose_stamped,(0.05,0.45,0.05))
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, -0.25, 0.4)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs3", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.1,0.8))
self.scene.add_box("box3", pose_stamped,(0.05,0.05,0.75))
pose_stamped.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.0, 0.3)) )
self.scene.add_box("obs4", pose_stamped,(0.1,0.5,0.1))
self.scene.add_box("box4", pose_stamped,(0.05,0.45,0.05))
obs = MarkerArray()
obj1 = Marker()
obj1.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj1.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj1.ns = 'obstacle'
obj1.id = 1
obj1.type = Marker.CUBE
obj1.action = Marker.ADD
obj1.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.25, 0.4)) )
obj1.scale.x = 0.1
obj1.scale.y = 0.1
obj1.scale.z = 0.8
obj1.color.r = 0.0
obj1.color.g = 1.0
obj1.color.b = 0.0
obj1.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj1)
obj2 = Marker()
obj2.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj2.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj2.ns = 'obstacle'
obj2.id = 2
obj2.type = Marker.CUBE
obj2.action = Marker.ADD
obj2.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.0, 0.8)) )
obj2.scale.x = 0.1
obj2.scale.y = 0.5
obj2.scale.z = 0.1
obj2.color.r = 0.0
obj2.color.g = 1.0
obj2.color.b = 0.0
obj2.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj2)
obj3 = Marker()
obj3.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj3.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj3.ns = 'obstacle'
obj3.id = 3
obj3.type = Marker.CUBE
obj3.action = Marker.ADD
obj3.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, -0.25, 0.4)) )
obj3.scale.x = 0.1
obj3.scale.y = 0.1
obj3.scale.z = 0.8
obj3.color.r = 0.0
obj3.color.g = 1.0
obj3.color.b = 0.0
obj3.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj3)
obj4 = Marker()
obj4.header.frame_id = "world_link"
obj4.header.stamp = rospy.Time(0)
obj4.ns = 'obstacle'
obj4.id = 4
obj4.type = Marker.CUBE
obj4.action = Marker.ADD
obj4.pose = convert_to_message( tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.5, 0.0, 0.3)) )
obj4.scale.x = 0.1
obj4.scale.y = 0.5
obj4.scale.z = 0.1
obj4.color.r = 0.0
obj4.color.g = 1.0
obj4.color.b = 0.0
obj4.color.a = 1.0
obs.markers.append(obj4)
self.marker_pub.publish(obs)