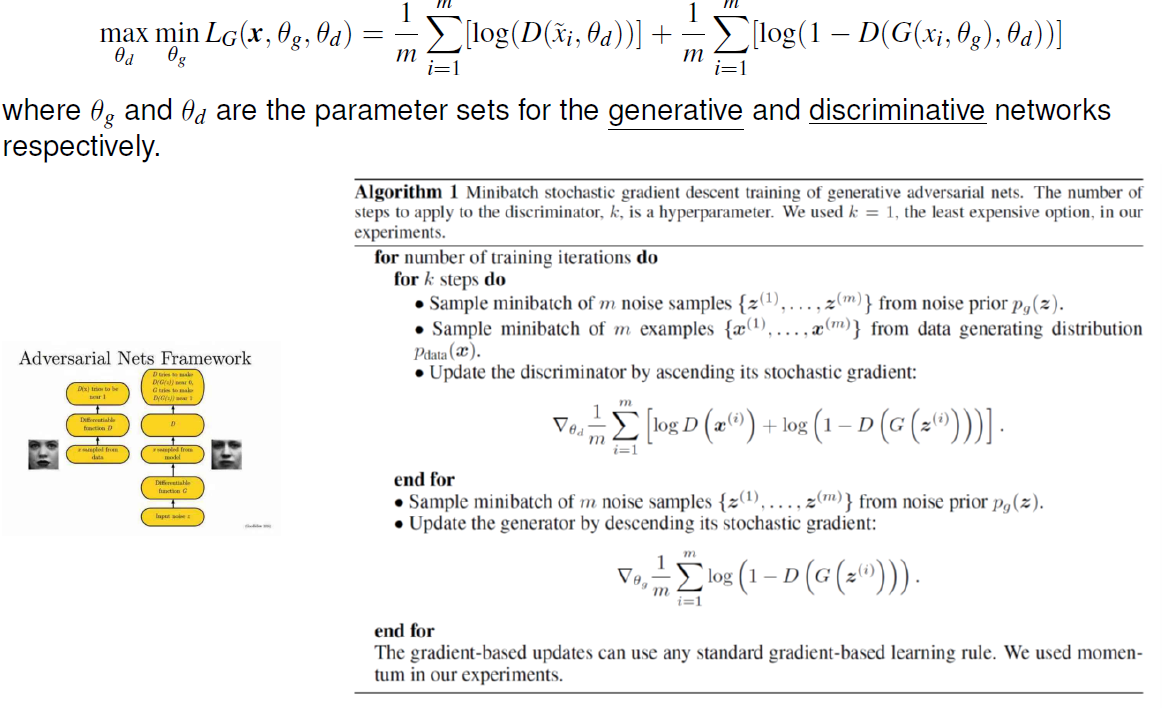
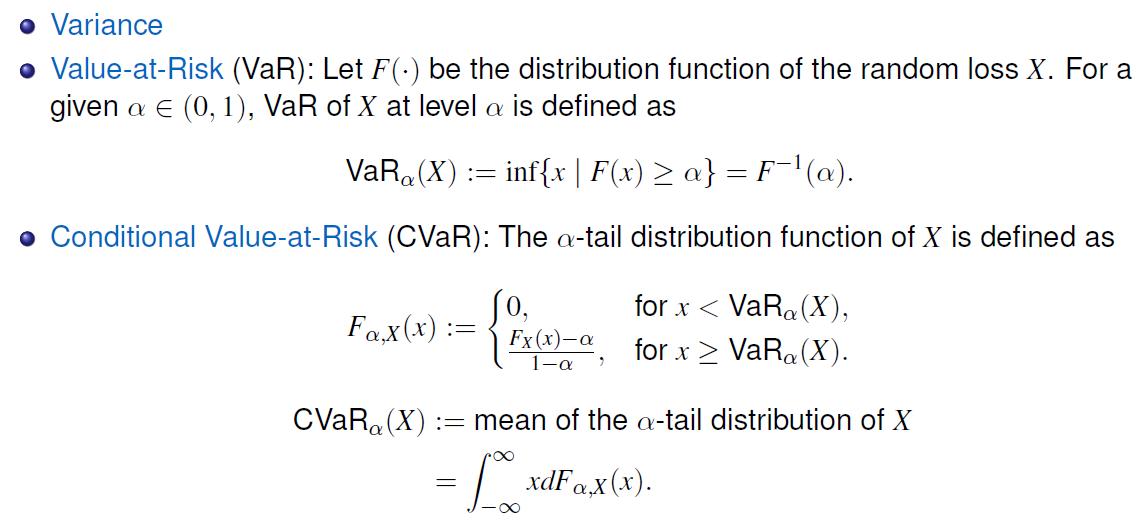
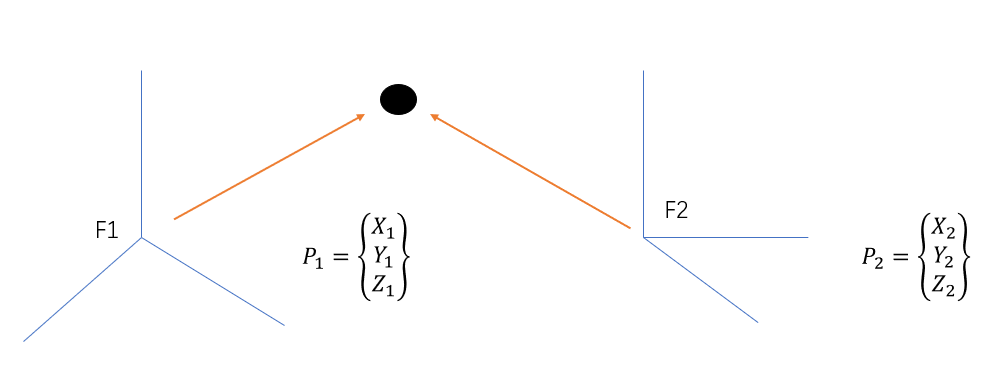
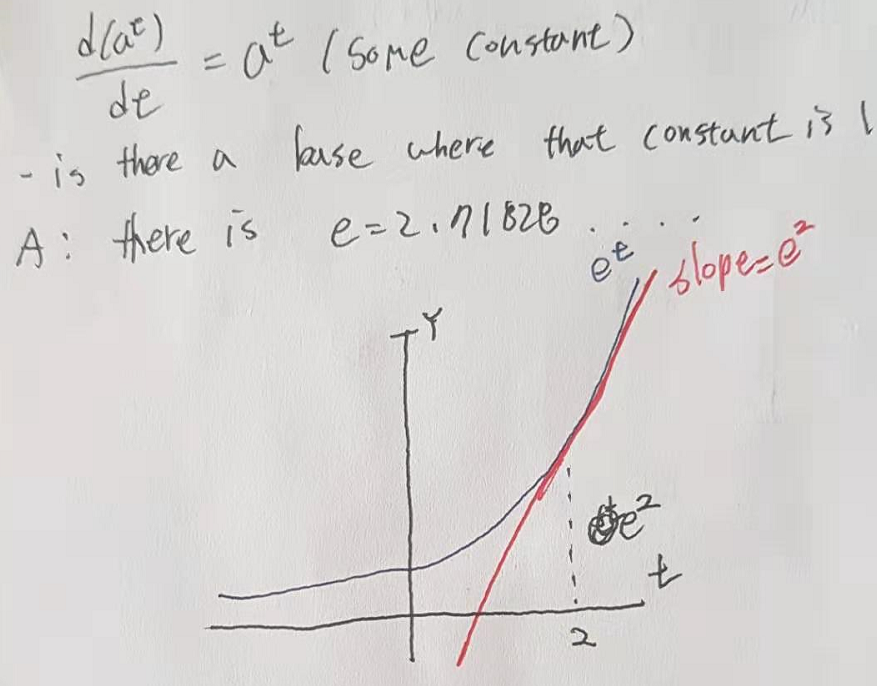
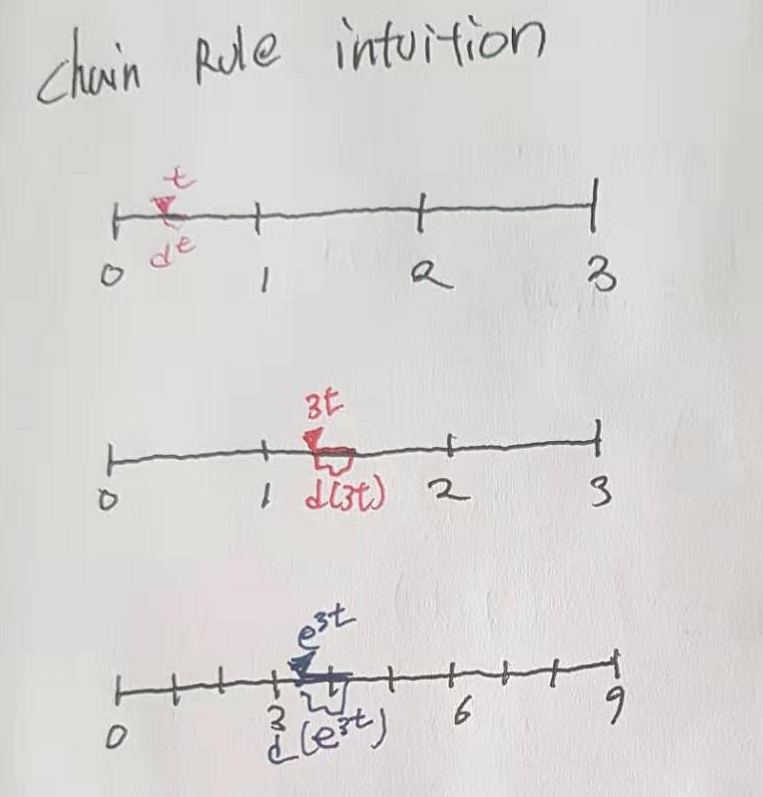
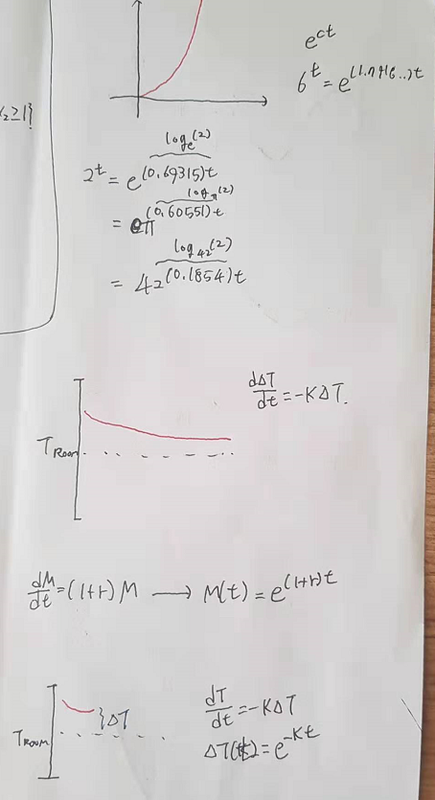
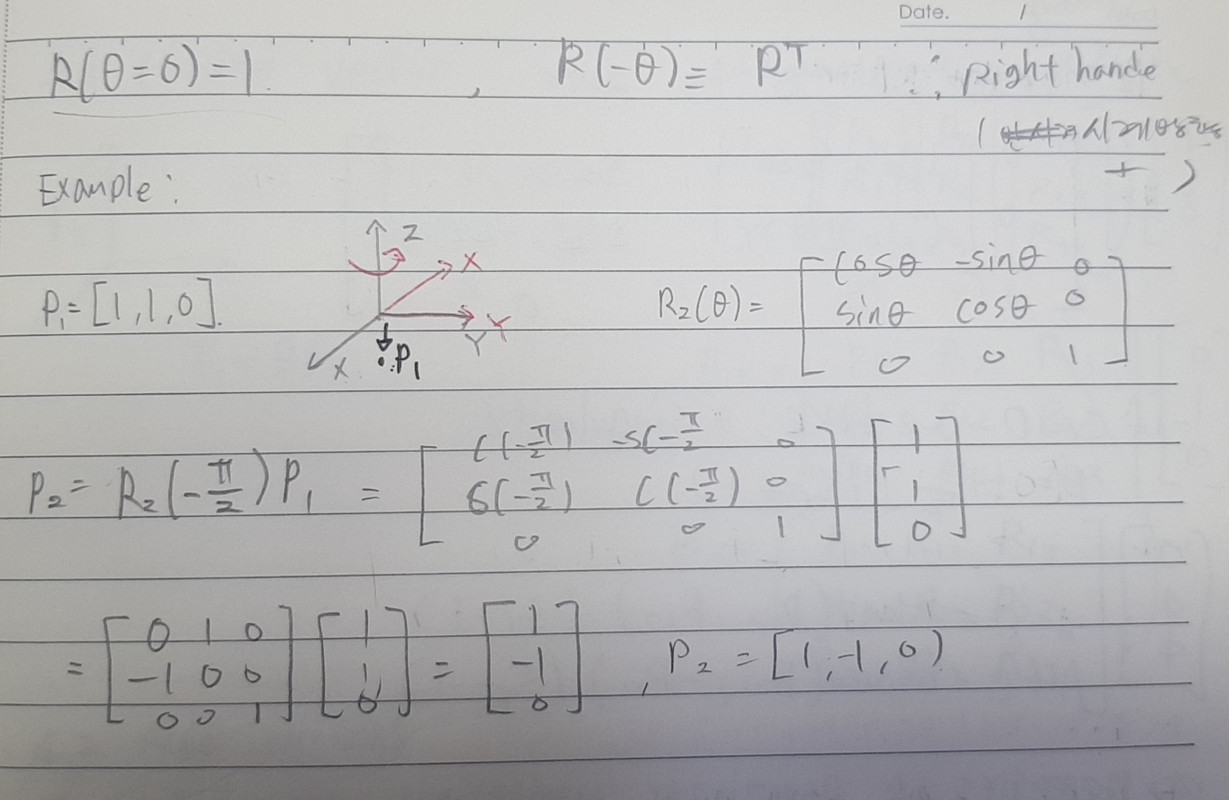2. TF tutorial
02 Oct 2019 | ROS
- to understand TF look at the my Transformation Frame post
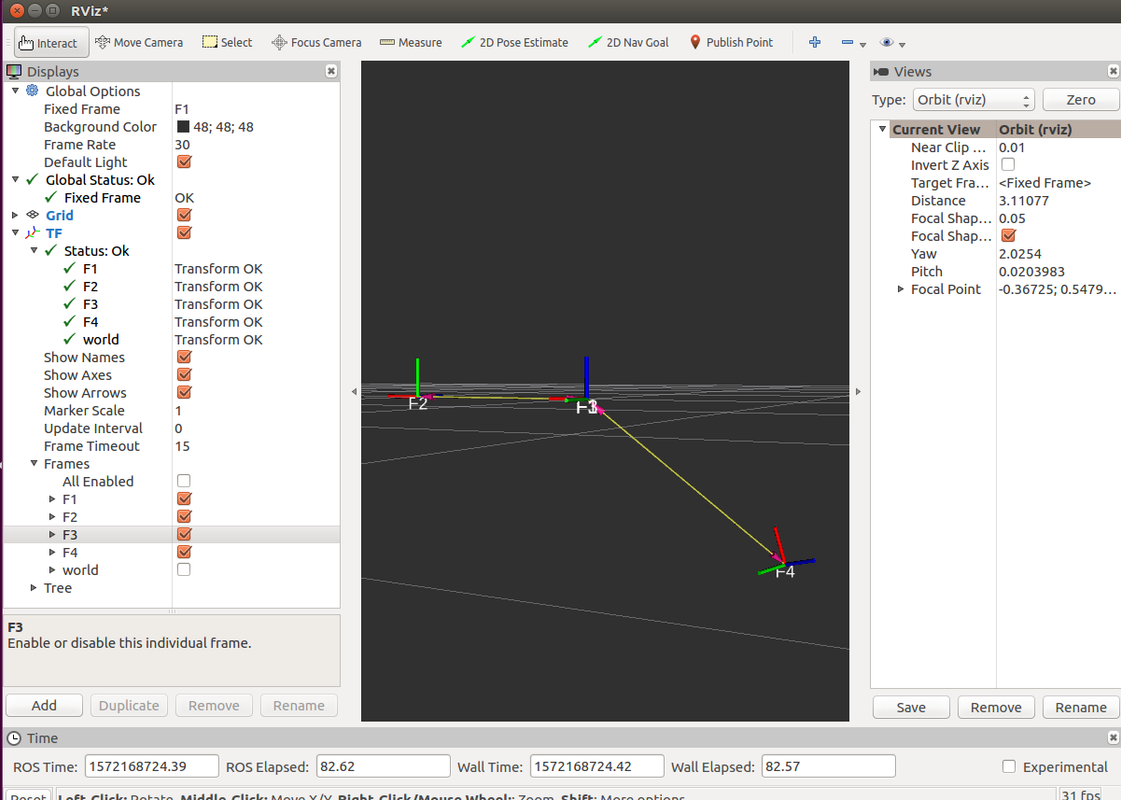
TF Example
TF_Example.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import numpy
import tf
import tf2_ros
import geometry_msgs.msg
def publish_transforms():
t1 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t1.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t1.header.frame_id = "world"
t1.child_frame_id = "F1"
t1.transform.translation.x = 1.0
t1.transform.translation.y = 1.0
t1.transform.translation.z = 0.0
q1 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
t1.transform.rotation.x = q1[0]
t1.transform.rotation.y = q1[1]
t1.transform.rotation.z = q1[2]
t1.transform.rotation.w = q1[3]
br.sendTransform(t1)
t2 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t2.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t2.header.frame_id = "F1"
t2.child_frame_id = "F2"
t2.transform.translation.x = 1.0
t2.transform.translation.y = 0.0
t2.transform.translation.z = 0.0
q2 = tf.transformations.quaternion_about_axis(1.57, (1,0,0))
t2.transform.rotation.x = q2[0]
t2.transform.rotation.y = q2[1]
t2.transform.rotation.z = q2[2]
t2.transform.rotation.w = q2[3]
br.sendTransform(t2)
T1 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.translation_matrix((1.0, 1.0, 0.0)),
tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q1))
T1_inverse = tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T1)
t3 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t3.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t3.header.frame_id = "F3"
t3.child_frame_id = "F4"
tr3 = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T1_inverse)
t3.transform.translation.x = tr3[0]
t3.transform.translation.y = tr3[1]
t3.transform.translation.z = tr3[2]
q3 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T1_inverse)
t3.transform.rotation.x = q3[0]
t3.transform.rotation.y = q3[1]
t3.transform.rotation.z = q3[2]
t3.transform.rotation.w = q3[3]
br.sendTransform(t3)
T2 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.translation_matrix((1.0, 0.0, 0.0)),
tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q2))
T2_inverse = tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T2)
t4 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t4.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t4.header.frame_id = "F2"
t4.child_frame_id = "F3"
tr4 = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T2_inverse)
t4.transform.translation.x = tr4[0]
t4.transform.translation.y = tr4[1]
t4.transform.translation.z = tr4[2]
q4 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T2_inverse)
t4.transform.rotation.x = q4[0]
t4.transform.rotation.y = q4[1]
t4.transform.rotation.z = q4[2]
t4.transform.rotation.w = q4[3]
br.sendTransform(t4)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('tf2_examples')
br = tf2_ros.TransformBroadcaster()
rospy.sleep(0.5)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
publish_transforms()
rospy.sleep(0.05)
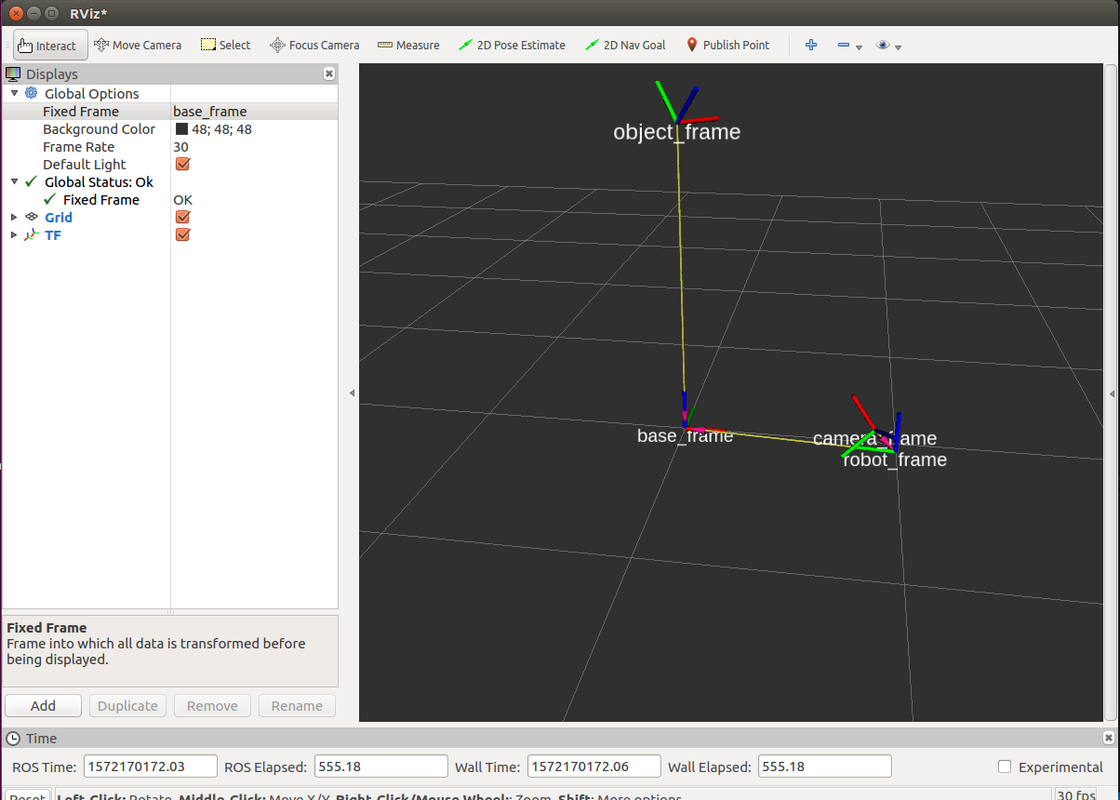
second Tutorial
second Tutorial.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import numpy
import tf
import tf2_ros
import geometry_msgs.msg
def message_from_transform(T):
msg = geometry_msgs.msg.Transform()
q = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T)
p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T)
msg.translation.x = p[0]
msg.translation.y = p[1]
msg.translation.z = p[2]
msg.rotation.x = q[0]
msg.rotation.y = q[1]
msg.rotation.z = q[2]
msg.rotation.w = q[3]
return msg
def publish_transforms():
object_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
object_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
object_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
object_transform.child_frame_id = "object_frame"
T_1 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.79,0.0,0.79)),
tf.transformations.translation_matrix([0.0,1.0,1.0]))
object_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T_1)
br.sendTransform(object_transform)
robot_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
robot_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
robot_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
robot_transform.child_frame_id = "robot_frame"
T_2 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.0,0.0,1.5)),
tf.transformations.translation_matrix([0.0,-1.0,0.0]))
robot_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T_2)
br.sendTransform(robot_transform)
camera_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
camera_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
camera_transform.header.frame_id = "robot_frame"
camera_transform.child_frame_id = "camera_frame"
T_3 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.translation_matrix([0.0,0.1,0.1]),
tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.,0.,0.)))
Tr = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_3),tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_2),T_1)
p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(Tr)
dir = numpy.cross(numpy.array([1,0,0]),numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]]))
theta = numpy.arccos(p[0]/numpy.linalg.norm(numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]])))
T_3 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(T_3,tf.transformations.rotation_matrix(theta,dir))
#p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T_3)
#theta = numpy.arccos(p[0]/numpy.linalg.norm(numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]])))
#T_3 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(T_3,tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(theta,0.0,0.0)))
camera_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T_3)
br.sendTransform(camera_transform)
# co = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
# co.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
# co.header.frame_id = "camera_frame"
# co.child_frame_id = "asd"
# Tr = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_3),tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_2),T_1)
# #p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(Tr)
# #theta = numpy.arccos(p[0]/numpy.linalg.norm(numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]])))
# co.transform = message_from_transform(Tr)
# #Tr = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(Tr,tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(theta,0.0,0.0)))
# br.sendTransform(co)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('project2_solution')
br = tf2_ros.TransformBroadcaster()
rospy.sleep(0.5)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
publish_transforms()
rospy.sleep(0.05)
Third Tutorial
Thrid Tutorial.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import numpy
import tf
import tf2_ros
import geometry_msgs.msg
def message_from_transform(T):
msg = geometry_msgs.msg.Transform()
q = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T)
translation = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T)
msg.translation.x = translation[0]
msg.translation.y = translation[1]
msg.translation.z = translation[2]
msg.rotation.x = q[0]
msg.rotation.y = q[1]
msg.rotation.z = q[2]
msg.rotation.w = q[3]
return msg
def publish_transforms():
object_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
object_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
object_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
object_transform.child_frame_id = "object_frame"
q1 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.79,0.0,0.79)
T1 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q1),tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.0,1.0,1.0)))
object_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T1)
br.sendTransform(object_transform)
robot_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
robot_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
robot_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
robot_transform.child_frame_id = "robot_frame"
q2= tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0,0,1.5)
T2 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q2), tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.0,-1.0,0.0)))
robot_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T2)
br.sendTransform(robot_transform)
camera_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
camera_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
camera_transform.header.frame_id = "robot_frame"
camera_transform.child_frame_id = "camera_frame"
#T1 is TBO
#T2 is TBR
TRC = tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.0,0.1,0.1))
TBC = numpy.dot(T2,TRC)
TCO = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(TBC),T1)
v1_n = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(TCO)
v1 = v1_n/numpy.linalg.norm(v1_n) # vector or matrix norm
x = [1,0,0]
w = numpy.cross(x,v1) #cross product
rt = numpy.arccos(numpy.dot(x,v1_n))
q3 = tf.transformations.quaternion_about_axis(rt,w)
T3 = numpy.dot(TRC,tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q3))
camera_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T3)
br.sendTransform(camera_transform)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('project2_solution')
br = tf2_ros.TransformBroadcaster()
rospy.sleep(0.5)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
publish_transforms()
rospy.sleep(0.05)
- to understand TF look at the my Transformation Frame post
TF Example
TF_Example.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import numpy
import tf
import tf2_ros
import geometry_msgs.msg
def publish_transforms():
t1 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t1.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t1.header.frame_id = "world"
t1.child_frame_id = "F1"
t1.transform.translation.x = 1.0
t1.transform.translation.y = 1.0
t1.transform.translation.z = 0.0
q1 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
t1.transform.rotation.x = q1[0]
t1.transform.rotation.y = q1[1]
t1.transform.rotation.z = q1[2]
t1.transform.rotation.w = q1[3]
br.sendTransform(t1)
t2 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t2.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t2.header.frame_id = "F1"
t2.child_frame_id = "F2"
t2.transform.translation.x = 1.0
t2.transform.translation.y = 0.0
t2.transform.translation.z = 0.0
q2 = tf.transformations.quaternion_about_axis(1.57, (1,0,0))
t2.transform.rotation.x = q2[0]
t2.transform.rotation.y = q2[1]
t2.transform.rotation.z = q2[2]
t2.transform.rotation.w = q2[3]
br.sendTransform(t2)
T1 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.translation_matrix((1.0, 1.0, 0.0)),
tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q1))
T1_inverse = tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T1)
t3 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t3.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t3.header.frame_id = "F3"
t3.child_frame_id = "F4"
tr3 = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T1_inverse)
t3.transform.translation.x = tr3[0]
t3.transform.translation.y = tr3[1]
t3.transform.translation.z = tr3[2]
q3 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T1_inverse)
t3.transform.rotation.x = q3[0]
t3.transform.rotation.y = q3[1]
t3.transform.rotation.z = q3[2]
t3.transform.rotation.w = q3[3]
br.sendTransform(t3)
T2 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.translation_matrix((1.0, 0.0, 0.0)),
tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q2))
T2_inverse = tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T2)
t4 = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
t4.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
t4.header.frame_id = "F2"
t4.child_frame_id = "F3"
tr4 = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T2_inverse)
t4.transform.translation.x = tr4[0]
t4.transform.translation.y = tr4[1]
t4.transform.translation.z = tr4[2]
q4 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T2_inverse)
t4.transform.rotation.x = q4[0]
t4.transform.rotation.y = q4[1]
t4.transform.rotation.z = q4[2]
t4.transform.rotation.w = q4[3]
br.sendTransform(t4)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('tf2_examples')
br = tf2_ros.TransformBroadcaster()
rospy.sleep(0.5)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
publish_transforms()
rospy.sleep(0.05)
second Tutorial
second Tutorial.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import numpy
import tf
import tf2_ros
import geometry_msgs.msg
def message_from_transform(T):
msg = geometry_msgs.msg.Transform()
q = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T)
p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T)
msg.translation.x = p[0]
msg.translation.y = p[1]
msg.translation.z = p[2]
msg.rotation.x = q[0]
msg.rotation.y = q[1]
msg.rotation.z = q[2]
msg.rotation.w = q[3]
return msg
def publish_transforms():
object_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
object_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
object_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
object_transform.child_frame_id = "object_frame"
T_1 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.79,0.0,0.79)),
tf.transformations.translation_matrix([0.0,1.0,1.0]))
object_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T_1)
br.sendTransform(object_transform)
robot_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
robot_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
robot_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
robot_transform.child_frame_id = "robot_frame"
T_2 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.0,0.0,1.5)),
tf.transformations.translation_matrix([0.0,-1.0,0.0]))
robot_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T_2)
br.sendTransform(robot_transform)
camera_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
camera_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
camera_transform.header.frame_id = "robot_frame"
camera_transform.child_frame_id = "camera_frame"
T_3 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.translation_matrix([0.0,0.1,0.1]),
tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.,0.,0.)))
Tr = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_3),tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_2),T_1)
p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(Tr)
dir = numpy.cross(numpy.array([1,0,0]),numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]]))
theta = numpy.arccos(p[0]/numpy.linalg.norm(numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]])))
T_3 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(T_3,tf.transformations.rotation_matrix(theta,dir))
#p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T_3)
#theta = numpy.arccos(p[0]/numpy.linalg.norm(numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]])))
#T_3 = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(T_3,tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(theta,0.0,0.0)))
camera_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T_3)
br.sendTransform(camera_transform)
# co = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
# co.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
# co.header.frame_id = "camera_frame"
# co.child_frame_id = "asd"
# Tr = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_3),tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(T_2),T_1)
# #p = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(Tr)
# #theta = numpy.arccos(p[0]/numpy.linalg.norm(numpy.array([p[0],p[1],p[2]])))
# co.transform = message_from_transform(Tr)
# #Tr = tf.transformations.concatenate_matrices(Tr,tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(theta,0.0,0.0)))
# br.sendTransform(co)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('project2_solution')
br = tf2_ros.TransformBroadcaster()
rospy.sleep(0.5)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
publish_transforms()
rospy.sleep(0.05)
Third Tutorial
Thrid Tutorial.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
import numpy
import tf
import tf2_ros
import geometry_msgs.msg
def message_from_transform(T):
msg = geometry_msgs.msg.Transform()
q = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_matrix(T)
translation = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(T)
msg.translation.x = translation[0]
msg.translation.y = translation[1]
msg.translation.z = translation[2]
msg.rotation.x = q[0]
msg.rotation.y = q[1]
msg.rotation.z = q[2]
msg.rotation.w = q[3]
return msg
def publish_transforms():
object_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
object_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
object_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
object_transform.child_frame_id = "object_frame"
q1 = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0.79,0.0,0.79)
T1 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q1),tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.0,1.0,1.0)))
object_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T1)
br.sendTransform(object_transform)
robot_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
robot_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
robot_transform.header.frame_id = "base_frame"
robot_transform.child_frame_id = "robot_frame"
q2= tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0,0,1.5)
T2 = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q2), tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.0,-1.0,0.0)))
robot_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T2)
br.sendTransform(robot_transform)
camera_transform = geometry_msgs.msg.TransformStamped()
camera_transform.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now()
camera_transform.header.frame_id = "robot_frame"
camera_transform.child_frame_id = "camera_frame"
#T1 is TBO
#T2 is TBR
TRC = tf.transformations.translation_matrix((0.0,0.1,0.1))
TBC = numpy.dot(T2,TRC)
TCO = numpy.dot(tf.transformations.inverse_matrix(TBC),T1)
v1_n = tf.transformations.translation_from_matrix(TCO)
v1 = v1_n/numpy.linalg.norm(v1_n) # vector or matrix norm
x = [1,0,0]
w = numpy.cross(x,v1) #cross product
rt = numpy.arccos(numpy.dot(x,v1_n))
q3 = tf.transformations.quaternion_about_axis(rt,w)
T3 = numpy.dot(TRC,tf.transformations.quaternion_matrix(q3))
camera_transform.transform = message_from_transform(T3)
br.sendTransform(camera_transform)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node('project2_solution')
br = tf2_ros.TransformBroadcaster()
rospy.sleep(0.5)
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
publish_transforms()
rospy.sleep(0.05)