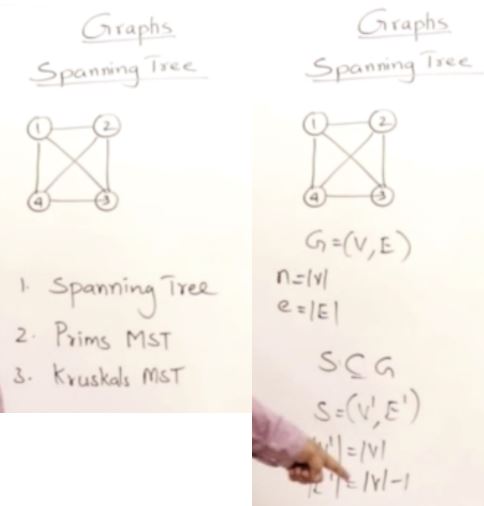
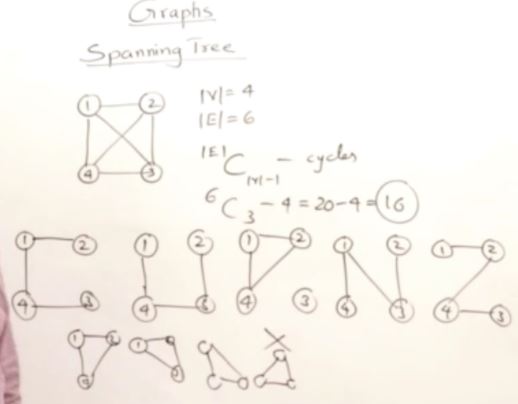
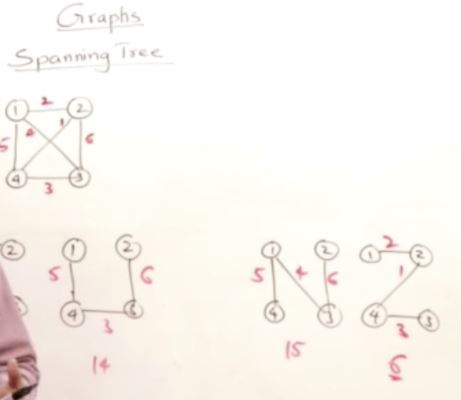
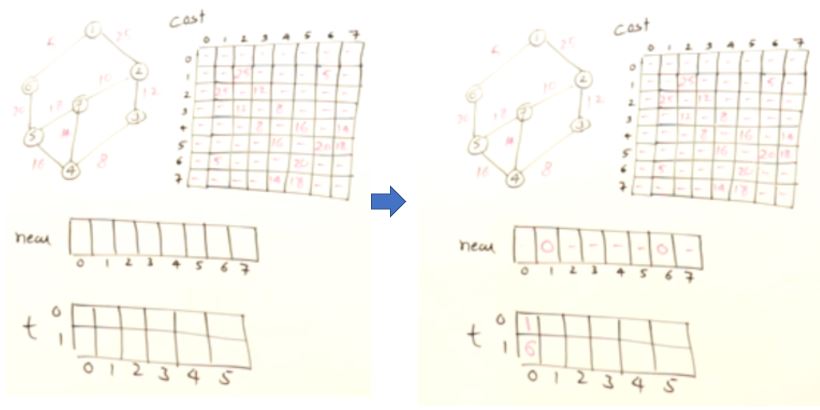
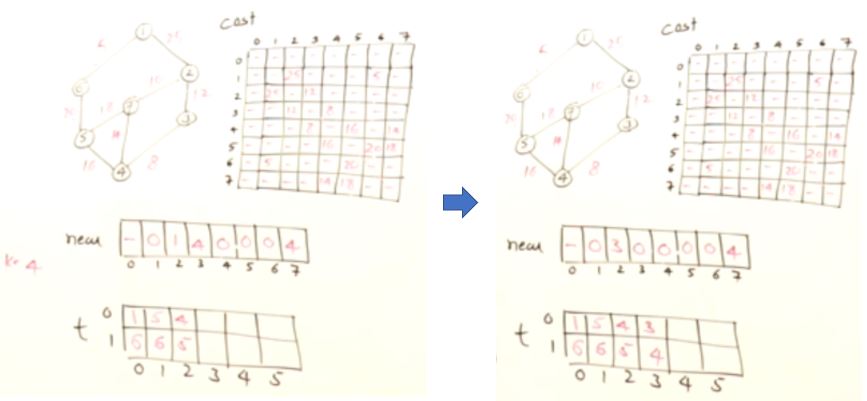
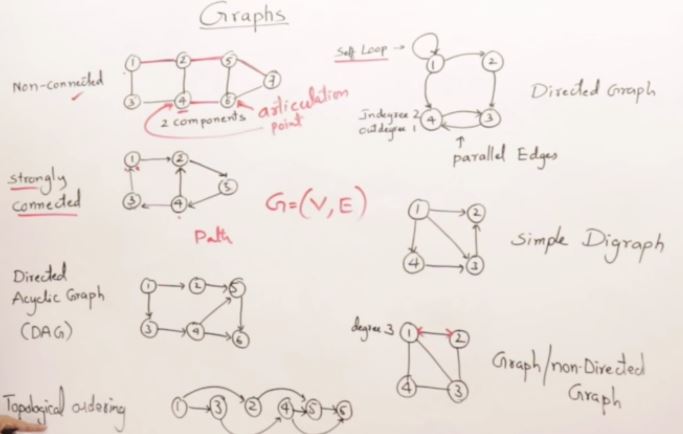
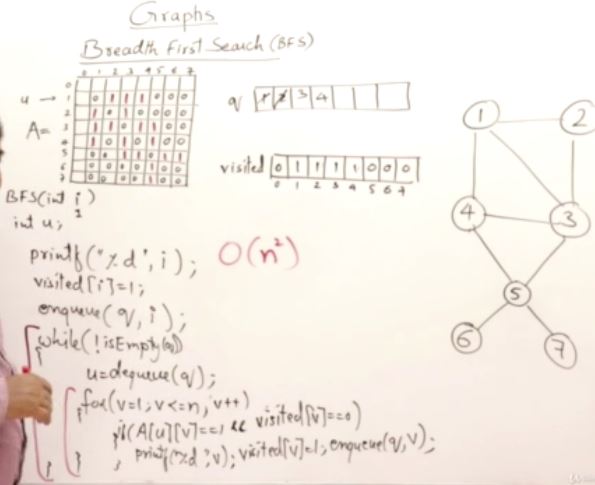
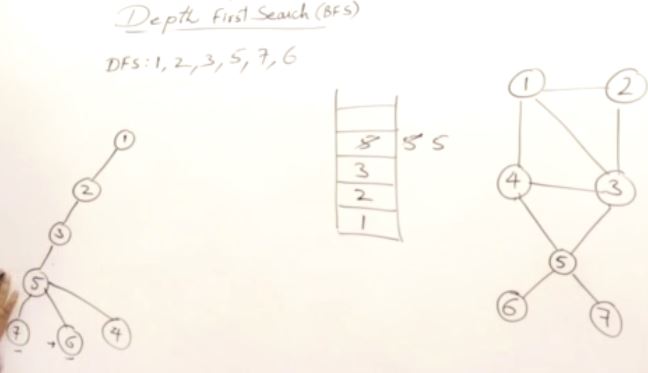
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// Based on Lecture
void DFS(int u, int A[][8], int n){
// initialize visit tracking array and stack
int visited[8] = {0};
stack<int> stk;
stk.emplace(u);
// Visit start vertex u
cout << u << ", " <<flush;
visited[u] = 1; // visited vertex u
// initial adjacent vertex
int v =0;
while(!stk.empty())
{
while(v<n)
{
if(A[u][v]==1 && visited[v] == 0)
{
stk.push(u); // suspend exploring current vertex u
u = v;
//Visit Current vertex u
cout << u << ", "<<flush;
visited[u] = 1;
v = -1; // increment will make this 0
}
v++;
}
v = u; // can set v= 0; but seeing v=u is better;
u = stk.top(); //return previous suspsended vertex
stk.pop();
}
}
// Simpler and adds elements to stack from end
void dfs(int u, int A[][8], int n)
{
int visited[8] = {0};
stack<int> stk;
stk.emplace(u);
while(!stk.empty())
{
u = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if(visited[u]!=1)
{
cout<< u << ", "<<flush;
visited[u] = 1;
for(int v = n -1; v>=0; v--)
{
if(A[u][v]==1 && visited[v]== 0)
{
stk.emplace(v);
}
}
}
}
}
int main (){
int A[8][8] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0}; // {} 이거 더 있어야 한다.
int u = 5;
cout << "DFS Vertex: " << u << "-> "<< flush;
DFS(u,A,8);
cout<<endl;
cout << "dfs Vertex: " << u << " -> " << flush;
dfs(u, A, 8);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}