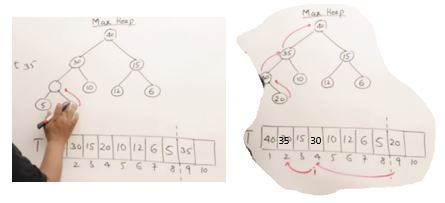
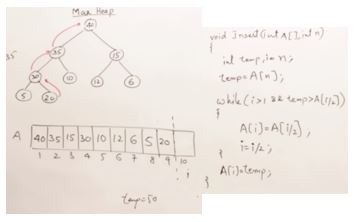
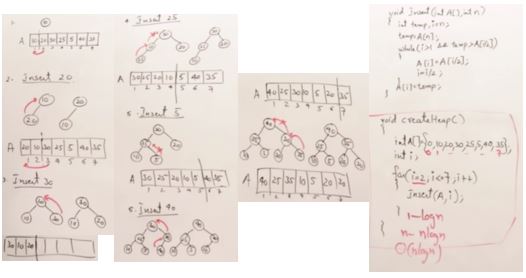
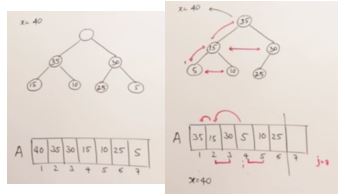
31. Sorting Technique 1
23 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
Intro
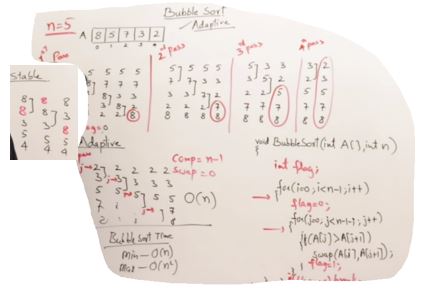
Bubble Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void swap_(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void BubbleSort(int* A, int n)
{
int flag = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n-1-i;j++)
{
if(A[j]>A[j+1])
{
swap_(&A[j],&A[j+1]);
flag = 1;
}
}
if(flag == 0)
{
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
BubbleSort(A,n);
Print(A,n,"A");
return 0;
}
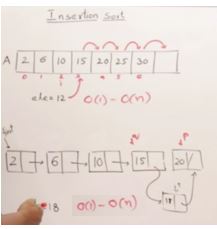
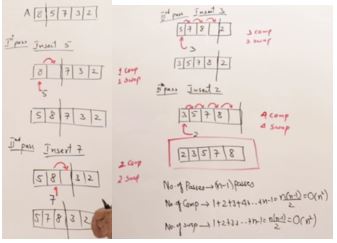
Insertion Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void insertionSort(int* A, int n)
{
for(int i = 1; i<n; i++)
{
int j = i - 1;
int x = A[i];
while(j>-1 && A[j]>x)
{
A[j+1] = A[j];
j--;
}
A[j+1] = x;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
insertionSort(A, n);
Print(A,n,"A");
return 0;
}
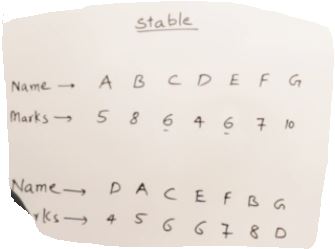
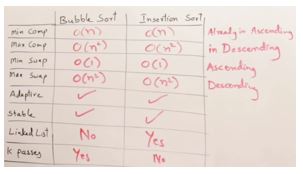
Compare Bubble sort and Insertion sort
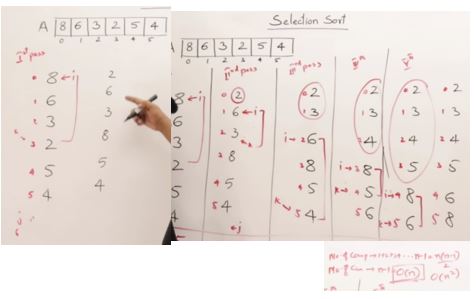
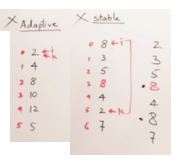
Selection Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int * x, int * y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void SelectionSort(int* A, int n)
{
for(int i =0; i<n-1; i++)
{
int j;
int k;
for(j=k=i; j<n; j++)
{
if(A[j]<A[k])
k = j;
}
Swap(&A[i], &A[k]);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
SelectionSort(A, n);
Print(A,n,"A");
return 0;
}
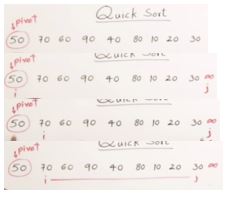
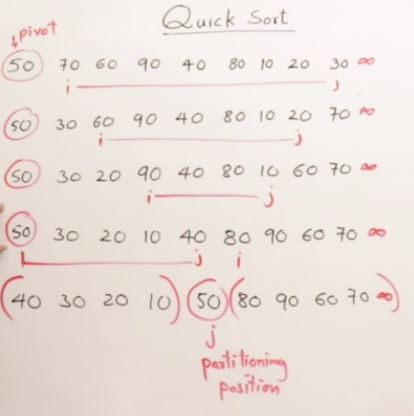
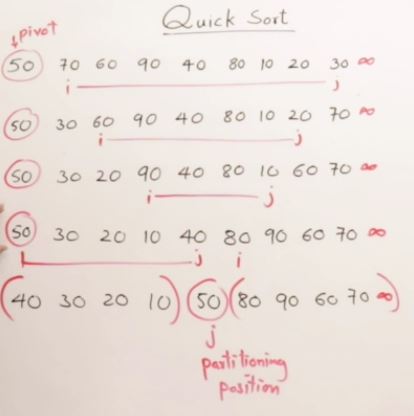
Quick Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
// first element pivot
int Partition(int* A, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = A[low];
int i = low+1;
int j = high;
while(true)
{
while(i<=j&&A[i]<=pivot)
{
i++;
}
while(A[j]>=pivot && j>=i)
{
j--;
}
if(j<i)
{
break;
}
else
{
// 위에 조건을 맞녹하지 않을 경우 즉 A[i]값이 피벗 보다 크고 A[j]가 피벗보다 작을경우
Swap(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
}
Swap(&A[low], &A[j]);
return j;
}
// first pivot
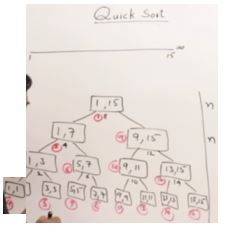
void QuickSort(int* A, int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int p = Partition(A,low,high);
QuickSort(A,low, p-1);
QuickSort(A,p+1, high);
}
}
// Quick Sort using INT_MAX or INFINITY
int Partition_infinity(int A[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = A[low];
int i = low;
int j = high;
do{
// increment i as long as elements are smaller/equal to pivot
do{i++;}while(A[i]<=pivot);
// Decrement j as long as elements are larger than pivot
do {j--;} while (A[j] > pivot);
if(i<j)
{
Swap(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
}while(i<j);
Swap(&A[low], &A[j]);
return j;
}
// using inifinity
void QuickSort_infinity(int* A, int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int p = Partition_infinity(A,low,high);
QuickSort_infinity(A,low, p);
QuickSort_infinity(A,p+1, high);
}
}
// Last Element is Pivot + without using INT_MAX or INFINITY
int partitionLast(int* A, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = A[high];
int i = low -1;
for(int j= low; j<=high-1;j++)
{
if(A[j]<pivot)
{
i++;
Swap(&A[i],&A[j]);
}
}
Swap(&A[i+1], &A[high]);
return i+1;
}
void QuicksortLast(int* A, int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int p = partitionLast(A, low, high); // A[p] in sorted position
QuicksortLast(A,low,p-1);
QuicksortLast(A,p+1,high);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
// First pivot
QuickSort(A, 0,n-1);
Print(A,n,"A");
cout << "Last Element as Pivot + w/o INT_MAX or Infinity" << endl;
int B[] = {11, 13, 7, 12, 16, 9, 24, 5, 10, 3};
Print(B, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]), "\t\tB");
// last pivot
QuicksortLast(B, 0, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0])-1);
Print(B, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]), " Sorted B");
cout<<endl;
cout << "First Element as Pivot + w/o INT_MAX or Infinity" << endl;
int C[] = {11, 13, 7, 12, 16, 9, 24, 5, 10, 3};
Print(C, sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0]), "\t\tC");
// int max or infinity
QuickSort_infinity(C, 0, sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0])-1);
Print(C, sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0]), "\t\tC");
return 0;
}
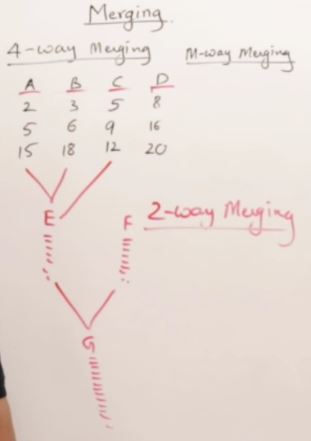
Merging
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void Merge(int x[], int y[], int z[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
while(i<m && j<n)
{
if(x[i]<y[j])
{
z[k++] = x[i++];
}
else
{
z[k++] = y[j++];
}
}
while(i<m)
{
z[k++] = x[i++];
}
while(j<n)
{
z[k++] = y[j++];
}
}
void MergeSingle(int* A, int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i = low;
int j = mid+1;
int k = low;
int B[high+1];
while(i<mid && j<high)
{
if(A[i]<A[j])
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
else
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
}
while(i<mid)
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
while(j<high)
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
for(int i = low; i<=high; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i];
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 10, 18, 20, 23};
int m = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, m, "\t A");
int B[] = {4, 9, 19, 25};
int n = sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]);
Print(B, n, "\t B");
int r = m+n;
int C[r];
Merge(A, B, C, m, n);
// Print function does not work for variable length array C
cout << "Sorted" << ": [" << flush;
for (int i=0; i<r; i++){
cout << C[i] << flush;
if (i < r-1){
cout << ", " << flush;
}
}
cout << "]" << endl;
cout << endl;
int D[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
Print(D, sizeof(D)/sizeof(D[0]), "\t\tD");
MergeSingle(D, 0, 3, 7);
Print(D, sizeof(D)/sizeof(D[0]), " Sorted D");
return 0;
}
Intro
Bubble Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void swap_(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void BubbleSort(int* A, int n)
{
int flag = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<n-1-i;j++)
{
if(A[j]>A[j+1])
{
swap_(&A[j],&A[j+1]);
flag = 1;
}
}
if(flag == 0)
{
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
BubbleSort(A,n);
Print(A,n,"A");
return 0;
}
Insertion Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void insertionSort(int* A, int n)
{
for(int i = 1; i<n; i++)
{
int j = i - 1;
int x = A[i];
while(j>-1 && A[j]>x)
{
A[j+1] = A[j];
j--;
}
A[j+1] = x;
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
insertionSort(A, n);
Print(A,n,"A");
return 0;
}
Compare Bubble sort and Insertion sort
Selection Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int * x, int * y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void SelectionSort(int* A, int n)
{
for(int i =0; i<n-1; i++)
{
int j;
int k;
for(j=k=i; j<n; j++)
{
if(A[j]<A[k])
k = j;
}
Swap(&A[i], &A[k]);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
SelectionSort(A, n);
Print(A,n,"A");
return 0;
}
Quick Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
// first element pivot
int Partition(int* A, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = A[low];
int i = low+1;
int j = high;
while(true)
{
while(i<=j&&A[i]<=pivot)
{
i++;
}
while(A[j]>=pivot && j>=i)
{
j--;
}
if(j<i)
{
break;
}
else
{
// 위에 조건을 맞녹하지 않을 경우 즉 A[i]값이 피벗 보다 크고 A[j]가 피벗보다 작을경우
Swap(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
}
Swap(&A[low], &A[j]);
return j;
}
// first pivot
void QuickSort(int* A, int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int p = Partition(A,low,high);
QuickSort(A,low, p-1);
QuickSort(A,p+1, high);
}
}
// Quick Sort using INT_MAX or INFINITY
int Partition_infinity(int A[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = A[low];
int i = low;
int j = high;
do{
// increment i as long as elements are smaller/equal to pivot
do{i++;}while(A[i]<=pivot);
// Decrement j as long as elements are larger than pivot
do {j--;} while (A[j] > pivot);
if(i<j)
{
Swap(&A[i], &A[j]);
}
}while(i<j);
Swap(&A[low], &A[j]);
return j;
}
// using inifinity
void QuickSort_infinity(int* A, int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int p = Partition_infinity(A,low,high);
QuickSort_infinity(A,low, p);
QuickSort_infinity(A,p+1, high);
}
}
// Last Element is Pivot + without using INT_MAX or INFINITY
int partitionLast(int* A, int low, int high)
{
int pivot = A[high];
int i = low -1;
for(int j= low; j<=high-1;j++)
{
if(A[j]<pivot)
{
i++;
Swap(&A[i],&A[j]);
}
}
Swap(&A[i+1], &A[high]);
return i+1;
}
void QuicksortLast(int* A, int low, int high)
{
if(low<high)
{
int p = partitionLast(A, low, high); // A[p] in sorted position
QuicksortLast(A,low,p-1);
QuicksortLast(A,p+1,high);
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {3,7,9,10,6,5,12,4,11,2};
int n = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A,n,"A");
// First pivot
QuickSort(A, 0,n-1);
Print(A,n,"A");
cout << "Last Element as Pivot + w/o INT_MAX or Infinity" << endl;
int B[] = {11, 13, 7, 12, 16, 9, 24, 5, 10, 3};
Print(B, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]), "\t\tB");
// last pivot
QuicksortLast(B, 0, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0])-1);
Print(B, sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]), " Sorted B");
cout<<endl;
cout << "First Element as Pivot + w/o INT_MAX or Infinity" << endl;
int C[] = {11, 13, 7, 12, 16, 9, 24, 5, 10, 3};
Print(C, sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0]), "\t\tC");
// int max or infinity
QuickSort_infinity(C, 0, sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0])-1);
Print(C, sizeof(C)/sizeof(C[0]), "\t\tC");
return 0;
}
Merging
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
void Print(T& A, int n, string c)
{
cout<< c << " : [" <<flush;
for(int i =0; i < n; i++)
{
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<n-1)
{
cout<<" ,"<<flush;
}
}
cout<<"]" <<endl;
}
void Swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp;
temp = * x;
* x = * y;
* y = temp;
}
void Merge(int x[], int y[], int z[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int k = 0;
while(i<m && j<n)
{
if(x[i]<y[j])
{
z[k++] = x[i++];
}
else
{
z[k++] = y[j++];
}
}
while(i<m)
{
z[k++] = x[i++];
}
while(j<n)
{
z[k++] = y[j++];
}
}
void MergeSingle(int* A, int low, int mid, int high)
{
int i = low;
int j = mid+1;
int k = low;
int B[high+1];
while(i<mid && j<high)
{
if(A[i]<A[j])
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
else
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
}
while(i<mid)
{
B[k++] = A[i++];
}
while(j<high)
{
B[k++] = A[j++];
}
for(int i = low; i<=high; i++)
{
A[i] = B[i];
}
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {2, 10, 18, 20, 23};
int m = sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);
Print(A, m, "\t A");
int B[] = {4, 9, 19, 25};
int n = sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]);
Print(B, n, "\t B");
int r = m+n;
int C[r];
Merge(A, B, C, m, n);
// Print function does not work for variable length array C
cout << "Sorted" << ": [" << flush;
for (int i=0; i<r; i++){
cout << C[i] << flush;
if (i < r-1){
cout << ", " << flush;
}
}
cout << "]" << endl;
cout << endl;
int D[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 3, 6, 7, 10};
Print(D, sizeof(D)/sizeof(D[0]), "\t\tD");
MergeSingle(D, 0, 3, 7);
Print(D, sizeof(D)/sizeof(D[0]), " Sorted D");
return 0;
}











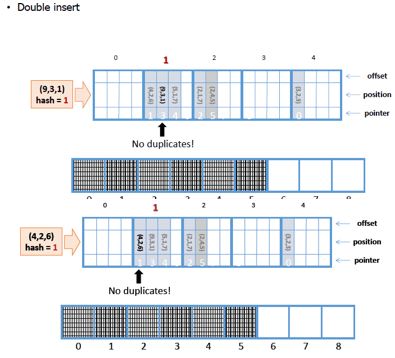
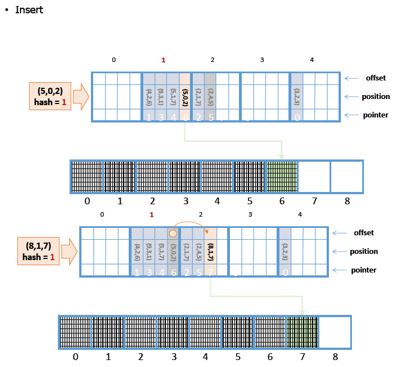
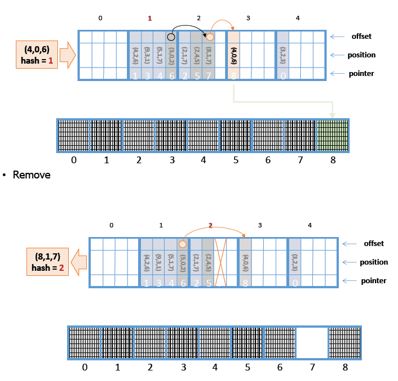
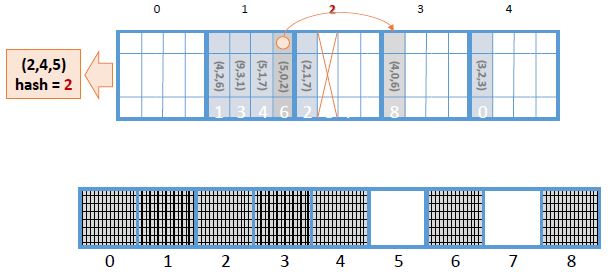







 <a
<a