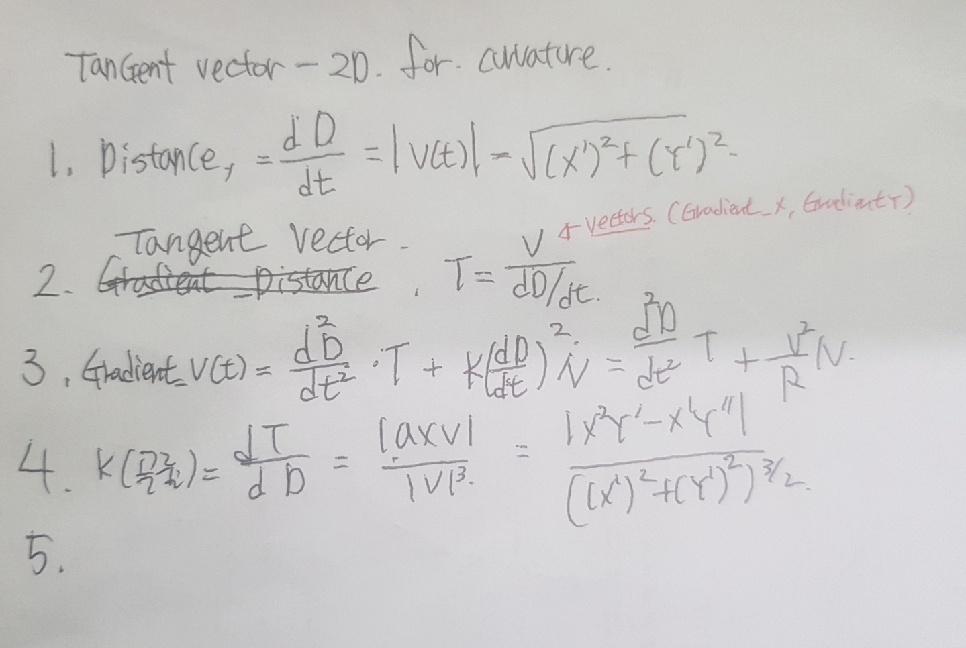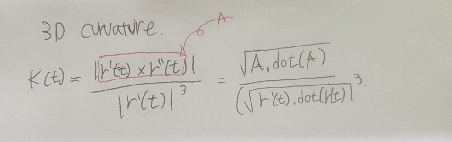with curavture, we are able to define an angle of a slope plane. the way to do is using plane parameter can get curvature.
the other one to detemine a slope plane,
set one vertical line and dot product normal vector, can define a angle of plane.
Consider a car driving along a curvy road. The tighter the curve, the more difficult the driving is. In math we have a number, the curvature, that describes this “tightness”. If the curvature is zero then the curve looks like a line near this point. While if the curvature is a large number, then the curve has a sharp bend.
Normal vector마다 곡률을 구할 수 있느데, 한번 해보자
2d case
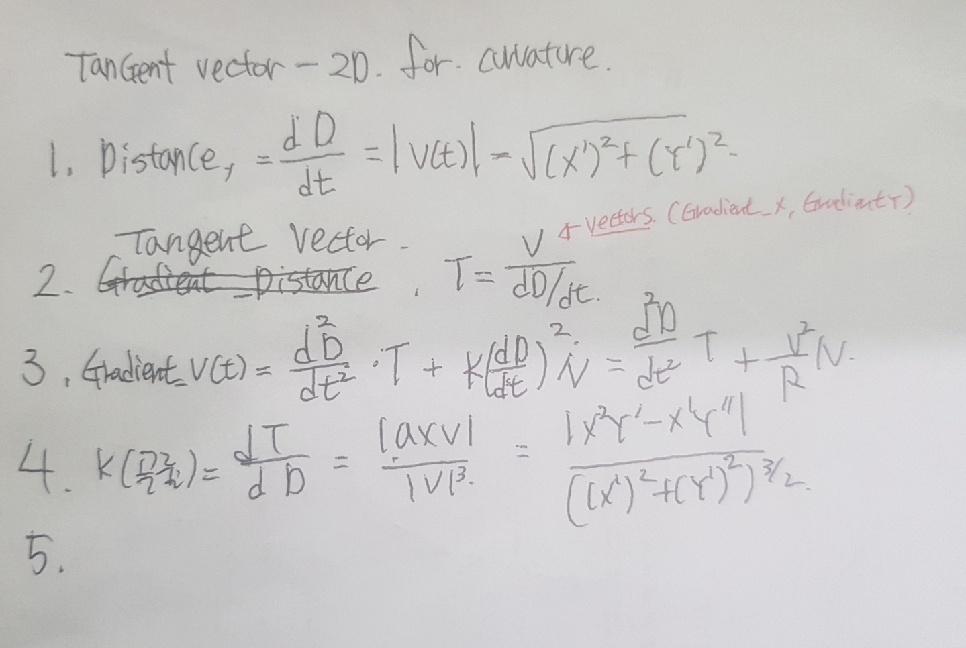
Fomular
k(t) = (x'y'' - x''y') / (x' * x' + y' * y')^(3/2)
Eigen::MatrixXf m(2,7);
m = [[1,1],[1.5,2],[2,3],[2.5,3.5],[3,4],[3.5,4.25],[4,4.5]]; //원래는 블라캣이다.
Eigen::Vector2f Gradient(7);
// Step 1 : Gradient(vector)
for(int idx = 0; idx < m.cols()-1; idx++)
{
Gradient[idx] = m.col(idx)-m.col(idx+1);
// Gradient stored result
// [[0.5 1. ]
// [0.5 1. ]
// [0.5 0.75 ]
// [0.5 0.5 ]
// [0.5 0.375]
// [0.5 0.25 ]
// [0.5 0.25 ]]
}
// Step 2 : 곡률 길이
std::vector<float> distance(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size(); idx++)
{
distance(idx) = sqrt(Gradient[idx].x() * Gradient[idx].x() + Gradient[idx].y() * Gradient[idx].y());
// distance result
// [1.11803399 1.11803399 0.90138782 0.70710678 0.625 0.55901699
// 0.55901699]
}
// Step 3: 벡터들에 대한 탄젠트 계산하기
Eigen::Vector2f Tangent(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size(); idx++)
{
Tangent[idx].x() = Gradient[idx].x() / distance(idx);
Tangent[idx].y() = Gradient[idx].y() / distance(idx);
}
// STEP 4: 탄젠트의 구성요소를 분리하고 기울기를 계산하여 법선 벡터를 찾는다.
std::vector<float> Gradient_distance(7)
Eigen::Vector2f G_Gradient(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size()-1; idx++)
{
Gradient_distance[idx] = distance[idx] - distance[idx+1];
G_Gradient[idx] = Gradient[idx] - Gradient[idx+1];
}
// STEP 5 : estimation Curve Rate of Vector
std::vector<float> curvature(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size(); idx++)
{
curavture[idx] = abs(G_Gradient.x() * Gradient.y() - Gradient.x() * G_Gradient.y())/((Gradient.x() * Gradient.x() + Gradient.y() * Gradient.y())**1.5);
// Curvature Result
// [0. 0.04472136 0.17067698 0.26516504 0.256 0.17888544
// 0. ]
}
3D Case
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NlcvU67YWpQ
Fomular
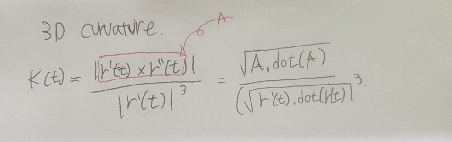
r'(t).cross(r''(t))= A;
k(t) = (sqrt(A.dot(A))) / (sqrt(r'.dot(r'))^3
Eigen::MatrixXf m(3,7);
m = [[1,1,1],[1.5,2,2],[2,3,3],[2.5,3.5,4],[3,4,5],[3.5,4.25,6],[4,4.5,7]]; //원래는 블라캣이다.
Eigen::Vector3f Gradient(7);
// Step 1 : Gradient(vector)
for(int idx = 0; idx < m.cols()-1; idx++)
{
Gradient[idx] = m.col(idx)-m.col(idx+1); // r'(t)
// Gradient stored result
// [[0.5 1. , 1]
// [0.5 1. , 1]
// [0.5 0.75 , 0.75]
// [0.5 0.5 , 0.5]
// [0.5 0.375, 0.375]
// [0.5 0.25 , 0.25]
// [0.5 0.25 , 0.25]]
}
// Step 2 : 곡률 길이
std::vector<float> distance(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size(); idx++)
{
distance(idx) = sqrt(Gradient[idx].x() * Gradient[idx].x() + Gradient[idx].y() * Gradient[idx].y() + Gradient[idx].z() * Gradient[idx].z());
// distance result
// [1.5 1.5 1,17260394 0.8660254038 0.7288689869 0.6123724357
// 0.6123724357]
}
// Step 3: 벡터들에 대한 탄젠트 계산하기
Eigen::Vector3f Tangent(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size(); idx++)
{
Tangent[idx].x() = Gradient[idx].x() / distance(idx);
Tangent[idx].y() = Gradient[idx].y() / distance(idx);
Tangent[idx].z() = Gradient[idx].z() / distance(idx);
}
// STEP 4: 탄젠트의 구성요소를 분리하고 기울기를 계산하여 법선 벡터를 찾는다.
std::vector<float> Gradient_distance(7)
Eigen::Vector3f G_Gradient(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size()-1; idx++)
{
Gradient_distance[idx] = distance[idx] - distance[idx+1];
G_Gradient[idx] = Gradient[idx] - Gradient[idx+1];
}
// STEP 5 : estimation Curve Rate of Vector
std::vector<float> curvature(7);
for(int idx = 0; idx < Gradient.size(); idx++)
{
Eigen::Vector3f Temp_Normal_vector;
Temp_Normal_vector = Gradient[idx].cross(G_Gradient[idx]);
curavture[idx] = sqrt(Temp_Normal_vector.dot(Temp_Normal_vector))/(sqrt(Gradient[idx].dot(Gradient[idx])))**3;
// Curvature Result
// [0. 0.04472136 0.17067698 0.26516504 0.256 0.17888544
// 0. ]
}
slope를 구할때도 많이 쓰이며, lidar에서는 포인트 클라우드 Feature Extraction을 위해 사용이 된다.
참고자료
about 2D
https://www.delftstack.com/ko/howto/numpy/curvature-formula-numpy/
all about curavture
https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Calculus/Supplemental_Modules_(Calculus)/Vector_Calculus/2%3A_Vector-Valued_Functions_and_Motion_in_Space/2.3%3A_Curvature_and_Normal_Vectors_of_a_Curve
https://openstax.org/books/calculus-volume-3/pages/3-3-arc-length-and-curvature




 <a
<a