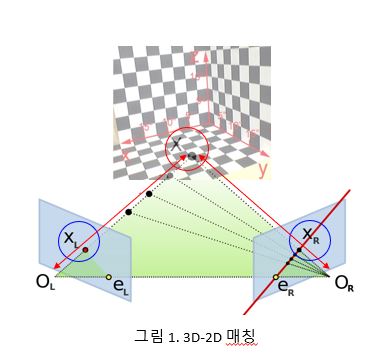
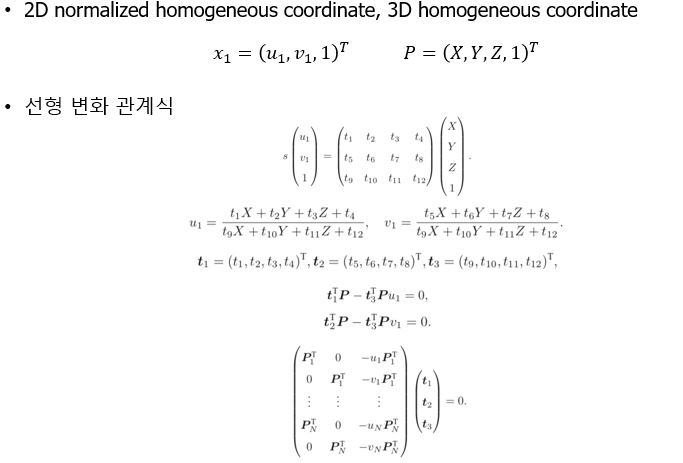
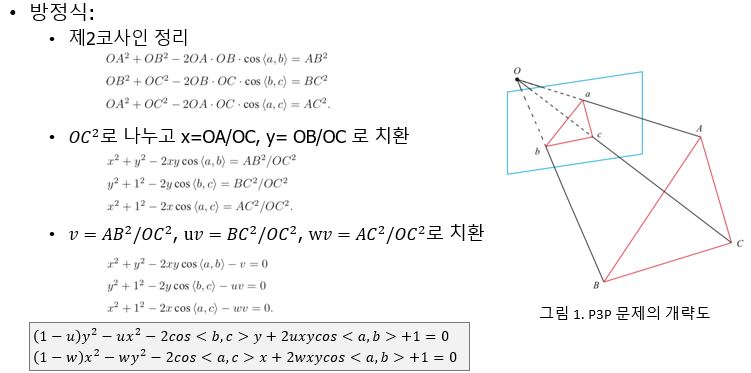
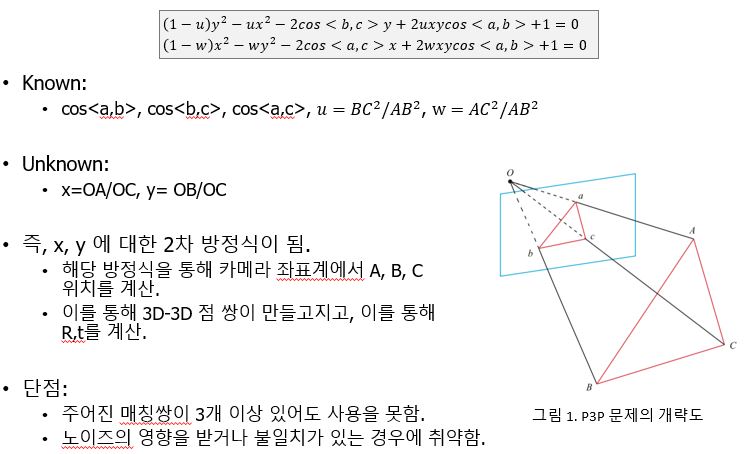
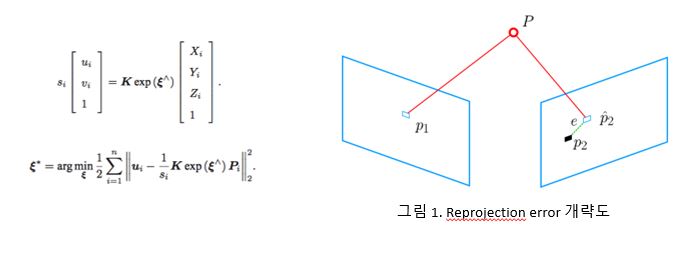
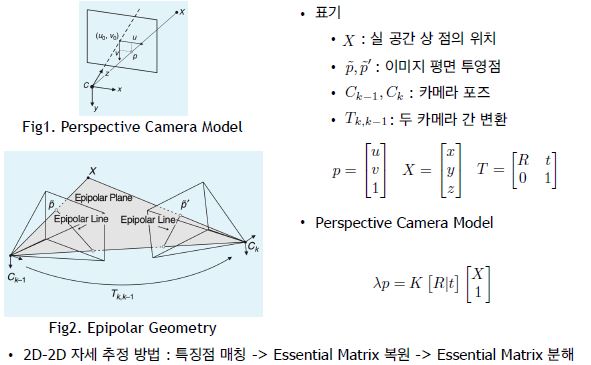
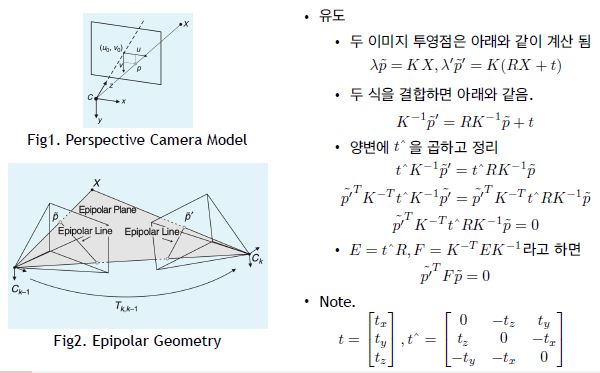
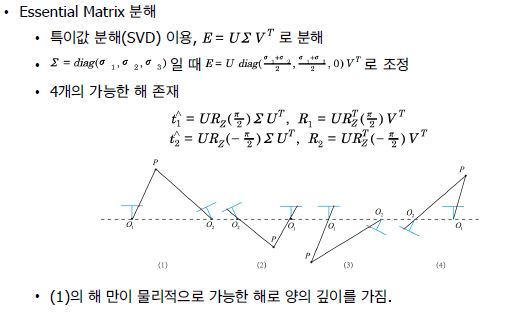
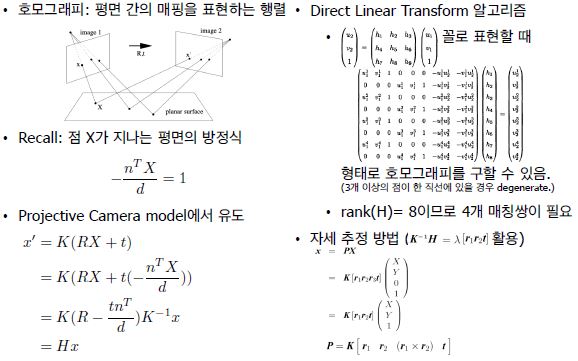
22. Queue
18 Jun 2020 | Algorithm
Queue using Array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Queue
{
private:
int size_;
int front_;
int rear;
int* Q;
public:
Queue(int size_);
~Queue();
void enqueue(int x);
int isFull();
void display();
int isEmpty();
void dequeue();
};
int Queue::isEmpty()
{
if(front_==rear)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void Queue::dequeue()
{
if(isEmpty())
{
cout<<"Queue Empty"<<endl;
}
else
{
front_++;
}
}
void Queue::display()
{
if(isEmpty())
{
cout<<"Queue is Empty"<<endl;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<size_;i++)
{
cout<<Q[i]<< " ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
int Queue::isFull()
{
if(rear==size_-1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int x)
{
if(isFull())
{
cout << "Queue Overflow" << endl;
}
else
{
rear++;
Q[rear]=x;
}
}
Queue::Queue(int size_)
{
this->size_ = size_;
front_ = -1;
rear = -1;
Q = new int[size_];
}
Queue::~Queue()
{
delete[] Q;
}
int main()
{
// Create Queue
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
Queue q(sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
//Enqueue
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
q.enqueue(A[i]);
}
// Display
q.display();
// Overflow
q.enqueue(10);
// Dequeue
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
q.dequeue();
}
// Underflow
q.dequeue();
}
Queue using Linked List
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class Queue{
private:
Node* front;
Node* rear;
public:
Queue();
~Queue();
void enqueue(int x);
int dequeue();
bool isEmpty();
void display();
};
Queue::Queue() {
front = nullptr;
rear = nullptr;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int x) {
Node* t = new Node;
if (t == nullptr){
cout << "Queue Overflow" << endl;
} else {
t->data = x;
t->next = nullptr;
if (front == nullptr){
front = t;
rear = t;
} else {
rear->next = t;
rear = t;
}
}
}
int Queue::dequeue() {
int x = -1;
Node* p;
if (isEmpty()){
cout << "Queue Underflow" << endl;
} else {
p = front;
front = front->next;
x = p->data;
delete p;
}
return x;
}
bool Queue::isEmpty() {
if (front == nullptr){
return true;
}
return false;
}
Queue::~Queue() {
Node* p = front;
while (front){
front = front->next;
delete p;
p = front;
}
}
void Queue::display() {
Node* p = front;
while (p){
cout << p->data << flush;
p = p->next;
if (p != nullptr){
cout << " <- " << flush;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
Queue q;
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
q.enqueue(A[i]);
}
q.display();
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
q.dequeue();
}
q.dequeue();
return 0;
}
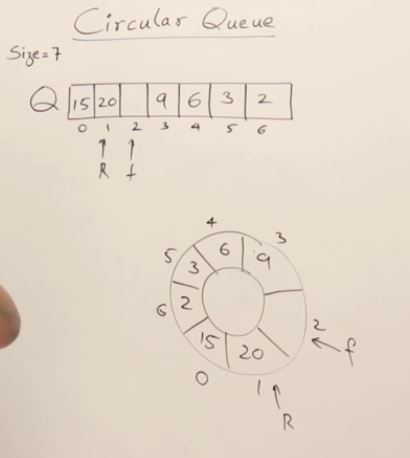
Circular Queue
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CircularQueue
{
private:
int size_;
int rear_;
int front_;
int* Q;
public:
CircularQueue(int size_);
~CircularQueue();
void enqueue(int x);
int isFull();
void Display();
int dequeue();
};
void CircularQueue::Display()
{
int i = front_ +1;
do{
cout<<Q[i]<<flush;
if(i<rear_)
{
cout<<" <- " << flush;
}
i = (i+1)%size_;
}while(i!=(rear_+1)%size_);
}
int CircularQueue::isFull()
{
if(rear_ == size_-1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
void CircularQueue::enqueue(int x)
{
if(isFull())
{
cout<< "Queue Overflow" << endl;
}
else
{
rear_ = (rear_+1)%size_;
Q[rear_] = x;
}
}
int CircularQueue::dequeue()
{
int x = -1;
if(front_==rear_)
{
cout<<"Queue Underflow"<<endl;
}
else
{
front_ = (front_+1)%size_;
x = Q[front_];
}
return x;
}
CircularQueue::CircularQueue(int size_)
{
this->size_ = size_;
rear_ =-1;
front_ = -1;
Q = new int[size_];
}
CircularQueue::~CircularQueue()
{
delete[] Q;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
CircularQueue cq(sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
// Enqueue
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++)
{
cq.enqueue(A[i]);
}
//Display
cq.Display();
cout<<endl;
// Over Flow
cq.enqueue(10);
//Dequeue
for(int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
cq.dequeue();
}
// Underflow
cq.dequeue();
return 0;
}
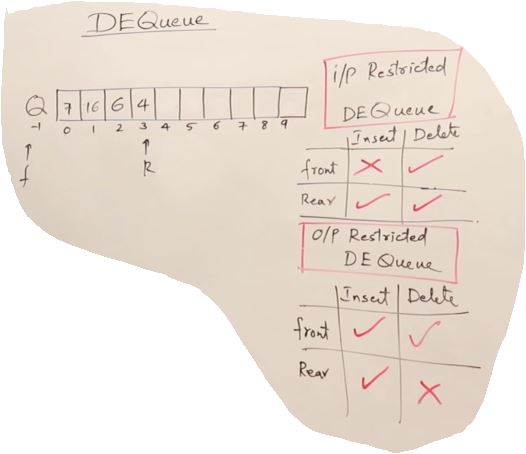
Double Ended Queue(DEQueue)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class DEQueue{
private:
int front;
int rear;
int size;
int* Q;
public:
DEQueue(int size);
~DEQueue();
void display();
void enqueueFront(int x);
void enqueueRear(int x);
int dequeueFront();
int dequeueRear();
bool isEmpty();
bool isFull();
};
DEQueue::DEQueue(int size) {
this->size = size;
front = -1;
rear = -1;
Q = new int [size];
}
DEQueue::~DEQueue() {
delete [] Q;
}
bool DEQueue::isEmpty() {
if (front == rear){
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool DEQueue::isFull() {
if (rear == size - 1){
return true;
}
return false;
}
void DEQueue::enqueueFront(int x) {
if (front == -1){
cout << "DEQueue Overflow" << endl;
} else {
Q[front] = x;
front--;
}
}
void DEQueue::enqueueRear(int x) {
if (isFull()){
cout << "DEQueue Overflow" << endl;
} else {
rear++;
Q[rear] = x;
}
}
int DEQueue::dequeueFront() {
int x = -1;
if (isEmpty()){
cout << "DEQueue Underflow" << endl;
} else {
x = Q[front];
front++;
}
return x;
}
int DEQueue::dequeueRear() {
int x = -1;
if (rear == -1){
cout << "DEQueue Underflow" << endl;
} else {
x = Q[rear];
rear--;
}
return x;
}
void DEQueue::display() {
for (int i=front+1; i<=rear; i++) {
cout << Q[i] << flush;
if (i < rear){
cout << " <- " << flush;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int B[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
DEQueue deq(sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
deq.enqueueRear(A[i]);
}
deq.display();
deq.enqueueRear(11);
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
deq.dequeueFront();
}
deq.dequeueFront();
cout << endl;
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]); i++){
deq.enqueueFront(B[i]);
}
deq.display();
deq.enqueueFront(10);
deq.enqueueFront(12);
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]); i++){
deq.dequeueRear();
}
deq.display();
deq.dequeueRear();
deq.dequeueRear();
return 0;
}
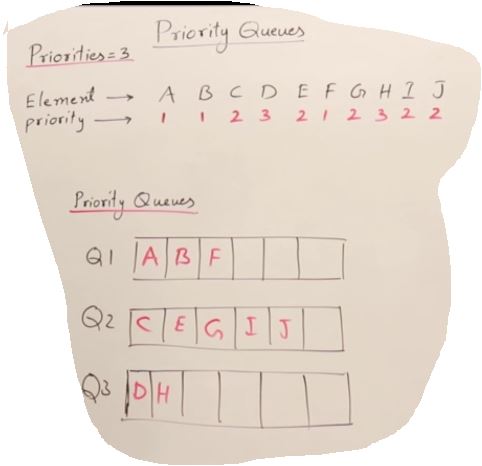
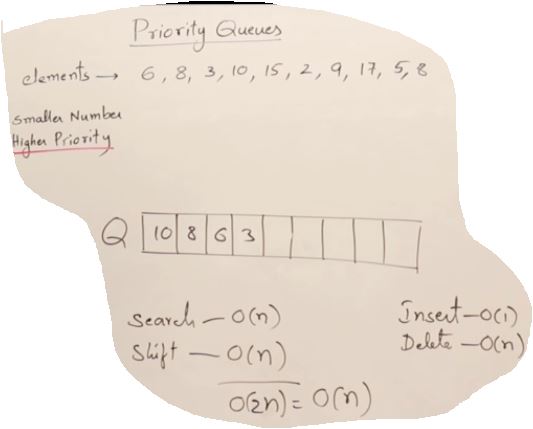
Priority Queue
- Limited set of priority
- Element Priority
Queue using 2 stacks
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Queue
{
private:
stack<int> e_stk;
stack<int> d_stk;
public:
Queue(){};
~Queue(){};
void enqueue(int x);
int dequeue();
};
int Queue::dequeue()
{
int x= -1;
if (d_stk.empty())
{
if(e_stk.empty())
{
cout << "Queue Underflow" << endl;
return x;
}
else
{
while (!e_stk.empty())
{
d_stk.push(e_stk.top());
e_stk.pop();
}
}
}
x = d_stk.top();
d_stk.pop();
return x;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int x)
{
e_stk.push(x);
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {1,3,5,7,9};
Queue q;
cout<<"Enqueue"<<flush;
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
q.enqueue(A[i]);
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0])-1)
{
cout<< "<-"<<flush;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout<< "Dequeue"<<flush;
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++)
{
cout << q.dequeue() << flush;
if (i < sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0])-1){
cout<<" <- " <<flush;
}
}
return 0;
}
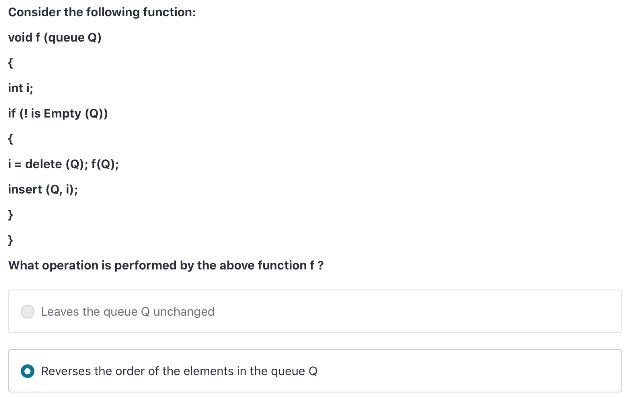
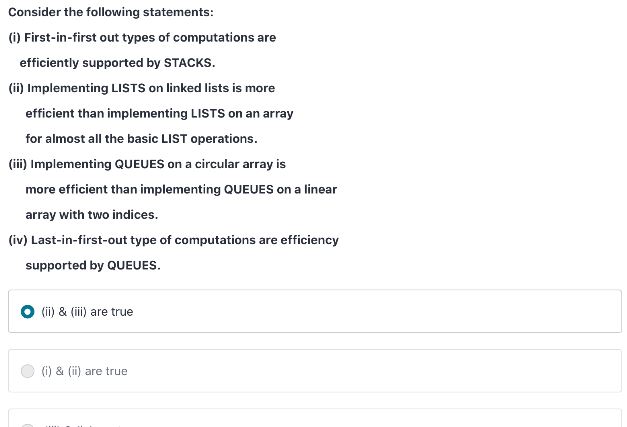
Quiz
Queue using Array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Queue
{
private:
int size_;
int front_;
int rear;
int* Q;
public:
Queue(int size_);
~Queue();
void enqueue(int x);
int isFull();
void display();
int isEmpty();
void dequeue();
};
int Queue::isEmpty()
{
if(front_==rear)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void Queue::dequeue()
{
if(isEmpty())
{
cout<<"Queue Empty"<<endl;
}
else
{
front_++;
}
}
void Queue::display()
{
if(isEmpty())
{
cout<<"Queue is Empty"<<endl;
}
else
{
for(int i=0; i<size_;i++)
{
cout<<Q[i]<< " ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
int Queue::isFull()
{
if(rear==size_-1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int x)
{
if(isFull())
{
cout << "Queue Overflow" << endl;
}
else
{
rear++;
Q[rear]=x;
}
}
Queue::Queue(int size_)
{
this->size_ = size_;
front_ = -1;
rear = -1;
Q = new int[size_];
}
Queue::~Queue()
{
delete[] Q;
}
int main()
{
// Create Queue
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
Queue q(sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
//Enqueue
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
q.enqueue(A[i]);
}
// Display
q.display();
// Overflow
q.enqueue(10);
// Dequeue
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
q.dequeue();
}
// Underflow
q.dequeue();
}
Queue using Linked List
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
class Queue{
private:
Node* front;
Node* rear;
public:
Queue();
~Queue();
void enqueue(int x);
int dequeue();
bool isEmpty();
void display();
};
Queue::Queue() {
front = nullptr;
rear = nullptr;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int x) {
Node* t = new Node;
if (t == nullptr){
cout << "Queue Overflow" << endl;
} else {
t->data = x;
t->next = nullptr;
if (front == nullptr){
front = t;
rear = t;
} else {
rear->next = t;
rear = t;
}
}
}
int Queue::dequeue() {
int x = -1;
Node* p;
if (isEmpty()){
cout << "Queue Underflow" << endl;
} else {
p = front;
front = front->next;
x = p->data;
delete p;
}
return x;
}
bool Queue::isEmpty() {
if (front == nullptr){
return true;
}
return false;
}
Queue::~Queue() {
Node* p = front;
while (front){
front = front->next;
delete p;
p = front;
}
}
void Queue::display() {
Node* p = front;
while (p){
cout << p->data << flush;
p = p->next;
if (p != nullptr){
cout << " <- " << flush;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
Queue q;
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
q.enqueue(A[i]);
}
q.display();
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
q.dequeue();
}
q.dequeue();
return 0;
}
Circular Queue
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CircularQueue
{
private:
int size_;
int rear_;
int front_;
int* Q;
public:
CircularQueue(int size_);
~CircularQueue();
void enqueue(int x);
int isFull();
void Display();
int dequeue();
};
void CircularQueue::Display()
{
int i = front_ +1;
do{
cout<<Q[i]<<flush;
if(i<rear_)
{
cout<<" <- " << flush;
}
i = (i+1)%size_;
}while(i!=(rear_+1)%size_);
}
int CircularQueue::isFull()
{
if(rear_ == size_-1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
void CircularQueue::enqueue(int x)
{
if(isFull())
{
cout<< "Queue Overflow" << endl;
}
else
{
rear_ = (rear_+1)%size_;
Q[rear_] = x;
}
}
int CircularQueue::dequeue()
{
int x = -1;
if(front_==rear_)
{
cout<<"Queue Underflow"<<endl;
}
else
{
front_ = (front_+1)%size_;
x = Q[front_];
}
return x;
}
CircularQueue::CircularQueue(int size_)
{
this->size_ = size_;
rear_ =-1;
front_ = -1;
Q = new int[size_];
}
CircularQueue::~CircularQueue()
{
delete[] Q;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
CircularQueue cq(sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
// Enqueue
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++)
{
cq.enqueue(A[i]);
}
//Display
cq.Display();
cout<<endl;
// Over Flow
cq.enqueue(10);
//Dequeue
for(int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
cq.dequeue();
}
// Underflow
cq.dequeue();
return 0;
}
Double Ended Queue(DEQueue)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class DEQueue{
private:
int front;
int rear;
int size;
int* Q;
public:
DEQueue(int size);
~DEQueue();
void display();
void enqueueFront(int x);
void enqueueRear(int x);
int dequeueFront();
int dequeueRear();
bool isEmpty();
bool isFull();
};
DEQueue::DEQueue(int size) {
this->size = size;
front = -1;
rear = -1;
Q = new int [size];
}
DEQueue::~DEQueue() {
delete [] Q;
}
bool DEQueue::isEmpty() {
if (front == rear){
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool DEQueue::isFull() {
if (rear == size - 1){
return true;
}
return false;
}
void DEQueue::enqueueFront(int x) {
if (front == -1){
cout << "DEQueue Overflow" << endl;
} else {
Q[front] = x;
front--;
}
}
void DEQueue::enqueueRear(int x) {
if (isFull()){
cout << "DEQueue Overflow" << endl;
} else {
rear++;
Q[rear] = x;
}
}
int DEQueue::dequeueFront() {
int x = -1;
if (isEmpty()){
cout << "DEQueue Underflow" << endl;
} else {
x = Q[front];
front++;
}
return x;
}
int DEQueue::dequeueRear() {
int x = -1;
if (rear == -1){
cout << "DEQueue Underflow" << endl;
} else {
x = Q[rear];
rear--;
}
return x;
}
void DEQueue::display() {
for (int i=front+1; i<=rear; i++) {
cout << Q[i] << flush;
if (i < rear){
cout << " <- " << flush;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int A[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int B[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
DEQueue deq(sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]));
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
deq.enqueueRear(A[i]);
}
deq.display();
deq.enqueueRear(11);
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++){
deq.dequeueFront();
}
deq.dequeueFront();
cout << endl;
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]); i++){
deq.enqueueFront(B[i]);
}
deq.display();
deq.enqueueFront(10);
deq.enqueueFront(12);
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(B)/sizeof(B[0]); i++){
deq.dequeueRear();
}
deq.display();
deq.dequeueRear();
deq.dequeueRear();
return 0;
}
Priority Queue
- Limited set of priority
- Element Priority
Queue using 2 stacks
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
class Queue
{
private:
stack<int> e_stk;
stack<int> d_stk;
public:
Queue(){};
~Queue(){};
void enqueue(int x);
int dequeue();
};
int Queue::dequeue()
{
int x= -1;
if (d_stk.empty())
{
if(e_stk.empty())
{
cout << "Queue Underflow" << endl;
return x;
}
else
{
while (!e_stk.empty())
{
d_stk.push(e_stk.top());
e_stk.pop();
}
}
}
x = d_stk.top();
d_stk.pop();
return x;
}
void Queue::enqueue(int x)
{
e_stk.push(x);
}
int main()
{
int A[] = {1,3,5,7,9};
Queue q;
cout<<"Enqueue"<<flush;
for(int i =0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]);i++)
{
q.enqueue(A[i]);
cout<<A[i]<<flush;
if(i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0])-1)
{
cout<< "<-"<<flush;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout<< "Dequeue"<<flush;
for (int i=0; i<sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0]); i++)
{
cout << q.dequeue() << flush;
if (i < sizeof(A)/sizeof(A[0])-1){
cout<<" <- " <<flush;
}
}
return 0;
}